按照《Leetcode101-A Leetcode Gringding Guide》 顺序记录。除此之外,开始正视代码书写规范。
ACM模式练习 1 2 3 next()、nextInt()、nextLine()都是Scanner内置的方法,他们的区别主要在于对于对空格的处理方式不同,以及返回值不同。 nextLine()方法,空格不作为两个字符串的间隔,而是看作字符串的一部分。 next()和nextInt()方法遇到空格时会停止读取,nextInt()的返回值为int类型,next()、nextLine()的返回值均为String类型。
1.A+B I 单纯简单计算两个数的和,但是有n组数据
输入包括两个正整数a,b(1 <= a, b <= 1000),输入数据包括多组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); while (in.hasNext()){ int a = in.nextInt(); int b = in.nextInt(); System.out.println(a + b); } } }
2.A+B II 需要先声明要输入多少组数字之和
输入第一行包括一个数据组数t(1 <= t <= 100)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); int a = in.nextInt(); while (a-- != 0 ){ int b = in.nextInt(); int c = in.nextInt(); System.out.println(b + c); } } }
3.A+B III 和第一题不一样的是碰到0 0 则结束
输入包括两个正整数a,b(1 <= a, b <= 10^9),输入数据有多组, 如果输入为0 0则结束输入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); while (in.hasNext()){ int a = in.nextInt(); int b = in.nextInt(); if (a == 0 && b == 0 ) break ; System.out.println(a + b); } } }
4.计算一系列数的和 I 先输入需要计算多少个数,然后求和,遇到第一个数为0则结束
输入数据包括多组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); while (in.hasNext()) { int count = in.nextInt(); if (count == 0 ) break ; int sum = 0 ; while (count-- != 0 ){ sum += in.nextInt(); } System.out.println(sum); } } }
5.计算一系列数的和 II 和第四题的区别是先声明需要输入多少组,而第四题是用0来结束的
输入的第一行包括一个正整数t(1 <= t <= 100), 表示数据组数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); int group = in.nextInt(); while (group-- != 0 ) { int count = in.nextInt(); int sum = 0 ; while (count-- != 0 ){ sum += in.nextInt(); } System.out.println(sum); } } }
6.计算一系列数的和 III 和4,5的区别是这个没有限制,只需要提供每组多少个数,也就是每行表示一组数据
输入数据有多组, 每行表示一组输入数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); while (in.hasNext()){ int count = in.nextInt(); int sum = 0 ; while (count-- != 0 ){ sum += in.nextInt(); } System.out.println(sum); } } }
7.计算一系列数的和 IV 这个题和上面的区别是 没有指定每组数字有多少个
输入数据有多组, 每行表示一组输入数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import java.util.Scanner;import java.util.Arrays;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); while (in.hasNextLine()){ String[] str = in.nextLine().split(" " ); int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length; i++){ sum += Integer.parseInt(str[i]); } System.out.println(sum); } } }
8.字符串排序 I 只排序一组数据,先输入这组需要排序多少个字符
输入有两行,第一行n
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import java.util.Scanner;import java.util.Arrays;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); int count = in.nextInt(); String[] str = new String [count]; for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++){ str[i] = in.next(); } Arrays.sort(str); for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++){ System.out.print(str[i] + " " ); } } }
9.字符串排序 II 和上一题的区别是不需要输入一组需要排序多少个字符 但是需要排序n组,也就是一次性输入一组的数据
多个测试用例,每个测试用例一行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import java.util.Scanner;import java.util.Arrays;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); while (in.hasNextLine()){ String[] str = in.nextLine().split(" " ); Arrays.sort(str); for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length; i++){ System.out.print(str[i] + " " ); } System.out.print('\n' ); } } }
10.字符串排序 III 这个和上一题的区别是输出格式是逗号隔开,上一题是空格,但是注意的是上一题最后一个字符后面是空格,这一题如果按照上一题的逻辑去做会输出一个逗号,而题目不希望出现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import java.util.Scanner;import java.util.Arrays;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); while (in.hasNextLine()){ String[] str = in.nextLine().split("," ); Arrays.sort(str); for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length - 1 ; i++){ System.out.print(str[i] + "," ); } System.out.println(str[str.length - 1 ]); } } }
11.A+B IV 和第一题的区别是数据范围不一样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); while (in.hasNext()){ long a = in.nextLong(); long b = in.nextLong(); System.out.println(a + b); } } }
360一道题 acm 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main (String args[]) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); String a,b; a = sc.nextLine(); b = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println(dna(a,b)); } public static int dna (String a, String b) { int c = 0 ; int d = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length(); i++) { if (a.charAt(i) == 'A' && b.charAt(i) != 'A' ) { c++; } if (a.charAt(i) == 'T' && b.charAt(i) != 'T' ) { d++; } } return Math.max(c,d); } }
ACM 二叉树输入 前序遍历为例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 package hi;import java.util.*;public class tree { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int n = sc.nextInt(); int [] arr = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { arr[i] = sc.nextInt(); } TreeNode root = construct(arr); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); preorder(root, list); System.out.print(list); } public static void preorder (TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) { if (root == null ) { return ; } list.add(root.val); preorder(root.left, list); preorder(root.right, list); } public static class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; public TreeNode (int val) { this .val = val; } public TreeNode (int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { this .val = val; this .left = left; this .right = right; } } public static TreeNode construct (final int [] arr) { List<TreeNode> treeNodeList = arr.length > 0 ? new ArrayList <>(arr.length) : null ; TreeNode root = null ; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { TreeNode node = null ; if (arr[i] != -1 ) { node = new TreeNode (arr[i]); } treeNodeList.add(node); if (i == 0 ) { root = node; } } for (int i = 0 ; i * 2 + 1 < arr.length; i++) { TreeNode node = treeNodeList.get(i); if (node != null ) { node.left = treeNodeList.get(2 * i + 1 ); if (i * 2 + 2 < arr.length) node.right = treeNodeList.get(2 * i + 2 ); } } return root; } }
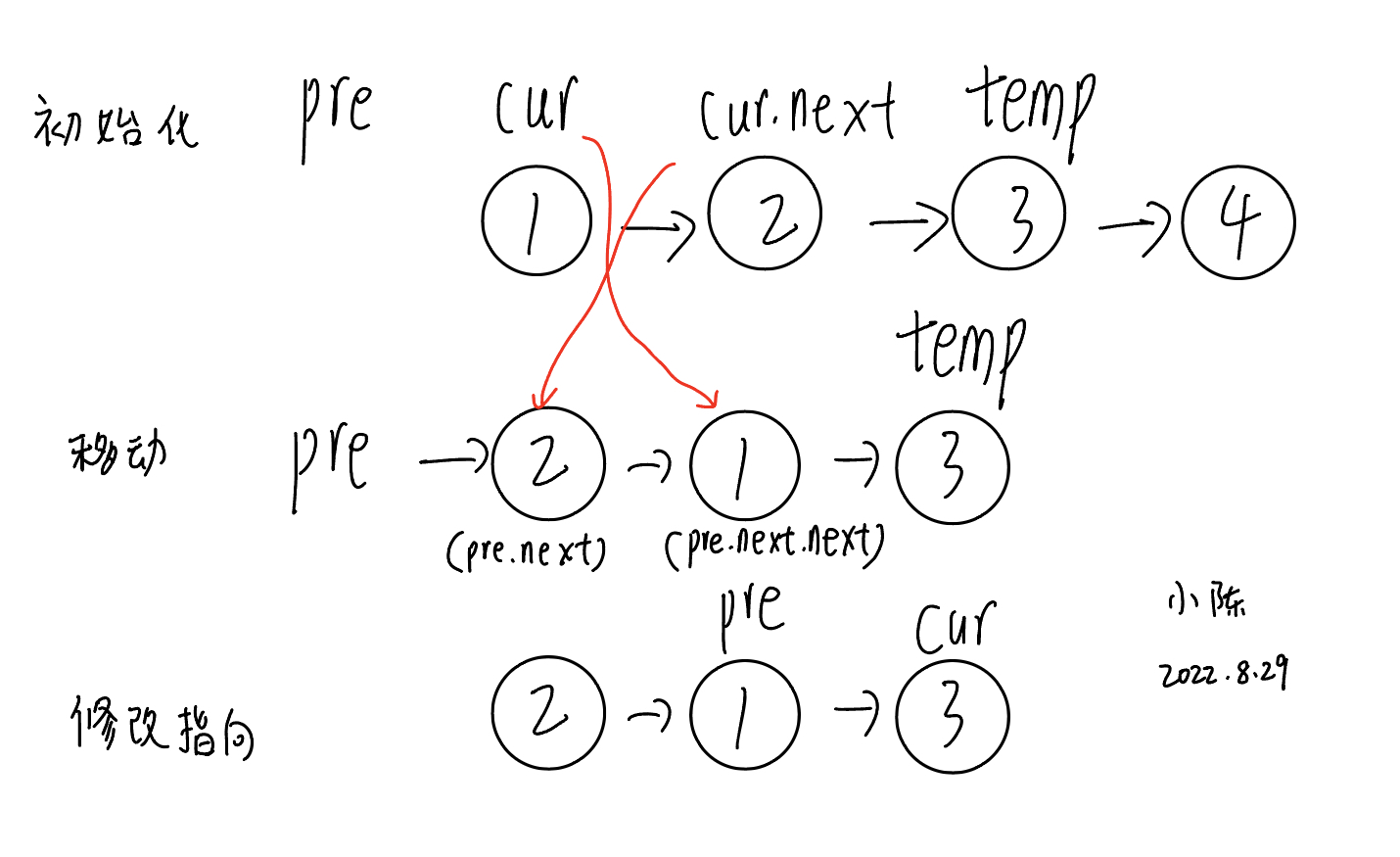
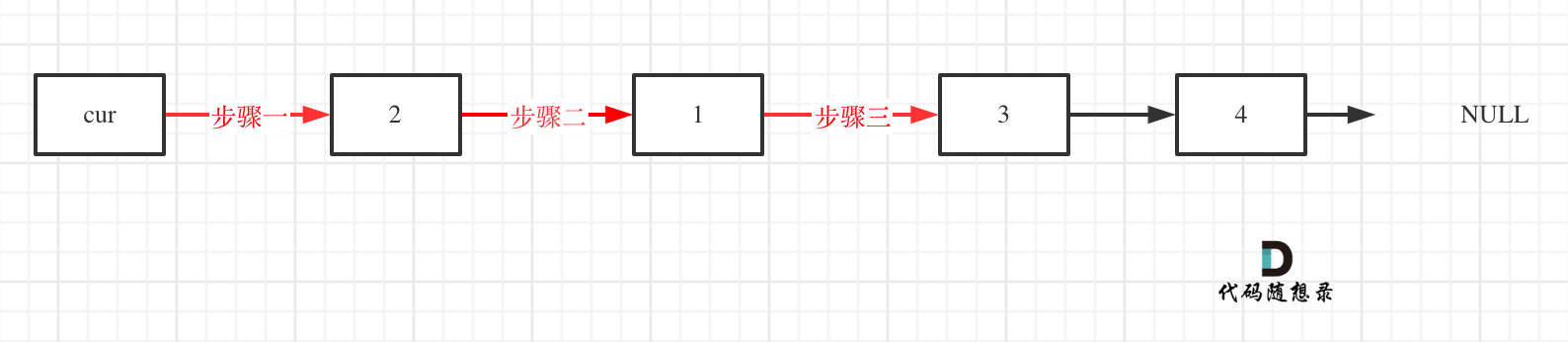
ACM 链表 反转链表为例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 package hi;import java.util.Scanner;public class listnode { static class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int val) { this .val = val; } ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this .val = val; this .next = next; } } public static void main (String args[]) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); String[] param = sc.nextLine().split(" " ); ListNode dump = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode cur = dump; for (String x : param) { cur.next = new ListNode (Integer.parseInt(x)); cur = cur.next; } ListNode res = reverse(dump.next); while (res != null ) { System.out.print(res.val); if (res.next != null ) { System.out.print("->" ); } res = res.next; } } public static ListNode reverse (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null ) { ListNode temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } }
贪心算法 445 分发饼干 easy 依次满足胃口最小的孩子。可以想到先排序,然后再去分配。注意当满足了孩子后,cookie再加一,因为一个饼干只能用一次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int findContentChildren (int [] g, int [] s) { Arrays.sort(g); Arrays.sort(s); int cookie = 0 , child = 0 ; while (child < g.length && cookie < s.length){ if (g[child] <= s[cookie]){ child++; } cookie++; } return child; } }
135 分发糖果 hard 首先建立一个数组,然后初始化为1,也就是每个人都先分到一颗糖。然后从左往右边遍历,如果右边的孩子得分高于左边,则右边的孩子糖果数=左边的孩子糖果数+1,注意这里不是直接加1.因为分数可能是依次增加,还要求分数高的糖果多。然后从右往左遍历,如果左边的孩子分数大于右边孩子分数并且左边孩子的糖果数不如右边孩子糖果数,则左边孩子糖果数=右边孩子糖果数+1,这种情况对应于左边分数大于右边。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int candy (int [] ratings) { int candys[] = new int [ratings.length]; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < ratings.length; i++){ candys[i] = 1 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < ratings.length-1 ; i++){ if (ratings[i+1 ] > ratings[i]){ candys[i+1 ] = candys[i] +1 ; } } for (int i = ratings.length-1 ; i > 0 ; i--){ if (ratings[i-1 ] > ratings[i] && candys[i-1 ] <= candys[i]){ candys[i-1 ] = candys[i] +1 ; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < ratings.length; i++){ count += candys[i]; } return count; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int candy (int [] ratings) { int [] left = new int [ratings.length]; int [] right = new int [ratings.length]; Arrays.fill(left, 1 ); Arrays.fill(right, 1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < ratings.length; i++) if (ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1 ]) left[i] = left[i - 1 ] + 1 ; int count = left[ratings.length - 1 ]; for (int i = ratings.length - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { if (ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1 ]) right[i] = right[i + 1 ] + 1 ; count += Math.max(left[i], right[i]); } return count; } } 作者:jyd 链接:https: 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
435 无重叠区间 medium(可动态规划) 这里学到了Arrays.sort()新写法,开头一直纠结怎么把书上C++的排序用java表达(java用得少)。这里是要移除区间的最小个数,贪心的策略是:在选择要保留区间时,选择的区间结尾越小,余留给其他区间的空间就越大,就能保留更多的区间。首先对尾巴进行递增排序,也就是每个区间的第二个数字排序。然后对prve赋值为第一个区间的尾巴。开始进入for循环,如果第二个区间的头是小于prev,也就是在第一个的区间内,需要进行移除,如果大于了prev,则保留区间,然后prev赋值给第二个区间的尾巴,以此类推。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(intervals)); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(intervals));
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int eraseOverlapIntervals (int [][] intervals) { if (intervals.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } Arrays.sort(intervals,new Comparator <int []>(){ public int compare (int [] interval1, int [] interval2) { return interval1[1 ]-interval2[1 ]; } }); int total = 0 , prev = intervals[0 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++){ if (intervals[i][0 ] < prev){ total++; } else { prev = intervals[i][1 ]; } } return total; } }
605 种花问题 easy 虽说是easy题,但是发现自己想的bug很多,看到了一个很清晰的解题方法:跳格法。注意题目是不能打破原来的种植规则!。情况1:当index遇到1的时候,也就是至少隔一格才能种花,所以i要跳两格。情况2:当index遇到0时候,如果下一格为0,则可以种花(此时n-1),并且顺便跳两格,这里还有个情况就是如果已经是最后一格了,那就也能种花,一开始会想,万一最后一格的前面一格是1呢?注意这个情况不会发生,因为你是跳格法,你跳的index就代表是可能种花的,只需要考虑后面就行。如果下一个格子为1(比如0100),则这格不能种花,则i要跳3格才可以种花。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public boolean canPlaceFlowers (int [] flowerbed, int n) { for (int i = 0 ; i < flowerbed.length && n >0 ;){ if (flowerbed[i] == 1 ){ i += 2 ; } else if ((flowerbed[i] ==0 && i == flowerbed.length-1 ) || (flowerbed[i] ==0 && flowerbed[i+1 ] == 0 )){ n--; i += 2 ; } else if (flowerbed[i] ==0 && flowerbed[i+1 ] == 1 ){ i +=3 ; } } return n <= 0 ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public boolean canPlaceFlowers (int [] flowerbed, int n) { for (int i = 0 ; i < flowerbed.length && n >0 ;){ if (flowerbed[i] == 1 ){ i += 2 ; } else if (i == flowerbed.length-1 || flowerbed[i+1 ] == 0 ){ n--; i += 2 ; } else { i += 3 ; } } return n <= 0 ; } }
452 用最少数量的箭引爆气球 medium(和435相似) 这个题我的思路是,首先还是对尾巴进行升序排列,然后赋值prev给第一个数的尾巴,开始进行for循环比较第二个数,如果prev大于第二个数的头,也就是这个箭还是可以穿过去,不需要考虑尾巴,因为题目说了头一定比尾巴小。然后如果prev比头小,就说明穿不过去了,这时候就箭的数目加1.以此类推,这个注意count初始值为1,因为本身至少都需要一支箭,可以试试只有一个区间,在循环内counnt是不增加的。这里和435比较:435是不重叠区间,而这里刚好是重叠区间。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public int findMinArrowShots (int [][] points) { if (points.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } Arrays.sort(points,new Comparator <int []>(){ public int compare (int [] points1, int [] points2) { if (points1[1 ] < points2[1 ]){ return -1 ; } else return 1 ; } }); int count = 1 ,prev = points[0 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < points.length; i++){ if (points[i][0 ] > prev){ count++; prev = points[i][1 ]; } } return count; } }
763 划分字母区间 medium 自己想的思路比较复杂,太冗余,而且可能考虑的东西不够全面。官方思路:首先用一个长度为26的数组a把每个字母的最后一个位置进行标记。设置start和end,开始循环字符串,访问每个字母,通过之前a来获取他的最后一个位置endc,令end=max(end,endc)。如果循环到i等于end,就说明之前的字母都包括在这个区间内,那就让长度写入partition,并令start=end+1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 List<Integer> partition = new ArrayList <Integer>(); last[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ] = i;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public List<Integer> partitionLabels (String s) { int start = 0 , end = 0 ; int [] last =new int [26 ]; List<Integer> partition = new ArrayList <Integer>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ last[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ] = i; } for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ end = Math.max(end, last[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ]); if (i == end){ partition.add(end - start + 1 ); start = end + 1 ; } } return partition; } }
122 买卖股票的最佳时机2 easy(可动态规划) 还是没有独立想出来,想得太复杂,一直纠结怎么用区间来解答。官方解答太多数学公式,总体来说就是只要选择贡献大于0的区间,然后一直累加利润,但是这个做法是不知道第几次买卖的,只能求利润,对于负数,则和0比较就行。秒呀!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int price = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++){ price += Math.max(0 , prices[i] - prices[i-1 ]); } return price; } }
406 根据身高重建队列 medium 网友思路 :首先遇到这种数对问题,先排序。根据第一个元素正向排序,根据第二个元素反向排序,或者根据第一个元素反向排序,根据第二个元素正向排序,往往能够简化解题过程。在本题目中,先对数对进行排序,按照数对的元素 1 降序排序,按照数对的元素 2 升序排序。原因是,按照元素 1 进行降序排序,对于每个元素,在其之前的元素的个数,就是大于等于他的元素的数量,而按照第二个元素正向排序,我们希望 k 大的尽量在后面,减少插入操作的次数。小陈补充:如果第一个位置降序,第二个位置也降序排,再按照这样写法去插入的话,有部分用例是不能通过的,比如a[[7,0],[6,1],[5,2]]下一个待插入的数是[5,0],按照算法应该插入到第一个位置,变成a[[5,0],[7,0],[6,1],[5,2]]这时候我们就发现[5,2]已经错误了,因为前面有三个数大于或者等于了。也就是你插入后,你得保证后面没有等于你的数插入,所以,第二个位置的排序,要升序!!!保证同胞小弟位置(第二个位置)先安排好。我们可以这样缕清楚,a里面已经插入的数都是比后面待插入的数大或者相等,如果后面待插入的数第二个位置比a的长度小,那么就是说他来选位置插,反之,他就插到最后面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 List<int []> list = new LinkedList <>();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int [][] reconstructQueue(int [][] people) { Arrays.sort(people, new Comparator <int []>(){ public int compare (int [] people1, int [] people2) { if (people1[0 ] != people2[0 ]){ return people2[0 ] - people1[0 ]; } else { return people1[1 ] - people2[1 ]; } } }); List<int []> list = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < people.length; i++){ if (list.size() > people[i][1 ]){ list.add(people[i][1 ],people[i]); } else { list.add(list.size(),people[i]); } } return list.toArray(new int [list.size()][]); } }
665 非递减数列 easy 第一次看题看错了,看成只移动一个数。这个题是改变一个数!虽然是easy,但是并不一定easy。网友解答很清晰 :本题是要维持一个非递减的数列,所以遇到递减的情况时(nums[i] > nums[i + 1]),要么将前面的元素缩小,要么将后面的元素放大。但是本题唯一的易错点就在这,如果将nums[i]缩小,可能会导致其无法融入前面已经遍历过的非递减子数列;如果将nums[i + 1]放大,可能会导致其后续的继续出现递减;所以要采取贪心的策略,在遍历时,每次需要看连续的三个元素,也就是瞻前顾后,遵循以下两个原则:需要尽可能不放大nums[i + 1],这样会让后续非递减更困难;如果缩小nums[i],但不破坏前面的子序列的非递减性;算法步骤:遍历数组,如果遇到递减:还能修改:修改方案1:将nums[i]缩小至nums[i + 1];修改方案2:将nums[i + 1]放大至nums[i];不能修改了:直接返回false;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public boolean checkPossibility (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 1 ){ return true ; } boolean flag = nums[0 ] <= nums[1 ] ? true : false ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length-1 ; i++){ if (nums[i] > nums[i+1 ]){ if (flag){ if (nums[i+1 ] >= nums[i-1 ]){ nums[i] = nums[i+1 ]; } else { nums[i+1 ] = nums[i]; } flag = false ; } else { return false ; } } } return true ; } }
双指针 167 两数之和2 easy 注意题目给的数组是非递减顺序排列(也就是总体递增,然后可能有两个相邻的数是相等),所以思路上很简单,两个变量去追踪这个数组,一头一尾巴,如果两数之和小于target,左边就需要移动一位,反之则右边需要移动一位。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] numbers, int target) { int j = numbers.length-1 ; int [] ans = new int [2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < numbers.length-1 && i < j;){ if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target) { ans[0 ] = i+1 ; ans[1 ] = j+1 ; } else if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] < target){ i++; } else if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] > target){ j--; } } return ans; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] numbers, int target) { int i = 0 ; int j = numbers.length-1 ; while (i < j){ int sum = numbers[i] + numbers[j]; if (sum == target){ break ; } else if (sum < target){ i++; } else if (sum > target){ j--; } } return new int []{i + 1 , j + 1 }; } }
88 合并两个有序数组 easy 题目给的是两个非递减数组,思路是用m,n来指向两个数组的尾巴,还有pos来定位。首先要注意是在数组1的基础上去排,不需要额外开辟一个数组。pos定位在数组1的尾巴,开始对比两个数组的尾巴,哪个大就先复制过去。这里最后要注意,如果数组1复制完了,但是数组2还有,务必要记得继续复制。反之如果数组2复制完了,则不需要操作,因为数组1本身就是非递减,而且返回的数组就是他自己。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public void merge (int [] nums1, int m, int [] nums2, int n) { int pos = m-- + n-- -1 ; while (m >= 0 && n >= 0 ){ nums1[pos--] = nums1[m] > nums2[n] ? nums1[m--] :nums2[n--]; } while (n >= 0 ){ nums1[pos--] = nums2[n--]; } } }
142 环形链表2 medium 这个题涉及了一些数学计算,感谢网友 讲解,这里复述一下:设置两个指针,一个为fast,一个为slow,fast每次走2步,slow每次走1步,设链表为a+b个节点,a为抵达环状的步数,b为环状的节点数。没有环状的链表很容易考虑,这里直接讲有环状的情况,也就是fast和slow会相遇:首先可以得到第一个关系式f=2s,这个是slow和fast的步数关系。第二个关系式是f=s+nb,因为fast比slow快,所以最终一定能追上,这时候呢,其实fast比slow多走了n个环。根据这两个关系,可以得到f=2nb ,s=nb 。接下来我们考虑,一个指针从头走到环状开头走过的步数k=a+nb ,当n为0,也就是你走了a步到了环状的门口,然后n=1的话,你相当于绕了一圈环,然后又到了门口。现在有了三个表达式,从head结点走到入环点需要走:a + nb, 而slow已经走了nb(之前推了相遇的时候他们两个的关系),那么slow再走a步就是入环点了,如何知道slow刚好走了a步?fast从新从head开始和slow指针一起走,再相遇时刚好就是a步。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head, slow = head; while (true ){ if (fast == null || fast.next == null ){ return null ; } fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow){ break ; } } fast = head; while (slow != fast){ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return fast; } }
76 最小覆盖子串 hard 依旧是网友 的思路,这个题在于需要考虑不少东西,这里简单描述一下:首先是建立一个128的ASCII列表,第一步先记录t中每个字符的数量。定义好l和r初始位置,还有用count去记录还需要的字符数量,这样就不用每次去查看need中哪个字符还大于0。开始while循环,用r去遍历整个S串,经过每个r的位置去提取字符c,首先判断c在need中的情况,如果是大于0,说明这个字符是符合t串的。然后减去一个count,代表已经找到了一个符合的字符,接下来是need中减去字符c的数量,注意,这里也包括不在t中的字符,不在t的中字符减去自然是为负数,代表这个字符是多余的。然后判断count为0的情况,count为0,代表已经找到符合的子串了,但是题目要求的size是最小的,所以可以缩减范围,当l小于r,并且里面有多余的字符,我们首先在need中加回去,然后移动l,然后开始重置size的大小,注意这时候的start变成新的l。接来下是移动l,看看还有没有更小的窗口,注意这里用start去保存这个开始的位置,而不是直接用l,这是有含义的,因为你的r是要遍历整个S串,这样你才知道哪个窗口是最小的,所以只有当size更小时候,我们才去更新更新start值,再加上size大小,就可以找到最小的串位置。这时候你无需当心l和r移动的位置了。务必务必注意,移动l的时候,请记得更新need和count以及l!!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public String minWindow (String s, String t) { int [] need = new int [128 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < t.length() ; i++){ need[t.charAt(i)]++; } int l = 0 , r = 0 , start = 0 , size = Integer.MAX_VALUE, count = t.length(); while (r < s.length()){ char c = s.charAt(r); if (need[c] > 0 ){ count--; } need[c]--; if (count == 0 ){ while (l < r && need[s.charAt(l)] < 0 ){ need[s.charAt(l)]++; l++; } if (r -l + 1 < size){ size = r - l + 1 ; start = l; } need[s.charAt(l)]++; count++; l++; } r++; } return size == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(start, start + size); }}
633 平方数之和 medium 和167的很像,这里网友 非常详细说明为什么i++和j–不会错过答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public boolean judgeSquareSum (int c) { long i = 0 ,j =(long ) Math.sqrt(c); while (i <= j){ long sum = i*i + j*j; if ( sum == c ){ return true ; } else if ( sum < c ){ i++; } else { j--; } } return false ; } }
680 验证回文字符串2 easy 这个题虽然是简单题,但是还是看了网友 思路:用双指针去对比,一个在头l,一个在尾巴r,当遇到不相等的情况,我们可以让l加1个位置,或者让r减去一个位置,因为题目说了可以最多删除一个字符,然后再用一个函数去对比子字符串。这里我一开始想到的是用一个计数器去判断删除的次数,后来发现其实不需要,比如abxbgga,要删除两次才行,你只要仔细看代码,发现只要一次之后不行就直接false了,所以不用考虑加一个计数器的问题,那么删除一个字符是体现在r-1或者l+1上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public boolean validPalindrome (String s) { int l = 0 , r = s.length()-1 ; while (l < r){ if (s.charAt(l) != s.charAt(r)){ return judegesub(s, l+1 , r) || judegesub(s, l, r-1 ); } l++; r--; } return true ; } public boolean judegesub (String s, int l, int r) { while (l < r){ if (s.charAt(l) != s.charAt(r)){ return false ; } l++; r--; } return true ; } }
524 通过删除字母匹配到字典里最长单词 medium 这个题我一开始考虑的是,首先跟上一个题的区别是,这个题的意思是可以删除好几个元素,然后第二个不同的是,这个题有多个词,是不是要用暴力算法一个个去看?看了官方解答后,发现被上一题绕进去了。大概重复下解法:用双指针思路,i和j分别指向t(字典中的词)和s的第一个字母,注意这里是每个字典的词都会遍历,然后如果匹配,则i和j同时移动一位,如果不匹配,i不动,j+1。直到最后i要是等于这个词的长度的话,就代表全部匹配到。注意这里是长度,长度和单词最后一个字符位置是相差1的。题目中说要长度最长和序号最低的。所以自然有一个长度对比以及序号对比,序号对比是用compareTo函数,这个是对比ASCII对比,也就是序号在前的话是小于0。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public String findLongestWord (String s, List<String> dictionary) { for (String t : dictionary) { System.out.print(t); System.out.print(" " ); } } } 关于compareTo: 返回值是整型,它是先比较对应字符的大小(ASCII码顺序)如果第一个字符和参数的第一个字符不等,结束比较,返回他们之间的长度差值,如果第一个字符和参数的第一个字符相等,则以第二个字符和参数的第二个字符做比较,以此类推,直至比较的字符或被比较的字符有一方结束。 如果参数字符串等于此字符串,则返回值 0 ; 如果此字符串小于字符串参数,则返回一个小于 0 的值; 如果此字符串大于字符串参数,则返回一个大于 0 的值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public String findLongestWord (String s, List<String> dictionary) { String res = "" ; for (String t : dictionary) { int i = 0 , j = 0 ; while (i < t.length() && j < s.length()) { if (t.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) { ++i; } ++j; } if (i == t.length()) { if (t.length() > res.length() || (t.length() == res.length() && t.compareTo(res) < 0 )) { res = t; } } } return res; } }
二分查找 69 Sqrt(x) easy 这个题是看了官方解法,其实思路就是二分法,每次寻找中间值,如果中间值的平方小于输入值,则把左边的边界设置为mid+1,反之如果大于输入值,则把右边界设置为mid-1,这里注意一个问题就是mid * mid前面要加long,不然超过范围。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int mySqrt (int x) { int l = 0 , r = x, ans = -1 ; while (l <= r) { int mid = l + (r - l) / 2 ; if ((long ) mid * mid <= x){ ans = mid; l = mid + 1 ; }else { r = mid - 1 ; } } return ans; } }
34 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置 medium 这里有一个网友的二分法模板 ,关于这个题,分了两步,首先是寻找第一个target,循环内部条件是num[mid]大于等于target,然后用模板1,寻找最后出现的target,用模板2。至于为什么分开模板1和2,有个网友解释很清楚:因为取左边第一个target时,当nums[mid]==target时,中间位置的右边元素一定不是target出现的第一个位置,所以下次搜索区间是[left,mid],right=mid;取最后一个target时,当nums[mid]==target时,中间位置的左边元素一定不是target出现的最后一个位置,所以下次搜索区间是[mid,right],left=mid。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 int bsearch_1 (int l, int r) { while (l < r) { int mid = (l + r)/2 ; if (check(mid)) r = mid; else l = mid + 1 ; } return l; } int bsearch_2 (int l, int r) { while (l < r) { int mid = ( l + r + 1 ) /2 ; if (check(mid)) l = mid; else r = mid - 1 ; } return l; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int [] searchRange(int [] nums, int target) { if (nums.length == 0 ) return new int []{-1 , -1 }; int l = 0 , r = nums.length - 1 ; while (l < r){ int mid = (l + r) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] >= target) r = mid ; else l = mid + 1 ; } if (nums[r] != target) return new int []{-1 ,-1 }; int L = r; l = 0 ; r = nums.length - 1 ; while (l < r){ int mid = (l + r + 1 ) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] <= target) l = mid ; else r = mid - 1 ; } return new int []{L,r}; } }
81 搜索旋转排序数组 II medium 找数组的目标数,这个题就是说本来的数组是增序的,但是现在相当于在中间断开,然后再连起来,就变成一个旋转数组。所以,旋转数组的特性的有一部分是增序的。先依旧找到中点位置,后面解释看代码。这个coder 把一些情况得很清楚。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public boolean search (int [] nums, int target) { int start = 0 , end = nums.length - 1 ; while (start <= end) { int mid = (start + end) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] == target){ return true ; } if (nums[start] == nums[mid]){ start++; } else if (nums[mid] <= nums[end]) { if (target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[end]) { start = mid + 1 ; }else { end = mid -1 ; } } else { if (target < nums[mid] && target >= nums[start]) { end = mid - 1 ; } else { start = mid + 1 ; } } } return false ; } }
154 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值 II hard 这个题也是旋转数组,和上个题的区别是,1.上个题是找target,这个题是找最小值。2.这个题旋转多次。这个作者解释得不错 ,把作者思路拷贝到了下面了,注意一下这个题,旋转后每个数字的序号保持原来不变,也就是原来是0位置,旋转后序号还是0。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution { public int findMin (int [] nums) { int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] == nums[right]) { right--; } else if (nums[mid] < nums[right]) { right = mid; } else if (nums[mid] > nums[right]) { left = mid + 1 ; } } return nums[right]; } }
540. 有序数组中的单一元素 meidum 这个题是找到唯一的单身狗,注意题目是升序的,不过貌似与升序没关系。这里先整理下官方的清晰解答:因为这个模块是讲二分法,所以不讲解暴力算法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int singleNonDuplicate (int [] nums) { int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left < right) { int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; if (mid % 2 == 1 ) mid--; if (nums[mid] == nums[mid+1 ]) { left = mid + 2 ; } else { right = mid; } } return nums[right]; } }
4 寻找两个正序数组的中位数 hard 这个题虽然看上去是可以合并起来去找,但是,由于有时间复杂度的要求,所以用二分法比较好,坦白说,确实hard。详细解释点击这里看解法三 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 class Solution { public double findMedianSortedArrays (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int length1 = nums1.length, length2 = nums2.length; int totallength = length1 + length2; if (totallength % 2 == 1 ){ int midIndex = totallength / 2 ; double median = getKthElement(nums1, nums2, midIndex + 1 ); return median; } else { int midIndex1 = totallength / 2 -1 , midIndex2 =totallength / 2 ; double median = (getKthElement(nums1, nums2, midIndex1 + 1 ) + getKthElement(nums1, nums2, midIndex2 + 1 )) / 2.0 ; return median; } } public int getKthElement (int [] nums1, int [] nums2, int k) { int length1 = nums1.length, length2 = nums2.length; int index1 = 0 , index2 = 0 ; int kthElement = 0 ; while (true ) { if (index1 == length1) { return nums2[index2 + k - 1 ]; } if (index2 == length2) { return nums1[index1 + k - 1 ]; } if (k == 1 ) { return Math.min(nums1[index1], nums2[index2]); } int half = k / 2 ; int newIndex1 = Math.min(index1 + half, length1) - 1 ; int newIndex2 = Math.min(index2 + half, length2) - 1 ; int pivot1 = nums1[newIndex1] ,pivot2 = nums2[newIndex2]; if (pivot1 <= pivot2) { k = k -(newIndex1 - index1 + 1 ); index1 = newIndex1 + 1 ; } else { k = k -(newIndex2 - index2 + 1 ); index2 = newIndex2 + 1 ; } } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 nums1:1 3 4 9 nums2:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 开始计算: length1=4 ,length2=9 totallength=13 判断为奇数,midIndex=6 传入到子函数(nums1,nums2,6 +1 ) 下面是子函数循环情况 下面说的 排 是指两个数组合并起来,从小到大排第几个的意思 length1=4 ,length2=9 正常情况 第一轮while half=7 /2 =3 newIndex1=3 -1 =2 ,newIndex2=3 -1 =2 [pivot]元素 1 3 [4 ] 9 1 2 [3 ] 4 5 6 7 8 9 可以看出nums2[2 ]的更小,把nums2[2 ]及其前面元素全部去掉,然后更新index2和k这里需要理解为什么更新k和index2,我们要找的数是排序第七个(不是从0 计算)的数,然后分别比较两个数组的nums[k/2 -1 ] nums1 中小于等于 pivot1 的元素有 nums1[0 .. k/2 -2 ] 共计 k/2 -1 个,本题也就是2 个 nums2 中小于等于 pivot2 的元素有 nums1[0 .. k/2 -2 ] 共计 k/2 -1 个,本题也就是2 个 然后取两个数组中比较小的pivot,本题是num2[2 ],可以推导,两个数组中小于等于 pivot 的元素共计不会超过 (k/2 -1 ) + (k/2 -1 ) <= k-2 个,也就是全部元素合并后小于等于nums2[2 ]元素的不超过5 个,如果按照等式左边是为4 个,因为是整除,如果按照等式右边就直接是5 个。 这样的话,即便取pivot本身最大也只能是第 k-1 小的元素,也就是6 ,但是按照上一行的分析,pivot元素是排第5 或者第6 ,本题的话实际是排第5 。 总之还不是第七个我们要找的元素。那么可以完全排除nums[2 ]和左边的元素,这时候就要更新k和index2 k更新:因为本身要找第7 个元素,现在已经排除了3 个元素了,所以k=7 -3 =4 ,也就是在剩下的数组中找排第四个的元素,具体写法是7 -(2 -0 +1 )=4 index2更新: index2=2 +1 =3 ,也就是从nums2[3 ]开始 index1依旧为0 第二轮while half=4 /2 =2 newIndex1=0 +2 -1 =1 ,newIndex2=3 +2 -1 =4 下面标记|,代表左边的元素也就消除。 1 [3 ] 4 9 1 2 3 | 4 [5 ] 6 7 8 9 经过比较后,nums1[1 ]及其左边消除 k更新:因为本身要找第4 个元素,现在已经排除了2 个元素了,所以k=4 -2 =2 ,也就是在剩下的数组中找排第二个的元素,具体写法是4 -(1 -0 +1 )=2 index1更新: index1=1 +1 =2 ,也就是从nums1[2 ]开始 index2依旧为3 第三轮while half=2 /2 =1 newIndex1=2 +1 -1 =2 ,newIndex2=3 +1 -1 =3 1 3 | [4 ] 9 1 2 3 | [4 ] 5 6 7 8 9 这里pivot元素相等,我们就假设上面的4 大于下面的4 ,由于两个数相等,所以我们无论去掉哪个数组中的都行,因为去掉 1 个总会保留 1 个的,所以没有影响。 经过比较后,nums2[3 ]及其左边消除。 k更新:因为本身要找第2 个元素,现在已经排除了1 个元素了,所以k=2 -1 =1 ,也就是在剩下的数组中找排第二个的元素,具体写法是2 -(0 -0 +1 )=1 index2更新: index2=3 +1 =4 ,也就是从nums2[4 ]开始 index1依旧为2 第四轮while k已经等于1 了,直接找剩下比较小的数就行。 1 3 | [4 ] 9 1 2 3 4 | [5 ] 6 7 8 9 答案就是4 当然还有注意边界的情况,本题没有涉及。 所谓边界的问题,也就是有可能其中一个数组过小,然后进行更新的时候会发现越界,这时候也就是这个小的数组数组全部已经小于第K个数据,然后我们之后关注大的数组找到k就行。
常用排序算法
快速排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import java.util.Arrays;public class sort { public static void main (String[] args) { int arr[] = {6 ,7 ,8 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,9 ,10 ,0 ,4 ,6 ,8 ,7 ,99 ,77 ,44 }; int temp[] = new int [arr.length]; int size = arr.length; quick_sort(arr, 0 , size); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); } public static void quick_sort (int [] arr,int left, int right) { if (left + 1 >= right) { return ; } int first = left, last = right - 1 , key = arr[first]; while (first <last) { while (first < last && arr[last] >= key) { --last; } arr[first] = arr[last]; while (first < last && arr[first] <= key) { ++first; } arr[last] = arr[first]; } arr[first] = key; quick_sort(arr, left, first); quick_sort(arr, first + 1 , right); }
插入排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static void insertion_sort (int [] arr, int size) { for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { for (int j = i; j > 0 && arr[j] < arr[j - 1 ]; j--) { int temp = arr[j-1 ]; arr[j-1 ] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } } }
选择排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public static void select_sort (int [] arr,int right) { int small; for (int i = 0 ; i < right - 1 ; i++) { small = i; for (int j = i + 1 ; j < right; j++) { if (arr[j] < arr[small]) { int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[small]; arr[small] = temp; } } } }
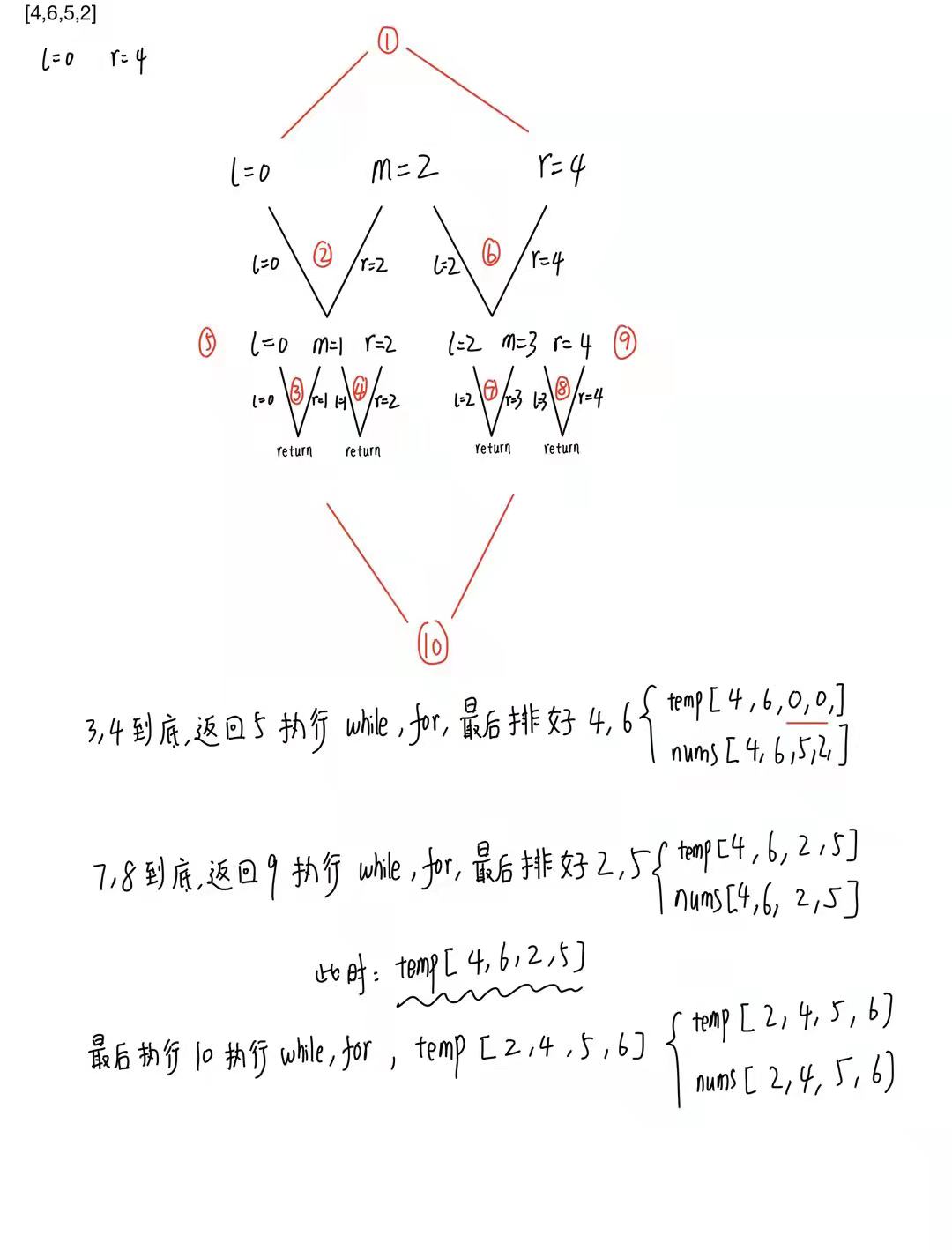
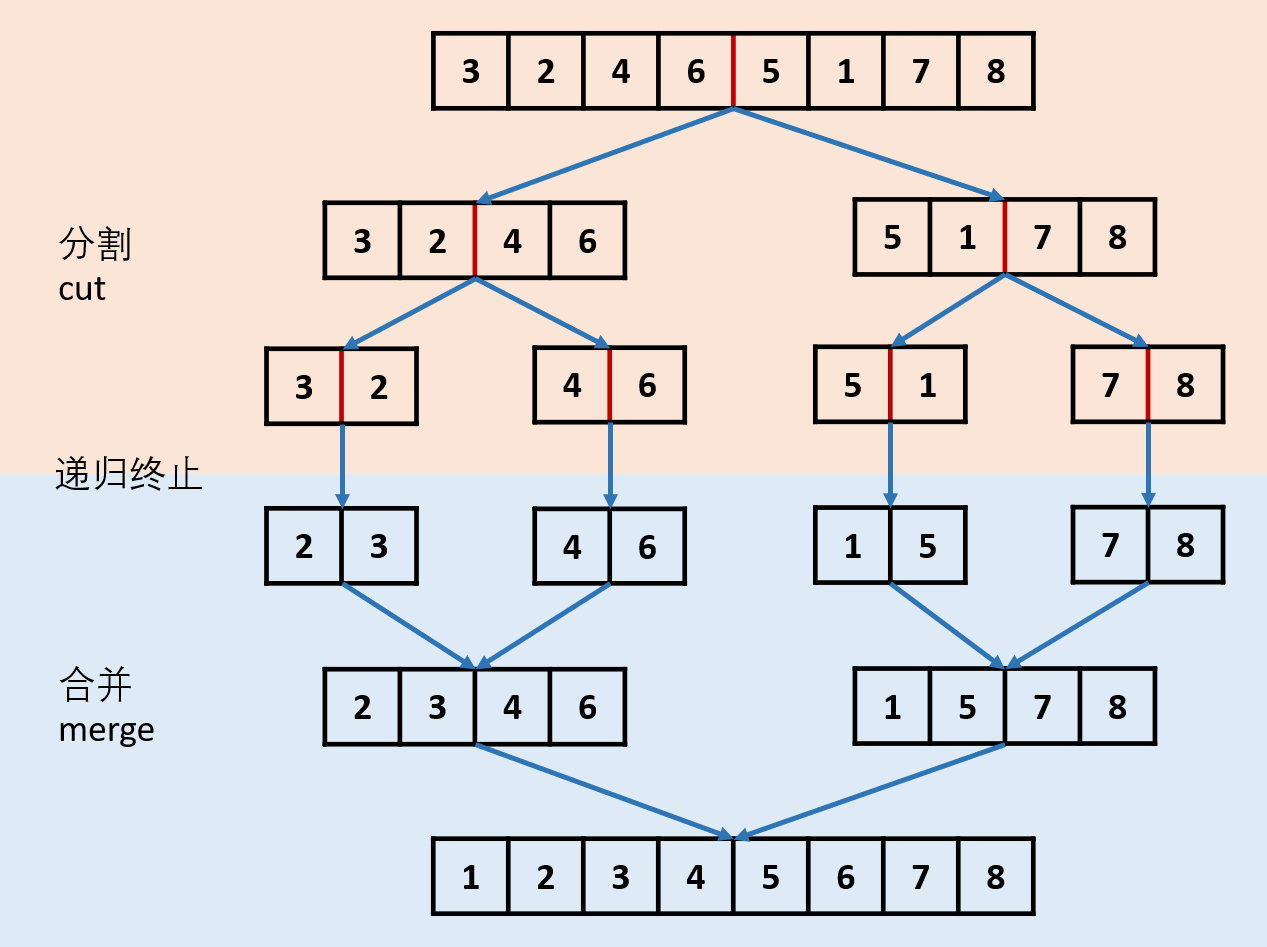
归并排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 void merge_sort (vector<int > &nums, int left, int right, vector<int > &temp) if (left + 1 >= right) { return ; } int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; merge_sort (nums, left, mid, temp); merge_sort (nums, mid, right, temp); int first = left, second = mid, i = left; while (first < mid || second < right) { if (second >= r || (nums[first] <= nums[second] && first < mid)) { temp[i++] = nums[first++]; } else { temp[i++] = nums[second++]; } } for (i = l; i < r; ++i) { nums[i] = temp[i]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public static void merge_sort (int [] arr,int left, int right, int [] temp) { if (left + 1 >= right) { return ; } int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; merge_sort(arr, left, mid, temp); merge_sort(arr, mid, right, temp); int first = left, second = mid, i = left; while (first < mid || second < right) { if (second >= right || (arr[first] <= arr[second] && first < mid)) { temp[i++] = arr[first++]; } else { temp[i++] = arr[second++]; } } for (i = left; i < right; i++) { arr[i] = temp[i]; } }
下面画图理解递归是怎么操作的。
冒泡排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public static void bubble_sort (int [] arr,int right) { for (int i = 1 ; i < right; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < right - i + 1 ; j++) { if (arr[j] < arr[j - 1 ]) { int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j - 1 ]; arr[j - 1 ] = temp; } } } }
215 数组中的第K个最大元素 medium 这个题结合1738来看。思路:寻找第K个大的元素,可以用快速排序法,快速排序就是每次选择一个枢轴元素,然后比他小的在左边,比他大的在右边,最终可以确定枢轴元素的最终位置。对比这个位置和第K大的位置,如果比这个位置小,就在左边递归,反之右边递归。需要注意一个点,就是选择枢轴元素要随机选,不然会遇到极端案例,导致时间复杂度高。当然本题实际执行只考虑了比枢轴元素大的数以及把大的元素放在左边,是为了符合题目第k大的元素,注意本题解法也是一开始把枢轴元素放在最右边。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 class Solution { public int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) { return quickSelect(nums, 0 , k - 1 , nums.length - 1 ); } private int quickSelect (int [] arr, int left, int kth, int right) { int curPartition = partition(arr, left, right); if (curPartition == kth) { return arr[curPartition]; } else if (curPartition < kth) { return quickSelect(arr, curPartition + 1 , kth, right); } else { return quickSelect(arr, left, kth, curPartition - 1 ); } } private int partition (int [] arr, int left, int right) { int pivotIndex = left + (int )(Math.random() * (right - left + 1 )); swap(arr, pivotIndex, right); int index = left - 1 ; for (int i = left; i < right; i++) { if (arr[i] >= arr[right]) { index += 1 ; swap(arr, index, i); } } index += 1 ; swap(arr, index, right); return index; } private void swap (int [] arr, int l, int r) { int temp = arr[l]; arr[l] = arr[r]; arr[r] = temp; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { public int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) { return quickSelect(nums, 0 , k - 1 , nums.length - 1 ); } private int quickSelect (int [] arr, int left, int kth, int right) { int curPartition = partition(arr, left, right); if (curPartition == kth) { return arr[curPartition]; } else if (curPartition < kth) { return quickSelect(arr, curPartition + 1 , kth, right); } else { return quickSelect(arr, left, kth, curPartition - 1 ); } } private int partition (int [] nums, int left, int right) { int pivotIndex = left + (int )(Math.random() * (right - left + 1 )); swap(nums, pivotIndex, left); int first = left, last = right, key = nums[first]; while (first < last) { while (first < last && nums[last] <= key) { --last; } nums[first] = nums[last]; while (first < last && nums[first] >= key) { ++first; } nums[last] = nums[first]; } nums[first] = key; return first;} private void swap (int [] arr, int l, int r) { int temp = arr[l]; arr[l] = arr[r]; arr[r] = temp; } }
347 前K个高频元素(桶排序) medium 首先用hash来创建一个key,value(频率)对应。然后再创建一个list,把相同频率的放在一个位置。最后从后往前面取出前k个来。也就是桶的思想。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int [] topKFrequent(int [] nums, int k) { LinkedHashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) { map.put(nums[i], map.get(nums[i]) + 1 ); } else { map.put(nums[i],1 ); } } List<Integer>[] ans=new List [nums.length + 1 ]; for (int num: map.keySet()){ int i=map.get(num); if (ans[i]==null ){ ans[i]=new ArrayList <>(); } ans[i].add(num); } int res[] = new int [k]; int count = 0 ; for (int i = ans.length - 1 ; i >= 0 && count <k; i--) { if (ans[i] != null ) { for (int j = 0 ; j < ans[i].size(); j++) { if (count < k) { res[count++] = ans[i].get(j); } else break ; } } } return res; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution { public int [] topKFrequent(int [] nums, int k) { LinkedHashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap <>(); int frequency = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) { map.put(nums[i], map.get(nums[i]) + 1 ); frequency = Math.max(map.get(nums[i]),frequency); } else { map.put(nums[i],1 ); frequency = Math.max(map.get(nums[i]),frequency); } } List<Integer>[] ans=new List [frequency + 1 ]; for (int num: map.keySet()){ int i=map.get(num); if (ans[i]==null ){ ans[i]=new ArrayList <>(); } ans[i].add(num); } int res[] = new int [k]; int count = 0 ; for (int i = ans.length - 1 ; i >= 0 && count <k; i--) { if (ans[i] != null ) { for (int j = 0 ; j < ans[i].size(); j++) { if (count < k) { res[count++] = ans[i].get(j); } else break ; } } } return res; } }
451 根据字符出现频率排序(桶排序) medium 这个题主要和上一题对比的话,我觉得主要是一些语法上,比如对字符处理和上一题对数字的处理是不太一样的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public String frequencySort (String s) { Map<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap <Character,Integer>(); int maxfreq = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); int frequency = map.getOrDefault(c, 0 ) + 1 ; map.put(c, frequency); maxfreq = Math.max(maxfreq, frequency); } StringBuffer[] buckets = new StringBuffer [maxfreq + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= maxfreq; i++) { buckets[i] = new StringBuffer (); } for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { char c = entry.getKey(); int frequency = entry.getValue(); buckets[frequency].append(c); } StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer (); for (int i = maxfreq; i > 0 ; i--) { StringBuffer bucket = buckets[i]; for (int j = 0 ; j < bucket.length(); j++) { for (int k = 0 ; k < i; k++) { sb.append(bucket.charAt(j)); } } } return sb.toString(); } }
75 颜色分类 medium 直接插入排序,但是貌似速度和内存都不占优势?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public void sortColors (int [] nums) { for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { for (int j = i; j > 0 && nums[j] < nums[j-1 ]; j--) { int temp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[j - 1 ]; nums[j - 1 ] = temp; } } } }
一切皆可搜索 695 岛屿的最大面积(DFS) medium 思路是深度优先遍历,分为主函数和辅助函数,主函数就是遍历每个点的位置,辅助函数就是dfs,设置好不满足的条件,满足条件的继续搜索。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { public int maxAreaOfIsland (int [][] grid) { int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < grid.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < grid[0 ].length; j++) { ans = Math.max(ans, dfs(grid, i, j)); } } return ans; } public int dfs (int [][] grid, int cur_i, int cur_j) { if (cur_i < 0 || cur_j < 0 || cur_i == grid.length || cur_j == grid[0 ].length || grid[cur_i][cur_j] != 1 ) { return 0 ; } grid[cur_i][cur_j] = 0 ; int [] index_i = {0 , 0 , 1 , -1 }; int [] index_j = {1 , -1 , 0 , 0 }; int ans = 1 ; for (int index = 0 ; index < 4 ; index++) { int next_inedx_i = cur_i + index_i[index]; int next_inedx_j = cur_j + index_j[index]; ans += dfs(grid, next_inedx_i, next_inedx_j); } return ans; } }
547 省份数量(DFS) medium 做这个题的时候陷入到上一题的思维了,做题还是太少了!本题中有多少个二维数组中有多少个一维数组就代表多少个城市,每个一维数组里面的位置代表本城市(也就是i和j相同)或者其他城市(i和j不一样),位置上为1代表有连接,也就是大家最后是属于一个省份的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {class Solution { public int findCircleNum (int [][] isConnected) { int citys = isConnected.length; boolean [] visited = new boolean [citys]; int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < citys; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { dfs(isConnected, visited, citys, i); sum++; } } return sum; } public void dfs (int [][] isConnected,boolean [] visited, int citys, int i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < citys; j++) { if (!visited[j] && isConnected[i][j] == 1 ) { visited[j] = true ; dfs(isConnected, visited, citys, j); } } } }
!417 太平洋大西洋水流问题(DFS) medium 一开始看了半天例子,以为那几点是形成河流的样子。ok,现在说下题目意思,是找出所有的点,这个点可以流向太平洋,也能流向大西洋 ,所以看例子的时候,单独看每一个点,然后需要自己画出流动方向。Leetcode 上写题解了,哈哈。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic (int [][] heights) { int n = heights.length; int m = heights[0 ].length; boolean [][] can_reach_p = new boolean [n][m]; boolean [][] can_reach_a = new boolean [n][m]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { dfs(heights, i, 0 , can_reach_p); dfs(heights, i, m - 1 , can_reach_a); } for (int j = 0 ; j < m; j++) { dfs(heights, 0 , j, can_reach_p); dfs(heights, n - 1 , j, can_reach_a); } List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < m; j++) { if (can_reach_a[i][j] && can_reach_p[i][j]) { res.add(List.of(i, j)); } } } return res; } public void dfs (int [][] heights, int i, int j, boolean [][] can_reach) { if (can_reach[i][j] == true ) { return ; } can_reach[i][j] = true ; int [] index_i = {0 , 0 , 1 , -1 }; int [] index_j = {1 , -1 , 0 , 0 }; for (int index = 0 ; index < 4 ; index++) { int next_index_i = i + index_i[index]; int next_index_j = j + index_j[index]; if (next_index_i >= 0 && next_index_i < heights.length && next_index_j >= 0 && next_index_j < heights[0 ].length && heights[i][j] <= heights[next_index_i][next_index_j]) { dfs(heights, next_index_i, next_index_j, can_reach); } } } }
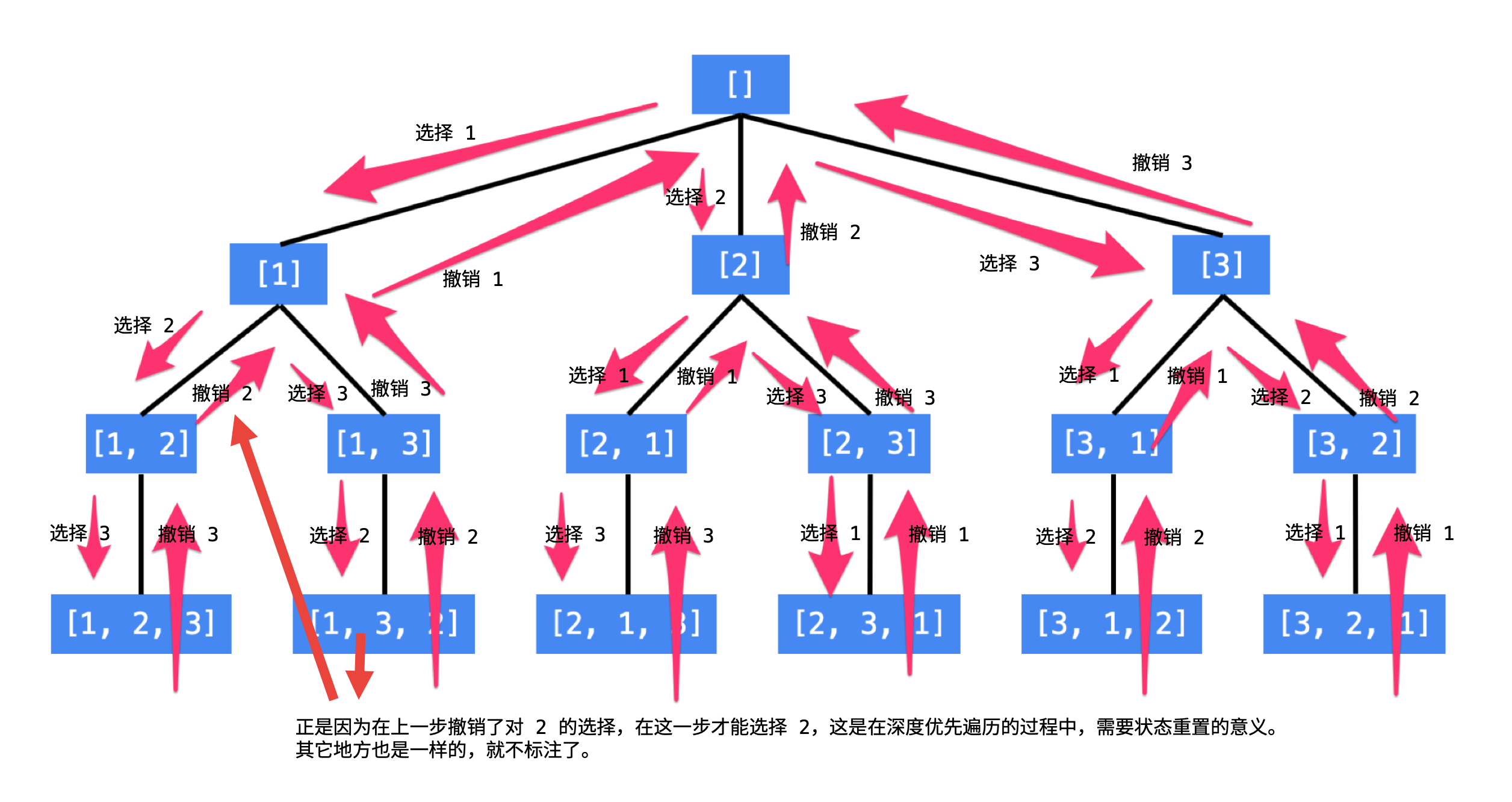
46 全排列(回溯法) medium DFS基本操作:[修改当前节点状态]->[递归子节点状态]。回溯法:[修改当前节点状态]->[递归子节点状态]->[回改当前节点状态]。回溯法是优先搜索的一种特殊状态。一般在排列,组合,选择类问题使用回溯法,这次官方那个视频讲解不错,本题就是按照这个思路来。
1 2 3 4 知识点 注意后面的new 的写法 栈:Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); list里面还有一个list: List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); int len = nums.length; boolean [] used = new boolean [len]; if (len == 0 ) { return res; } Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); dfs(nums, len, 0 , path, used, res); return res; } public void dfs (int [] nums,int len, int depth, Deque<Integer> path, boolean [] used, List<List<Integer>> res) { if (depth == len) { res.add(new ArrayList (path)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { if (used[i] == true ) { continue ; } path.addLast(nums[i]); used[i] = true ; dfs(nums, len, depth + 1 , path, used, res); used[i] = false ; path.removeLast(); } } }
下面引用一张别人图片 来描述这个算法流程。
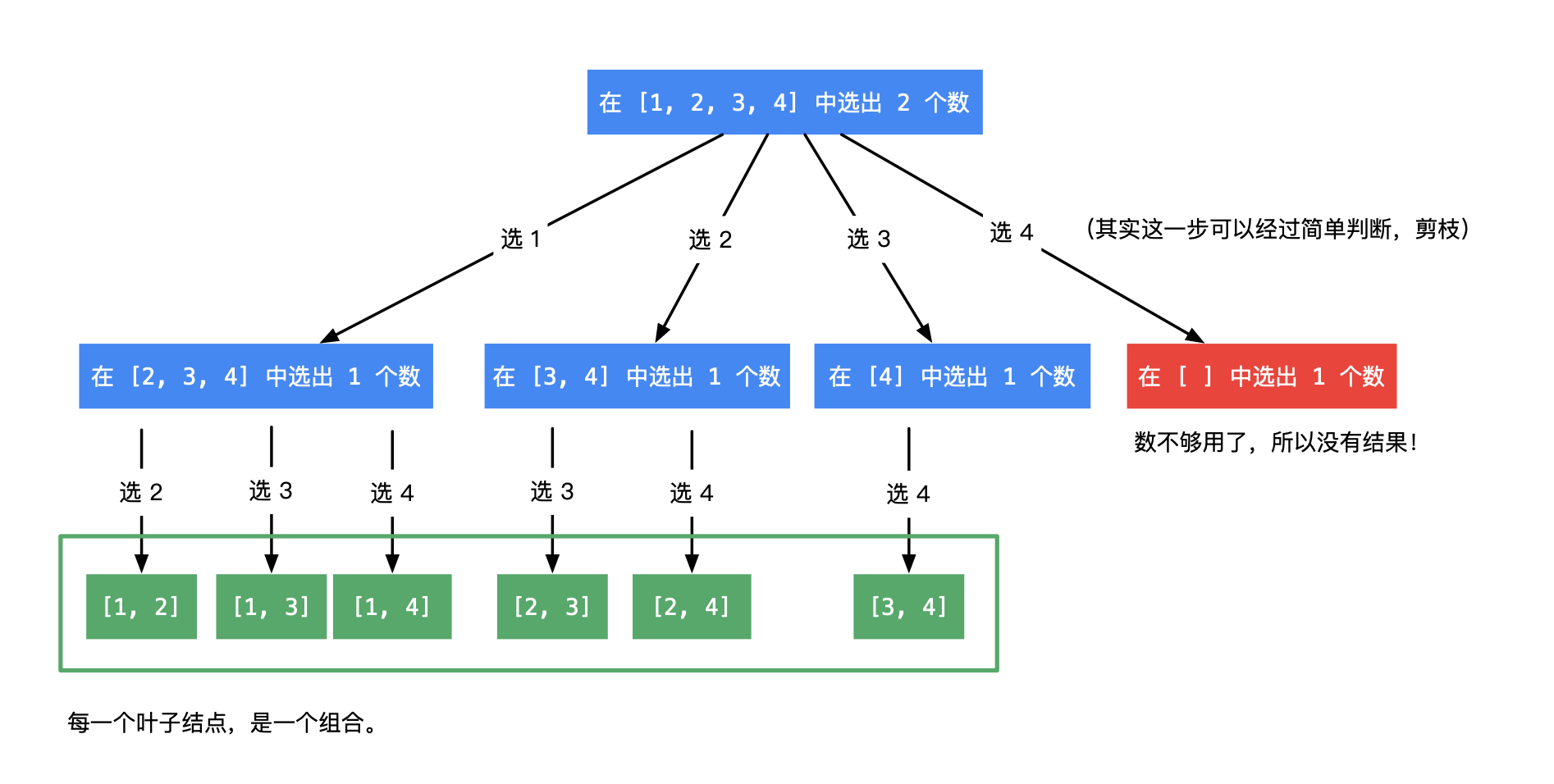
77 组合(回溯法) medium 注意排列是不重复的,组合是的话[1,2]和[2,1]是一个情况,还有不能对自己组合哦。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) { boolean [] used =new boolean [n]; List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (k <= 0 || n < k) { return res; } Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); int [] nums = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { nums[i] = i + 1 ; } dfs(nums, n, k, 0 , path, used, res); return res; } public void dfs (int [] nums, int n, int k, int begin, Deque<Integer> path, boolean [] used, List<List<Integer>> res) { if (path.size() == k) { res.add(new ArrayList (path)); return ; } for (int i = begin; i < n; i++ ) { if (used[i] == true ) { continue ; } used[i] = true ; path.addLast(nums[i]); dfs(nums, n, k, i + 1 , path, used, res); used[i] = false ; path.removeLast(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 import java.util.ArrayDeque;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Deque;import java.util.List;public class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (k <= 0 || n < k) { return res; } Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); dfs(n, k, 1 , path, res); return res; } private void dfs (int n, int k, int begin, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) { if (path.size() == k) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = begin; i <= n; i++) { path.addLast(i); dfs(n, k, i + 1 , path, res); path.removeLast(); } } } 作者:liweiwei1419 链接:https: 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
用下大佬的图理解这个题
79 单词搜索(回溯法) medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 class Solution { public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int m = board.length; int n = board[0 ].length; boolean [][] visited = new boolean [m][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { boolean flag = backtracking(i, j, board, word, visited, 0 ); if (flag) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public boolean backtracking (int i, int j, char [][] board, String word, boolean [][] visited, int pos) { if (board[i][j] != word.charAt(pos) || visited[i][j] ==true ) { return false ; } else if (pos == word.length() - 1 ) { return true ; } visited[i][j] = true ; int [] index_i = {0 , 0 , 1 , -1 }; int [] index_j = {1 , -1 , 0 , 0 }; boolean result = false ; for (int index = 0 ; index < 4 ; index++) { int next_index_i = i + index_i[index]; int next_index_j = j + index_j[index]; if (next_index_i >= 0 && next_index_i < board.length && next_index_j >= 0 && next_index_j < board[0 ].length) { boolean flag = backtracking(next_index_i, next_index_j, board, word, visited, pos + 1 ); if (flag) { result = true ; break ; } } } visited[i][j] = false ; return result; } }
下面这个是按照书上思路改写的,但是错误,先放着,未来会修改(已修改,看下面),初步判断是因为find不是全局变量。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int m = board.length; int n = board[0 ].length; boolean [][] visited = new boolean [m][n]; boolean find = false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { backtracking(i, j, board, word, find, visited, 0 ); } } return find; } public void backtracking (int i, int j, char [][] board, String word, boolean find, boolean [][] visited, int pos) { if (i < 0 || i >= board.length || j < 0 || j >= board[0 ].length) { return ; } if (board[i][j] != word.charAt(pos) || visited[i][j] || find) { return ; } if (pos == word.length() - 1 ) { find = true ; return ; } visited[i][j] = true ; backtracking(i + 1 , j, board, word, find, visited, pos + 1 ); backtracking(i - 1 , j, board, word, find, visited, pos + 1 ); backtracking(i, j + 1 , board, word, find, visited, pos + 1 ); backtracking(i, j - 1 , board, word, find, visited, pos + 1 ); visited[i][j] = false ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { private boolean find = false ; public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { if (board == null ) return false ; boolean [][] visited = new boolean [board.length][board[0 ].length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < board.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < board[0 ].length; j++) { backTracking(i, j, board, word, visited, 0 ); } } return find; } public void backTracking (int i, int j, char [][] board, String word, boolean [][] visited, int pos) { if (i < 0 || i >= board.length || j < 0 || j >= board[0 ].length || visited[i][j] || board[i][j] != word.charAt(pos) || find) return ; if (pos == word.length() - 1 ) { find = true ; return ; } visited[i][j] = true ; backTracking(i - 1 , j, board, word, visited, pos + 1 ); backTracking(i + 1 , j, board, word, visited, pos + 1 ); backTracking(i, j - 1 , board, word, visited, pos + 1 ); backTracking(i, j + 1 , board, word, visited, pos + 1 ); visited[i][j] = false ; } }
51 N皇后(回溯法) hard 久闻的经典题!题目要求就是任何两个皇后都不能在同一行、同一列以及同一条斜线上。思考:斜线怎么判断?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 class Solution { List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) { char [][] board = new char [n][n]; for (char [] c : board) { Arrays.fill(c, '.' ); } backtracking(board, 0 ); return res; } public void backtracking (char [][] board, int row) { if (row == board.length) { res.add(charToList(board)); return ; } int n = board[row].length; for (int col = 0 ; col < n; col++) { if (!isValid(board, row, col)) { continue ; } board[row][col] = 'Q' ; backtracking(board, row + 1 ); board[row][col] = '.' ; } } public boolean isValid (char [][] board, int row, int col) { int n = board.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (board[i][col] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i = row - 1 , j = col + 1 ; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) { if (board[i][j] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i = row - 1 , j = col - 1 ; i >= 0 && j >=0 ; i--, j--) { if (board[i][j] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } return true ; } public List charToList (char [][] board) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (char [] c : board) { list.add(String.copyValueOf(c)); } return list; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 本题有很多需要学习的写法 1. for (char [] c : board) { System.out.print("1" ); } 本句输出是1111 ,也就是说,对于Arrays.fill(c, '.' )每次操作,都是[., ., ., .],一次性把每行的4 个位置都填充上,然后一共操作4 次而不是16 次。 2. Arrays.fill(c, '.' );for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){ System.out.print(Arrays.toString(board[i])); } 输出结果是: [., ., ., .][., ., ., .][., ., ., .][., ., ., .] 3. for (char [] c : board) { list.add(String.copyValueOf(c)); } 首先为什么要这么操作,因为输入是一个二维数组来的,最后的输出要符合题目输出,把每一个一维数组加到list中! 这一段的操作是这样看,首先是输入一个已经摆放好皇后的棋盘 String.copyValueOf是返回字符串 然后char c是提取每一行出来,比如第一行.Q..然后add到list中,最后扫描完所有行list是这样[.Q.., ...Q, Q..., ..Q.],然后再res.add进去。
934 最短的桥(DFS+BFS) medium 一般广度优先遍历用于求最短路径或者可达性问题。本题实际上就是求两个岛屿之间的最短距离,先任意找到一个岛,然后用广度优先搜索寻找和另外一个岛屿的最短距离。结合了书和该作者 的想法。做完这个题其实还是有点不理解,因为首先是找到了第一个岛后就break掉了,那怎么知道其他岛与其他岛会不会有更小的距离呢?经过我的探索,终于知道了,因为题目样例中有且仅有两个岛!!!!!!不会出现第三个岛!!!!务必知道挨着的1是属于一个岛!!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 有个地方需要注意,两个陆地挨着的属于一个岛。比如[[1 ,0 ,0 ],[1 ,0 ,0 ],[0 ,0 ,0 ]]这种情况是一个岛,当然了,这个用例是不能被输入的,因为必须要有两个岛。还有这个题返回的是必须翻转0 的数目。 class Solution { public int shortestBridge (int [][] grid) { int [][] direction = new int [][]{{1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 }, {0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }}; int n = grid.length; int m = grid[0 ].length; int ans = -1 ; boolean flag = false ; Deque<int []> point = new ArrayDeque <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (flag == true ) break ; for (int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++) { if (grid[i][j] == 1 ) { dfs(grid, point, i, j); flag = true ; break ; } } } while (!point.isEmpty()) { int size = point.size(); ans++; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { int [] node = point.poll(); for (int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j++) { int next_x = node[0 ] + direction[j][0 ]; int next_y = node[1 ] + direction[j][1 ]; if (next_x < 0 || next_x >= grid.length || next_y < 0 || next_y >= grid[0 ].length || grid[next_x][next_y] == 2 ) { continue ; } if (grid[next_x][next_y] == 1 ) { return ans; } grid[next_x][next_y] = 2 ; point.add(new int []{next_x, next_y}); } } } return ans; } public void dfs (int [][] grid, Deque<int []> point, int i, int j) { if (i < 0 || i >= grid.length || j < 0 || j >= grid[0 ].length || grid[i][j] == 2 || grid[i][j] != 1 ) { return ; } grid[i][j] = 2 ; point.add(new int []{i, j}); dfs(grid, point, i - 1 , j); dfs(grid, point, i + 1 , j); dfs(grid, point, i, j - 1 ); dfs(grid, point, i, j + 1 ); } }举个例子: 现在两个岛是这样的,就是一个L型和中间一块小岛 [[1 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ],[1 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ],[1 ,0 ,1 ,0 ,0 ],[1 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ],[1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ]] 下面最左边的9 和7 代表队列中的元素个数,hello具体位置在上面代码看,表达进入for 循环,hello右边是ans的大小,最右边是取出来的坐标。可以看到,先把L型岛坐标全部放进队列,然后一个个坐标取出来再再看四周(并且也把四周的点加入到队列),第一轮发现是没有碰到陆地的,所以到了第二轮,第二轮是7 因为L型右边的坐标围起来是7 个,然后开始继续找,到了2 ,1 坐标,可以知道右边一个位置是1 ,这时候已经找到了,返回ans。 9 hello 0 0 0 hello 0 1 0 hello 0 2 0 hello 0 3 0 hello 0 4 0 hello 0 4 1 hello 0 4 2 hello 0 4 3 hello 0 4 4 7 hello 1 0 1 hello 1 1 1 hello 1 2 1
126 单词接龙2(回溯+BFS) hard 单词只差一个字母的可以连接成节点,思考如何去判断只相差一个字母?回溯也就是深度优先搜索的一个应用,用于找出所有情况,BFS也就是找到最短路径,合起来就是找出所有的最短路径。这个题和上一个题差不多。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 class Solution { public List<List<String>> findLadders (String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) { List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList <>(); Set<String> dict = new HashSet <>(wordList); if (!dict.contains(endWord)) { return res; } dict.remove(beginWord); Map<String, Integer> steps = new HashMap <>(); steps.put(beginWord, 0 ); Map<String, List<String>> from = new HashMap <>(); int step = 1 ; boolean found = false ; int wordlen = beginWord.length(); Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(beginWord); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { String currword = queue.poll(); char [] chararray = currword.toCharArray(); for (int j = 0 ; j < wordlen; j++) { char origin = chararray[j]; for (char c = 'a' ; c <= 'z' ; c++) { chararray[j] = c; String nextword = String.valueOf(chararray); if (steps.containsKey(nextword) && step == steps.get(nextword)) { from.get(nextword).add(currword); } if (!dict.contains(nextword)) { continue ; } dict.remove(nextword); queue.add(nextword); from.putIfAbsent(nextword, new ArrayList <>()); from.get(nextword).add(currword); steps.put(nextword, step); if (nextword.equals(endWord)) { found = true ; } } chararray[j] = origin; } } step++; if (found) { break ; } } if (found) { Deque<String> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); path.add(endWord); backtracking(from, path ,beginWord ,endWord ,res); } return res; } public void backtracking (Map<String, List<String>> from, Deque<String> path, String beginWord, String cur, List<List<String>> res) { if (cur.equals(beginWord)) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (String preucrsor : from.get(cur)) { path.addFirst(preucrsor); backtracking(from, path, beginWord, preucrsor, res); path.removeFirst(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 map和hashmap区别? queue和Deque区别? add offer等操作区别? contains和containskey区别? put和putIfAbsent区别:put在放入数据时,如果放入数据的key已经存在与Map中,最后放入的数据会覆盖之前存在的数据,而putIfAbsent在放入数据时,如果存在重复的key,那么putIfAbsent不会放入值。 测试的时候发现下面两种写法都是可以的,可以百度下他们的不同。 Deque<String> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); Deque<String> path = new ArrayList <>();
130 被围绕的区域 medium 采用深度优先遍历递归,首先要理解就是只有被X包围的区域O才被替换,所以在边界的O是不能被替换的,延伸下去的话,和边界O相连的O也是不能够被替换的,所以这个题目的思想就是,从边界O下手,然后找到和这个边界O相连的O,然后把他们都替换成一个字符#,最后再做一次全局的遍历,把没被替换成O的换成X,把#恢复成O。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution { public void solve(char[][] board) { if (board == null || board.length == 0) { return; } int n = board.length, m = board[0].length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) { boolean isEdge = i == 0 || i == n - 1 || j == 0 || j == m - 1; if (isEdge && board[i][j] == 'O') { //只需要从边界下手,其他地方不需要 dfs(board, i ,j); } } } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { //都遍历完了,再全局遍历进行更换字符 for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { if (board[i][j] == 'O') { board[i][j] = 'X'; } if (board[i][j] == '#') { board[i][j] = 'O'; } } } } public void dfs(char [][]board, int i ,int j) { //深度优先遍历 if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= board.length || j >= board[0].length || board[i][j] == 'X' || board[i][j] == '#') { //边界条件以及本来是X和#的不需要操作 return; } board[i][j] = '#'; dfs(board, i + 1, j); dfs(board, i - 1, j); dfs(board, i , j + 1); dfs(board, i , j - 1); } }
257 二叉树的所有路径 easy 深度优先遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) { List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>(); constructpath(root, "", paths); return paths; } public void constructpath(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> paths) { if (root != null) { StringBuffer temppath = new StringBuffer(path); //注意这里,每次递归都对变量path进行拷贝构造 temppath.append(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { //到了叶子节点就代表结束了 paths.add(temppath.toString()); } else { temppath.append("->"); constructpath(root.left, temppath.toString(), paths); constructpath(root.right, temppath.toString(), paths); } } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 对于append和add的用法总结: 1.append Java里只有StringBuffer和StringBuild才有append方法,Sting里是没有append方法的 2.add List集合列表中添加元素
47 全排列2 medium 和46 的区别是,这个题是有重复数字的,而且重复数字不是有序的,而是打乱的。官网的题解更简洁
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); int len = nums.length; boolean[] used = new boolean[len]; if (len == 0) { return res; } Arrays.sort(nums); //区别1,首先要对数列进行排序 Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>(); dfs(nums, len, 0, path, used, res); return res; } public void dfs(int[] nums, int len, int depth, Deque<Integer> path, boolean[] used, List<List<Integer>> res) { if (depth == len) { res.add(new ArrayList(path)); return; } for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { if (used[i] == true || (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false)) { //区别2,还要判断和前一个数是不是一样的,这里used[i - 1] == false不好理解,下面单独解释 continue; } path.addLast(nums[i]); used[i] = true; dfs(nums, len, depth + 1, path, used, res); used[i] = false; path.removeLast(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 这个题首先要排序哦 i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]这个很好理解,就是重复的数字不要再进行了,但是used[i - 1] == false这个其实是不好理解的,我在做的时候就在想为什么还要多加这个条件呢?。 来自网友1的解释(vis和上面used作用一样): 加上 !vis[i - 1]来去重主要是通过限制一下两个相邻的重复数字的访问顺序 举个栗子,对于两个相同的数11,我们将其命名为1a1b, 1a表示第一个1,1b表示第二个1; 那么,不做去重的话,会有两种重复排列 1a1b, 1b1a, 我们只需要取其中任意一种排列; 为了达到这个目的,限制一下1a, 1b访问顺序即可。 比如我们只取1a1b那个排列的话,只有当visit nums[i-1]之后我们才去visit nums[i], 也就是如果!visited[i-1]的话则continue 来自网友2的解释: for循环保证了从数组中从前往后一个一个取值,再用if判断条件。所以nums[i - 1]一定比nums[i]先被取值和判断。如果nums[i - 1]被取值了,那vis[i - 1]会被置1,只有当递归再回退到这一层时再将它置0。每递归一层都是在寻找数组对应于递归深度位置的值,每一层里用for循环来寻找。所以当vis[i - 1] == 1时,说明nums[i - 1]和nums[i]分别属于两层递归中,也就是我们要用这两个数分别放在数组的两个位置,这时不需要去重。但是当vis[i - 1] == 0时,说明nums[i - 1]和nums[i]属于同一层递归中(只是for循环进入下一层循环),也就是我们要用这两个数放在数组中的同一个位置上,这就是我们要去重的情况。
40 组合总和 II medium 深度优先遍历,务必注意解集不能包含重复组合,每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次,这个博主解释不错 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) { int len = candidates.length; List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (len == 0 ) { return res; } Arrays.sort(candidates); Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(len); dfs(candidates, len, 0 , target, path, res); return res; } private void dfs (int [] candidates, int len, int begin, int target, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) { if (target == 0 ) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) { if (target - candidates[i] < 0 ) { break ; } if (i > begin && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1 ]) { continue ; } path.addLast(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates, len, i + 1 , target - candidates[i], path, res); path.removeLast(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) { int len = candidates.length; List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(candidates); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <Integer>(); dfs(candidates, len, target, 0 , res, path); return res; } private void dfs (int [] candidates, int len,int target, int begin, List<List<Integer>> res, LinkedList<Integer> path) { if (target == 0 ) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) { if (target - candidates[i] < 0 ) { break ; } if (i > begin && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1 ]) { continue ; } path.add(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates, len, target - candidates[i], i + 1 , res, path); path.removeLast(); } } }
37 解数独 hard 未完成 310 最小高度树 medium 未完成 动态规划 dp三要素,定义状态,初始状态,状态转移
70 爬楼梯 easy 题目说可以跨一步或者两步,动态规划最重要就是有一个状态转移方程,f(x)=f(x−1)+f(x−2),你可以理解为,我走到x级的时候,我的方案数量就是走到x-1级的所有数量加上我走到x-2级的所有数量。怎么理解呢?比如我知道x-1级的所有方案数量,我再走一步就可以到达x级,同理,x-2级也是这样。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int climbStairs (int n) { if (n <= 2 ) { return n; } int pre2 = 1 , pre1 = 2 , cur = 0 ; for (int i = 2 ; i < n ; i++) { cur = pre1 + pre2; pre2 = pre1; pre1 = cur; } return cur; } }
198 打家劫舍 medium 直接说大于两间房的情况,那么有两种情况1.偷窃第k间房屋,那么就不能偷窃第k-1间房屋,偷窃总金额为前k-2间房屋的最高总金额与第k间房屋的金额之和。2.不偷窃第k间房屋,偷窃总金额为前k−1间房屋的最高总金额。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int rob (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int len = nums.length; if (len == 1 ) { return nums[0 ]; } int first = nums[0 ], second = Math.max(nums[0 ],nums[1 ]); for (int i = 2 ; i < len; i++) { int temp = second; second = Math.max(first + nums[i], second); first = temp; } return second; } }
413 等差数列划分 medium 首先要注意至少是三个元素才可以,其次注意子数组也算,比如[1,2,3,4]这个就可以有[1, 2, 3]、[2, 3, 4] 和 [1,2,3,4] 三个等差数组。下面t++是不太好理解的,可以看官方解释。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int numberOfArithmeticSlices (int [] nums) { int len = nums.length; if (len == 1 || len == 2 ) { return 0 ; } int d = nums[1 ] - nums[0 ], t = 0 , ans = 0 ; for (int i = 2 ; i < len; i++) { if (nums[i] - nums[i - 1 ] == d) { ++t; } else { d = nums[i] - nums[i - 1 ]; t = 0 ; } ans += t; } return ans; } }
64 最小路径和 medium 首先要注意,路径只能向下或者向右,其次,返回的是最后路径的大小,而不是路径本身。本方法是创建一个最小路径的矩阵,也就是每个位置记录从左上角到这里最小值,最后返回右下角位置的值即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int minPathSum (int [][] grid) { if (grid == null || grid.length == 0 || grid[0 ].length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int rows = grid.length, columns = grid[0 ].length; int [][] dp = new int [rows][columns]; dp[0 ][0 ] = grid[0 ][0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < rows; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + grid[i][0 ]; } for (int j = 1 ; j < columns; j++) { dp[0 ][j] = dp[0 ][j - 1 ] + grid[0 ][j]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < columns; j++) { dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]) + grid[i][j]; } } return dp[rows - 1 ][columns - 1 ]; } }
542 01矩阵 medium 和上一题一样,构建一个距离矩阵,但是本题又和上一题不太一样哦,是寻找每个元素距离0最近的距离。只有 水平向左移动 和 竖直向上移动,只有 水平向右移动 和 竖直向下移动。本题的思路是这个点周围的邻居到0的最小距离+1就是这个点到0的最短距离。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution { public int [][] updateMatrix(int [][] mat) { int m = mat.length, n = mat[0 ].length; int [][] dist = new int [m][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { Arrays.fill(dist[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2 ); } for (int i = 0 ;i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (mat[i][j] == 0 ) { dist[i][j] = 0 ; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (i - 1 >= 0 ) { dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i][j], dist[i - 1 ][j] + 1 ); } if (j - 1 >= 0 ) { dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i][j], dist[i][j - 1 ] + 1 ); } } } for (int i = m - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { for (int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { if (i + 1 < m) { dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i][j], dist[i + 1 ][j] + 1 ); } if (j + 1 < n) { dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i][j], dist[i][j + 1 ] + 1 ); } } } return dist; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 为啥只用左上和右下就行? 用最简单的只有一个0 的来示例(来自网友的图) 1111 1111 1011 1111 左上(左邻居和上邻居)之后变成(其中-表示int 最大值) ---- ---- -012 -123 接下来的右下就是取某个点的右上和左下其中比较小的值 加一 就行 现在根据已知的右下角这一坨 已经可以推出其余的全部了 比如左下角那一坨 ---- ---- 1012 2123 右上角那一坨 -234 -123 1012 2123 还有最终左上角的那一坨 3234 2123 1012 2123 我自己的一个小例子 10 01 左上后 m0 m1 右下后 10 21
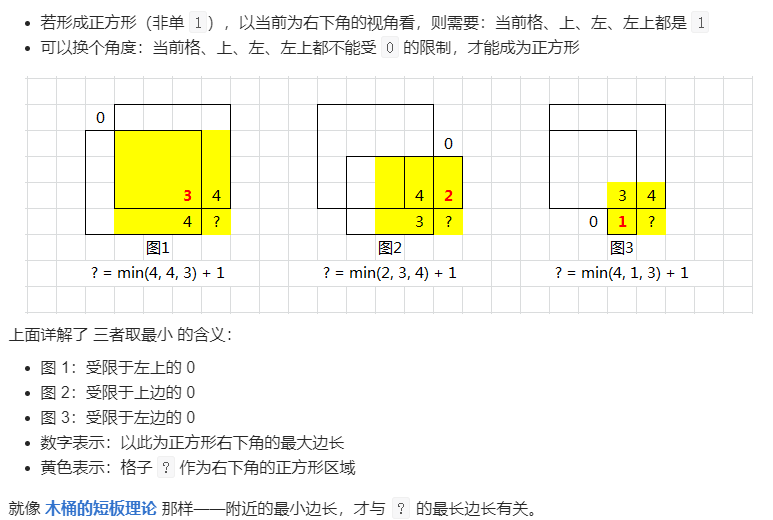
221 最大正方形 medium 首先需要注意,dp[i][j]是以i,j坐标为右下角的正方形边长。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int maximalSquare (char [][] matrix) { if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0 ].length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int maxsize = 0 ; int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0 ].length; int [][] dp = new int [m][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (matrix[i][j] == '1' ) { if (i == 0 || j == 0 ) { dp[i][j] = 1 ; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ], dp[i - 1 ][j]), dp[i][j - 1 ]) +1 ; } } maxsize = Math.max(maxsize, dp[i][j]); } } return maxsize * maxsize; } }
下面一个图来自网友,解释了为什么用左边,上边,左斜上边的最小值。
279 完全平方数 medium 推荐看这个作者 的讲解,非常好
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int numSquares (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < n + 1 ; i++) { dp[i] = i; for (int j = 1 ; i - j * j >=0 ; j++) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - j * j] + 1 ); } } return dp[n]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int numSquares (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j * j <= i ; j++) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - j * j] + 1 ); } } return dp[n]; } }
91 解码方法 medium 这个题思考了比较久,题解是根据书上改成java的,虽然比较长,但是好理解。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int numDecodings (String s) { int n = s.length(); if (n == 0 ) return 0 ; int prev = s.charAt(0 ) -48 ; if (prev == 0 ) return 0 ; if (n == 1 ) return 1 ; int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp,1 ); for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { int cur = s.charAt(i - 1 ) - 48 ; if ((prev == 0 || prev > 2 ) && cur == 0 ) { return 0 ; } if (prev == 1 || prev == 2 && cur < 7 ) { if (cur!=0 ) { dp[i] = dp[i - 2 ] + dp[i - 1 ]; } else { dp[i] = dp[i - 2 ]; } } else { dp[i] = dp[i - 1 ]; } prev = cur; } return dp[n]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 理解过程 这个题是返回解码方法的总数, 首先定义一个长为n+1的数组,dp[2]就表示前2个数的解码方法总数,所以最后返回dp[n]就代表题目要求的答案了。 如果第一个数字就是0,那不用问,永远解不出来,规则上01和1是不一样的,没有01这个解码。 其次声明好dp数组,长度为n+1,并且全部位置初始化为1,后面会讲到为什么f[0]也要设置为1。 我们要清楚,声明了prev和cur,就是为了看看当前数和前一个数能不能组合起来解码. 进入判断循环,i从2开始,这是为了配合dp数组,因为我们说了dp[i]表示前i个数的解: 那么cur就是s[i - 1]了,这是s数组的第二个数,prev我们在前面已经声明了。 首先就是判断无法解码的情况,也就是cur为0,prev也为0或者prev大于2,既不能自己单独解码,也不能和前面组合解码。 然后判断可以解码的情况,有组合解码和单独解码 组合解码又分为11~19,21~26,因为10和20比较特殊,前者既能单独解码,又能组合解码,后者只能单独解码的两位数 然后单独解码就是只能单独一个解码 下一轮判断,把cur变成prev 为什么f[0]也为1? 这里摘抄了网友的一个不错的理解: f[0]代表前0个数字的方案数,这样的状态定义其实是没有实际意义的,但是f[0]的值需要保证边界是对的,即f[1]和f[2]是对的。 比如说,第一个数不为0,那么解码前1个数只有一种方法,将其单独解码,即f[1] = f[1 - 1] = 1。 解码前两个数,如果第1个数和第2个数可以组合起来解码,那么f[2] = f[1] + f[0] = 2 ,否则只能单独解码第2个数,即f[2] = f[1] = 1。 因此,在任何情况下f[0]取1都可以保证f[1]和f[2]是正确的,所以f[0]应该取1。 然后的话,我们在代码中有一个10和20的特殊解码,dp[i] = dp[i - 2]。因为这里说了如果只能单独解码的话,就f[1] = f[1 - 1] = 1。 实在不能理解。试试s=20,s=23,尝试自己去理解一下。
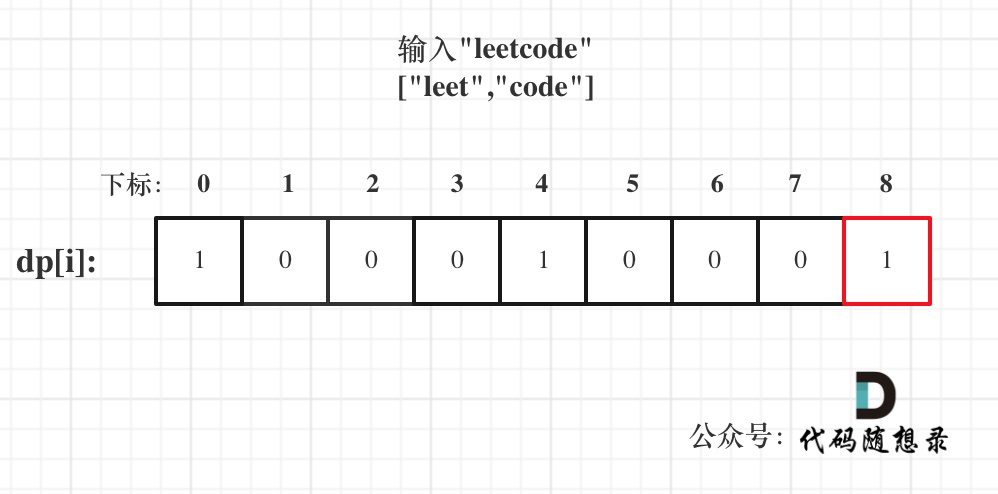
139 单词拆分 medium 这道题类似于完全平方数分割。然后看到评论题解说用背包问题:单词就是物品,字符串s就是背包,完全背包问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public boolean wordBreak (String s, List<String> wordDict) { int n = s.length(); boolean [] dp = new boolean [n + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = true ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (wordDict.contains(s.substring(j,i)) && dp[j] == true ) { dp[i] = true ; } } } return dp[n]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 卡哥将得很详细,复制一下记录 单词就是物品,字符串s就是背包,单词能否组成字符串s,就是问物品能不能把背包装满。 拆分时可以重复使用字典中的单词,说明就是一个完全背包! 动规五部曲分析如下: 1.确定dp数组以及下标的含义 dp[i] : 字符串长度为i的话,dp[i]为true,表示可以拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。 2.确定递推公式 如果确定dp[j] 是true,且 [j, i] 这个区间的子串出现在字典里,那么dp[i]一定是true。(j < i )。 所以递推公式是 if([j, i] 这个区间的子串出现在字典里 && dp[j]是true) 那么 dp[i] = true。 3.dp数组如何初始化 从递归公式中可以看出,dp[i] 的状态依靠 dp[j]是否为true,那么dp[0]就是递归的根基,dp[0]一定要为true,否则递归下去后面都都是false了。 那么dp[0]有没有意义呢? dp[0]表示如果字符串为空的话,说明出现在字典里。 但题目中说了“给定一个非空字符串 s” 所以测试数据中不会出现i为0的情况,那么dp[0]初始为true完全就是为了推导公式。 下标非0的dp[i]初始化为false,只要没有被覆盖说明都是不可拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。 4.确定遍历顺序 题目中说是拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词,所以这是完全背包。 还要讨论两层for循环的前后循序。 如果求组合数就是外层for循环遍历物品,内层for遍历背包。 如果求排列数就是外层for遍历背包,内层for循环遍历物品。 本题最终要求的是是否都出现过,所以对出现单词集合里的元素是组合还是排列,并不在意! 那么本题使用求排列的方式,还是求组合的方式都可以。 即:外层for循环遍历物品,内层for遍历背包 或者 外层for遍历背包,内层for循环遍历物品 都是可以的。 但本题还有特殊性,因为是要求子串,最好是遍历背包放在外循环,将遍历物品放在内循环。 如果要是外层for循环遍历物品,内层for遍历背包,就需要把所有的子串都预先放在一个容器里。(如果不理解的话,可以自己尝试这么写一写就理解了) 所以最终我选择的遍历顺序为:遍历背包放在外循环,将遍历物品放在内循环。内循环从前到后。 5.举例推导dp[i] 以输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"]为例,dp状态如图: (在下方) dp[s.size()]就是最终结果。 ps: 五部曲中第一部是最困难的. 一般都是遵循"题目问什么, 就把`dp[]设置成什么 作者:carlsun-2 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-break/solution/dai-ma-sui-xiang-lu-139-dan-ci-chai-fen-50a1a/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
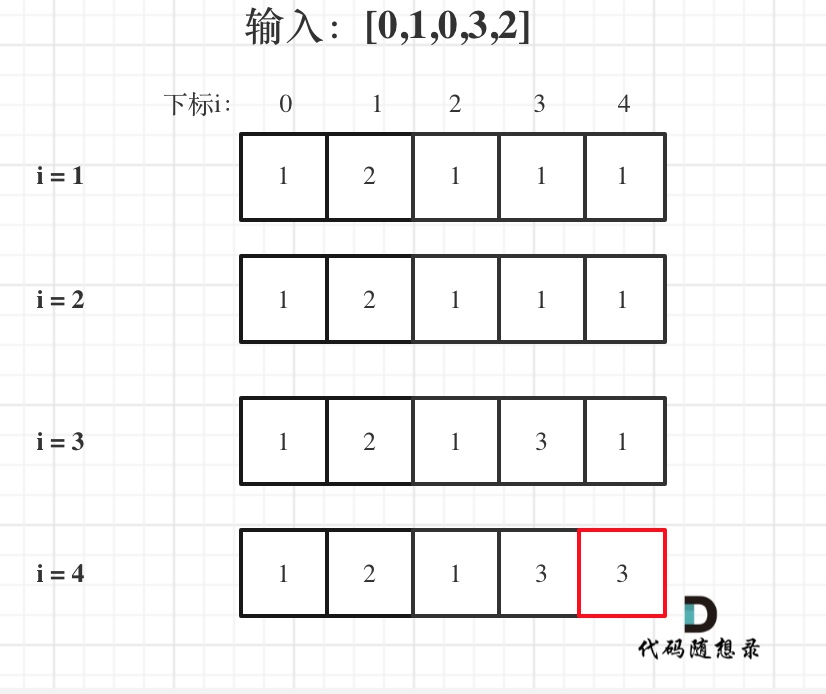
300 最长递增子序列 medium 首先说明题目说的升序是严格升序,比如777长递增子序列就只有7,也就是长度只有1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int [] dp = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(dp,1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (nums[i] > nums[j]) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1 ); } } } int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { res = Math.max(res,dp[i]); } return res; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 卡哥动态规划五部曲 最长上升子序列是动规的经典题目,这里dp[i]是可以根据dp[j] (j < i)推导出来的,那么依然用动规五部曲来分析详细一波: 1. dp[i]的定义dp[i]表示i之前包括i的以nums[i]结尾最长上升子序列的长度 2. 状态转移方程位置i的最长升序子序列等于j从0 到i-1 各个位置的最长升序子序列 + 1 的最大值。 所以:if (nums[i] > nums[j]) dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1 ); 注意这里不是要dp[i] 与 dp[j] + 1 进行比较,而是我们要取dp[j] + 1 的最大值。 3. dp[i]的初始化每一个i,对应的dp[i](即最长上升子序列)起始大小至少都是1. 4. 确定遍历顺序dp[i] 是有0 到i-1 各个位置的最长升序子序列 推导而来,那么遍历i一定是从前向后遍历。 5. 举例推导dp数组输入:[0 ,1 ,0 ,3 ,2 ],dp数组的变化如下:
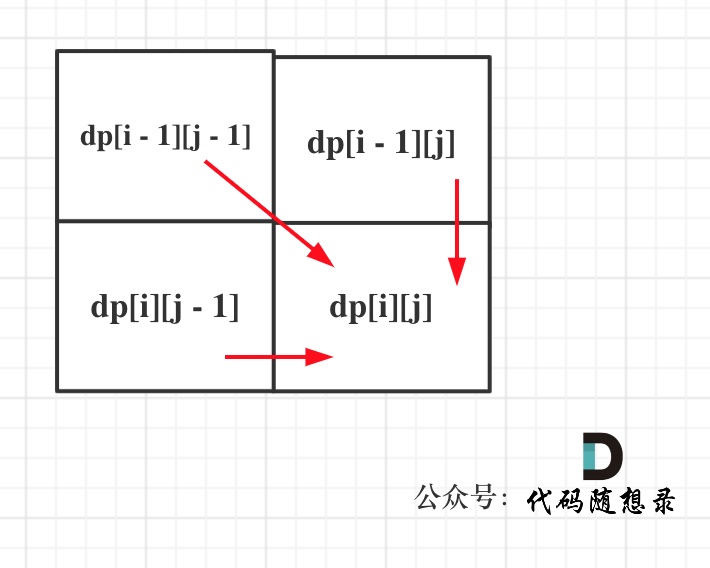
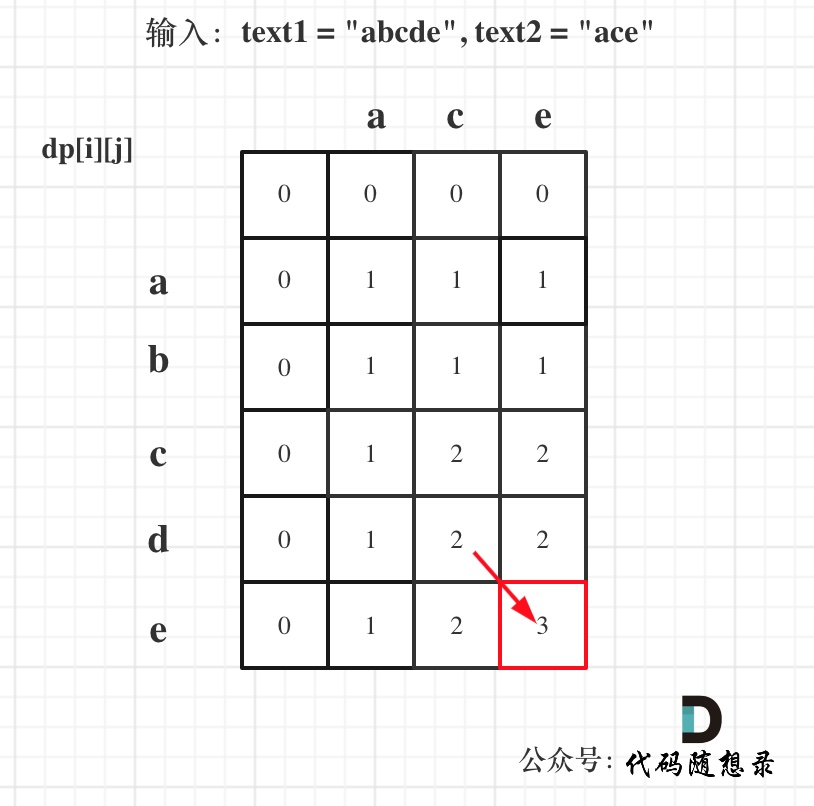
1143 最长公共子序列 medium 需要注意的是本题要求:”ace” 是 “abcde” 的子序列,但 “aec” 不是 “abcde” 的子序列。本题单纯是动态规划,不是背包问题哦。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int longestCommonSubsequence (String text1, String text2) { int n = text1.length(), m = text2.length(); int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][m + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { if (text1.charAt(i - 1 ) == text2.charAt(j - 1 )) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j - 1 ], dp[i - 1 ][j]); } } } return dp[n][m]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 卡哥的解释比较好懂 1. 确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义dp[i][j]:长度为[0 , i - 1 ]的字符串text1与长度为[0 , j - 1 ]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列为dp[i][j] 有同学会问:为什么要定义长度为[0 , i - 1 ]的字符串text1,定义为长度为[0 , i]的字符串text1不香么? 这样定义是为了后面代码实现方便,如果非要定义为为长度为[0 , i]的字符串text1也可以,大家可以试一试! 2. 确定递推公式主要就是两大情况: text1[i - 1 ] 与 text2[j - 1 ]相同,text1[i - 1 ] 与 text2[j - 1 ]不相同 如果text1[i - 1 ] 与 text2[j - 1 ]相同,那么找到了一个公共元素,所以dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; 如果text1[i - 1 ] 与 text2[j - 1 ]不相同,那就看看text1[0 , i - 2 ]与text2[0 , j - 1 ]的最长公共子序列 和 text1[0 , i - 1 ]与text2[0 , j - 2 ]的最长公共子序列,取最大的。 即:dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); 3. dp数组如何初始化先看看dp[i][0 ]应该是多少呢? test1[0 , i-1 ]和空串的最长公共子序列自然是0 ,所以dp[i][0 ] = 0 ; 同理dp[0 ][j]也是0 。 其他下标都是随着递推公式逐步覆盖,初始为多少都可以,那么就统一初始为0 。 4. 从递推公式,可以看出,有三个方向可以推出dp[i][j],如图:(下面第一张图) 5. 举例推导dp数组以输入:text1 = "abcde" , text2 = "ace" 为例,dp状态如图: (下面第二张图)
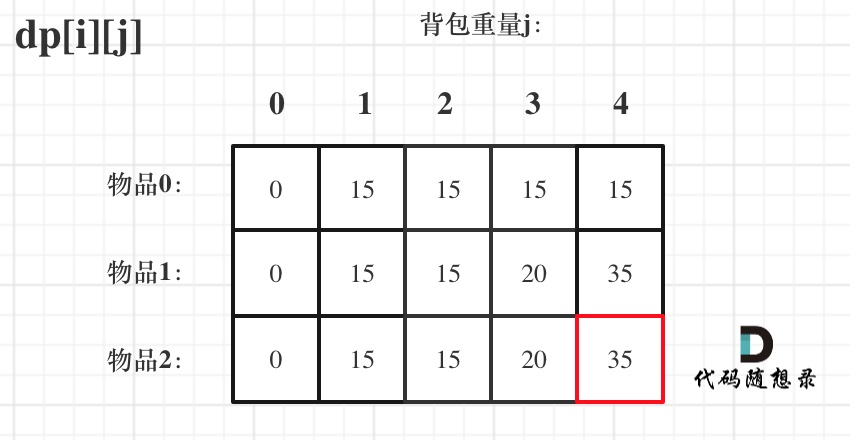
416 分割等和子集 medium(0-1背包) 本题是0-1背包问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public boolean canPartition (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) { return false ; } int sum = 0 ; for (int num:nums){ sum += num; } if (sum % 2 != 0 ) return false ; int target = sum / 2 ; int [] dp = new int [target + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <nums.length; i++) { for (int j = target; j >= nums[i]; j--) { dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]); } } return target == dp[target]; } }
具体看Carl的解释 ,写得挺好,需要好好理解转移方程Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0 -1 背包问题和完全背包问题的区别的是,一个是物品只能拿一次,一个物品无限拿。循环上也有区别: 0 -1 背包问题物品的迭代放外层,里层的体积或价值逆向遍历,物品放外面,循环完就没了,也就是物品只能拿一次。完全背包对物品的迭代放里层,外层的体积或价值正向遍历,物品放里面,每次外层循环都会重新循环物品,也就是物品是无限拿的。 本题可以对比看看139 。 简单说明几点 dp[j] 表示: 容量为j的背包,所背的物品价值可以最大为dp[j],我们本题的容量是sum/2 + 1 来确定的,本题上的dp[j]表示背包总容量是j,最大可以凑成j的子集总和为dp[j] 本题,相当于背包里放入数值,那么物品i的重量是nums[i],其价值也是nums[i]。 所以递推公式:dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]);
背包问题全理解 下面是背包问题总结(Carl的笔记加上我自己的理解):
二维dp数组01背包
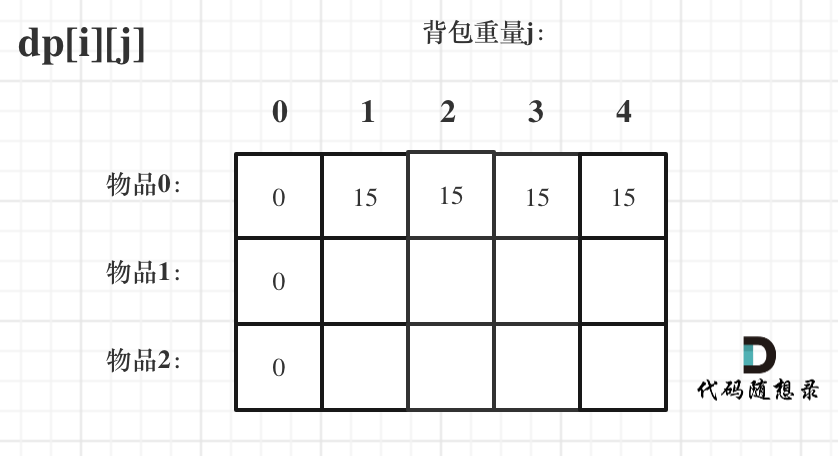
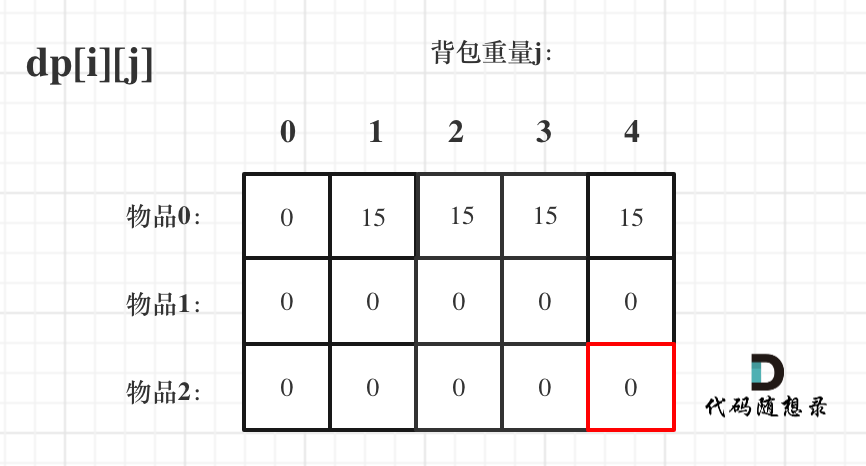
2.确定递推公式
那么可以有两个方向推出来dp[i][j],
不放物品i:由dp[i - 1][j]推出,即背包容量为j,里面不放物品i的最大价值,此时dp[i][j]就是dp[i - 1][j]。(其实就是当物品i的重量大于背包j的重量时,物品i无法放进背包中,所以被背包内的价值依然和前面相同。)
这里一开始不能理解dp[i - 1][j - weight[i]] + value[i],因为我一开始想,万一背包里面本来就有东西,为什么仅仅判断j>weight[i]就说能放进去呢?是我多虑了,因为二维数组覆盖了所有情况呀。
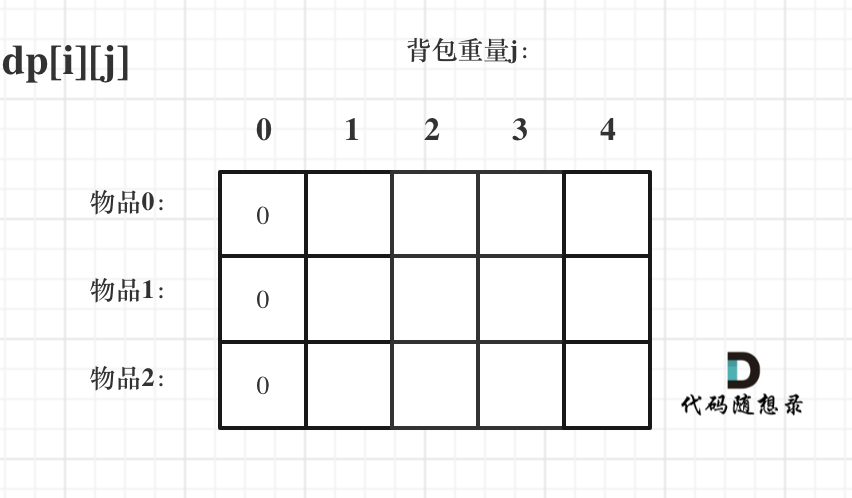
3.dp数组如何初始化
首先从dp[i][j]的定义出发,如果背包容量j为0的话,即dp[i][0],无论是选取哪些物品,背包价值总和一定为0。如图:
状态转移方程 dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - weight[i]] + value[i]); 可以看出i 是由 i-1 推导出来,那么i为0的时候就一定要初始化。
dp[0][j],即:i为0,存放编号0的物品的时候,各个容量的背包所能存放的最大价值。
那么很明显当 j < weight[0]的时候,dp[0][j] 应该是 0,因为背包容量比编号0的物品重量还小。
当j >= weight[0]时,dp[0][j] 应该是value[0],因为背包容量放足够放编号0物品。
其实从递归公式: dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - weight[i]] + value[i]); 可以看出dp[i][j] 是由左上方数值推导出来了,那么 其他下标初始为什么数值都可以,因为都会被覆盖。
初始-1,初始-2,初始100,都可以!
但只不过一开始就统一把dp数组统一初始为0,更方便一些。
4.确定遍历顺序
其实都可以!! 不过这里针对的是二维数组。
5.举例推导dp数组
一维dp数组01背包
2.一维dp数组的递推公式
dp[j]可以通过dp[j - weight[i]]推导出来,dp[j - weight[i]]表示容量为j - weight[i]的背包所背的最大价值。
dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i] 表示 容量为 j - 物品i重量 的背包 加上 物品i的价值。(也就是容量为j的背包,放入物品i了之后的价值即:dp[j])
此时dp[j]有两个选择,一个是取自己dp[j] 相当于 二维dp数组中的dp[i-1][j],即不放物品i,一个是取dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i],即放物品i,指定是取最大的,毕竟是求最大价值,
所以递归公式为:
1 dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]);
3.一维dp数组如何初始化
dp[j]表示:容量为j的背包,所背的物品价值可以最大为dp[j],那么dp[0]就应该是0,因为背包容量为0所背的物品的最大价值就是0。
那么dp数组除了下标0的位置,初始为0,其他下标应该初始化多少呢?
看一下递归公式:dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]);
dp数组在推导的时候一定是取价值最大的数,如果题目给的价值都是正整数那么非0下标都初始化为0就可以了。
这样才能让dp数组在递归公式的过程中取的最大的价值,而不是被初始值覆盖了。
那么我假设物品价值都是大于0的,所以dp数组初始化的时候,都初始为0就可以了。
4.一维dp数组遍历顺序
1 2 3 4 5 6 for (int i = 0 ; i < weight.size(); i++) { for (int j = bagWeight; j >= weight[i]; j--) { dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]); } }
这里大家发现和二维dp的写法中,遍历背包的顺序是不一样的!
二维dp遍历的时候,背包容量是从小到大,而一维dp遍历的时候,背包是从大到小。
为什么呢?
倒序遍历是为了保证物品i只被放入一次!。但如果一旦正序遍历了,那么物品0就会被重复加入多次!
看完之后发现,也就是二维数组必须要顺着,如果用一维数组处理,要倒着,至于为什么这里需要好好看卡哥的网站 。
474 一和零 medium (0-1背包) 注意这个不是多重背包问题。本题就是0-1背包问题。具体看卡哥解释
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int findMaxForm (String[] strs, int m, int n) { int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; for (String str:strs) { int onenum = 0 , zeronum = 0 ; for (char c : str.toCharArray()) { if (c == '0' ) { zeronum++; } else { onenum++; } } for (int i = m; i >= zeronum; i--) { for (int j = n; j >= onenum; j--) { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - zeronum][j - onenum] + 1 ); } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
322 零钱兑换 medium(完全背包) 每种币的数量是无限,本题属于完全背包问题。注意这个题要取最小的。讲解链接。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Solution { public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) { int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= amount; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < coins.length; j++) { if (i- coins[j] >= 0 && dp[i - coins[j]] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1 ); } } } if (dp[amount] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) return -1 ; return dp[amount]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) { int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < coins.length; i++) { for (int j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++) { if ((dp[j - coins[i]]) != Integer.MAX_VALUE) { dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - coins[i]] + 1 ); } } } if (dp[amount] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) return -1 ; return dp[amount]; } }
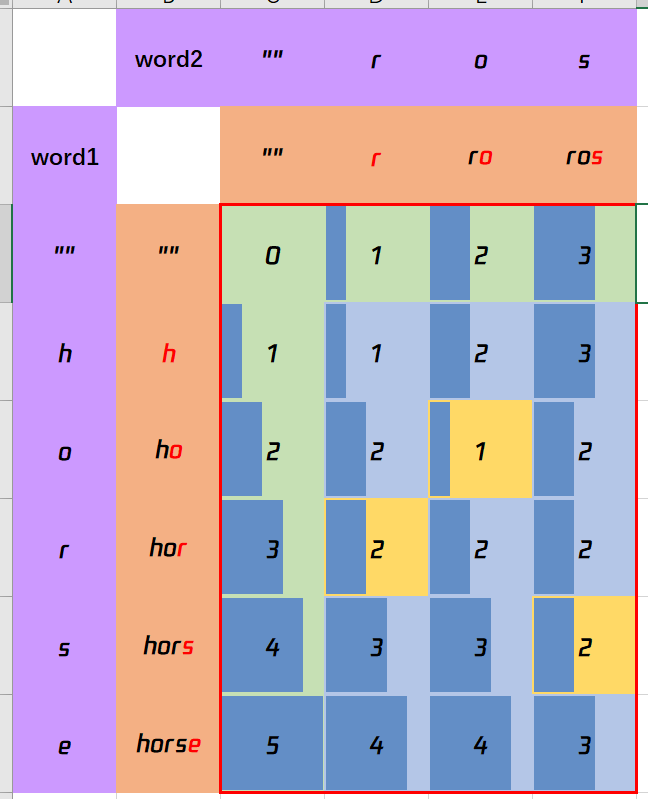
72 编辑距离 hard 注意word1变成word2,中间的操作不需要指定多少次,反正直到变成word2,增删替都能无数次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int m = word1.length(), n = word2.length(); int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ;i <=m; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = i; } for (int j = 0 ; j <=n; j++) { dp[0 ][j] = j; } for (int i = 1 ; i <=m ;i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <=n; j++) { if (word1.charAt(i - 1 ) == word2.charAt(j - 1 )) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]), dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]) + 1 ; } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 这个需要理解几个点,跟其他动态规划有点不一样,但是又是相似的套路。 1.dp[i][j]含义:dp[i][j] 表示以下标i-1为结尾的字符串word1,和以下标j-1为结尾的字符串word2,最近编辑距离为dp[i][j]。 注意是到这个位置结尾的单词,而不是整个单词。 时刻理解dp含义!时刻理解dp含义!时刻理解dp含义!时刻理解dp含义! 2.注意删除操作和增加操作是一回事 理解 word1 上的删除等价 word2 上的增加, word1 上的增加等价于 word2 上的删除,另外一个博主的理解:dp[i-1][j-1] 表示替换操作,dp[i-1][j] 表示删除操作,dp[i][j-1] 表示插入操作。 按照我自己理解把 删除操作:我们这时候要删掉word这个位置的元素,那么我向word1前推一个字符查看那时候的步数,也就是dp[i-1],j位置不变,然后再加上删除这个操作就可以+1步数。 替换操作:word1和word2这个位置没有删除,没有添加,那就同时推前面一个元素。 增加操作(等价于word2删除):word1这个位置要增加元素操作,然后我们知道word1的增加等价于word2删除,那就dp[j-1]推前一个位置,i不变。 3.初始化和其他方法很不同,因为我们要理解dp[i][0]的含义,dp[i][0] :以下标i-1为结尾的字符串word1,和空字符串word2,最近编辑距离为dp[i][0]。 那么dp[i][0]就应该是i,对word1里的元素全部做删除操作,即:dp[i][0] = i,相反dp[0][j]就是对元素进行添加。 注意上面是i,而不是word1的长度,而不是word1的长度,而不是word1的长度,而不是word1的长度,务必时刻理解dp[i][j]的含义。
借一张图理解,比如ho和ro那个黄色格子(2,2)的意思就是(1,1)一样的步数,那么(1,1)的理解就是h变成r的过程步数,怎么变不重要,我们只关心步数。
650 只有两个键的键盘 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int minSteps (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= i / 2 ; j++) { if (i % j == 0 ) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[j] + i / j); } } } return dp[n]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 注意复制是一次操作,粘贴又是一次操作 总体思路:对每一个格子i(i个A),如果i可以被j除尽,说明j个A可以通过复制粘贴得到i个A,复制粘贴次数为i / j。 每个格子的意义:得到目前数量个A需要的最少操作次数 递推公式:dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[j] + i / j)dp[i]=min(dp[i],dp[j]+i/j),其中i % j == 0i 初始化:1个A不需要操作,初始化为0 作者:Reconcile 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/2-keys-keyboard/solution/dong-tai-gui-hua-jie-fa-by-reconcile-t3fr/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。 这里举个例子,dp[1]~dp[5]的情况是0 2 3 4 5 到了dp[6],答案也是5,因为6可以复制3的情况,然后再粘贴,那么3本身需要3次,6/3=2,3+2=5。也就是i/j是复制粘贴的次数。 这里理解下为什么是i/j次,比如dp[8], 如果我们是复制dp[2]的情况,需要8/2=4次,首先复制AA,然后粘贴三次,一共四次操作加上dp[2]操作。 如果复制dp[4]的情况,8/4=2,首先复制AAAA,然后粘贴一次,一共2次操作加上dp[4]操作。 如果复制dp[1]的情况,8/1=8,首先复制A,然后粘贴七次,一共8次操作加上dp[1]操作。 当然,上面的情况要比较然后取最小值。
10 正则表达式匹配 hard(未完成) 121 买卖股票的最佳时机 easy 这个题目的股票只买卖一次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { if (prices == null || prices.length == 0 ) return 0 ; int length = prices.length; int [][] dp = new int [length][2 ]; int result = 0 ; dp[0 ][0 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[0 ][1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < length; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], -prices[i]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + prices[i], dp[i - 1 ][1 ]); } return dp[length - 1 ][1 ]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int n = prices.length; int low = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { low = Math.min(low, prices[i]); result = Math.max(result, prices[i] - low); } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int n = prices.length; int [] dp = new int [n]; int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (prices[j] - prices[i] > 0 ) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], prices[j] - prices[i]); result = Math.max(result, dp[i]); } } } return result; } }
188 买卖股票的最佳时机 IV 这个题目是可以最多交易K次,也就是你交易的次数可以少于k,但是必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票,而且利润要最大化。k为1,也就是可以买一次,卖一次,这个算交易一次。k为2,也就是一共可以买2次,卖两次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int k, int [] prices) { if (prices.length == 0 ) return 0 ; int n = prices.length; int [][] dp = new int [n][2 * k + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < 2 * k; i += 2 ) { dp[0 ][i] = -prices[0 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 2 * k - 1 ; j += 2 ) { dp[i][j + 1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j + 1 ], dp[i - 1 ][j] - prices[i]); dp[i][j + 2 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j + 2 ], dp[i - 1 ][j + 1 ] + prices[i]); } } return dp[n - 1 ][k * 2 ]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 重点理解 dp长度是dp[price.length][2 * k + 1] 也就是每一天都有2k+1个状态 务必清楚dp[i][j]的意思是第i天买入股票的状态是j 最少有3个状态,0代表不操作,1代表第一次买入,2代表第第一次卖出,如果你的k是2,那么也许还有第二次买入,第二次卖出,当然了,你的交易次数最大是k,不一定非要用完k 首先是初始化,dp[0][i] = -prices[0];表示买入,因为你买入就是钱是负数,然后如果卖出的话,当前价格加上上次买入的状态,就是你的利润,如-1+5=4,一开始我们买入价格是1,置为负数,然后卖出的时候价格是4,就可以得到利润了,还需要注意我们必须买入第二次的时候,第一次已经交易完毕了,不能连续买入而没有卖出,所以,只要是买入状态,就是负数。 其次是状态的改变: dp[i][1]状态有两个情况,我们上面说1就是买入状态,但是这里需要更详细说明,1可能是两个操作,买入和不操作状态。 不操作就是延续前一天的状态:dp[i - 1][1]:前一天买入的状态 买入就是dp[i - 1][0] - price[0]:前一天不操作的状态 dp[i][2]状态有两个情况,我们上面说2就是卖出状态,但是这里需要更详细说明,2可能是两个操作,卖出和不操作状态。 不操作就是延续前一天的状态:dp[i - 1][2]:前一天不操作的状态 卖出就是dp[i - 1][1] + price[i]:前一天买了股票的钱再加上今天卖出的价格
309 最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期 medium 和上一题的区别是,多了一个冷冻期,也就是卖出的第二天不能买入股票,卡哥笔记 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int n = prices.length; if (n == 0 || prices == null ) return 0 ; int [][] dp = new int [n][4 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][3 ] - prices[i], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] - prices[i])); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][3 ]); dp[i][2 ] = dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + prices[i]; dp[i][3 ] = dp[i - 1 ][2 ]; } return Math.max(dp[n - 1 ][1 ], Math.max(dp[n - 1 ][2 ], dp[n - 1 ][3 ])); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 主要是理解四个状态的情况和初始化的情况,具体看卡哥的笔记,这里简单写4个状态的意思 0:买入股票状态(今天买入股票,或者是之前就买入了股票然后没有操作) 1:两天前就卖出了股票,度过了冷冻期,一直没操作,今天保持卖出股票状态 2:今天卖出了股票 3:今天为冷冻期状态,但冷冻期状态不可持续,只有一天! 其中1和2都是属于卖出股票的状态,只是分成更细的。
213 53 343 583 646 376 494 714 分治法 241 为运算表达式设计优先级 medium 注意本题只有加减乘三个符号,没有除号,这个博主讲得是最详细容易理解的 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 class Solution { public List<Integer> diffWaysToCompute (String expression) { return divideAndConquer(expression.toCharArray()); } public static List<Integer> divideAndConquer (char [] expression) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (isOneNum(expression)){ int num = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<expression.length;i++){ num = num*10 +expression[i]-'0' ; } res.add(num); return res; } for (int i=0 ;i<expression.length;i++){ if (!Character.isDigit(expression[i])){ char [] left = new char [i]; char [] right = new char [expression.length-i-1 ]; System.arraycopy(expression,0 ,left,0 ,i); System.arraycopy(expression,i+1 ,right,0 ,expression.length-i-1 ); List<Integer> leftList = divideAndConquer(left); List<Integer> rightList = divideAndConquer(right); List<Integer> tempRes = calculate(leftList,rightList,expression[i]); for (Integer num:tempRes){ res.add(num); } } } return res; } public static List<Integer> calculate (List<Integer> listOne,List<Integer> listTwo,char operator) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i=0 ;i<listOne.size();i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<listTwo.size();j++){ res.add(calculateTwoNums(listOne.get(i),listTwo.get(j),operator)); } } return res; } public static Integer calculateTwoNums (int num1,int num2,char operator) { switch (operator) { case '+' : return num1+num2; case '-' : return num1-num2; default : return num1*num2; } } public static boolean isOneNum (char [] expression) { for (int i=0 ;i<expression.length;i++){ if (!Character.isDigit(expression[i])) return false ; } return true ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 System.arraycopy()是一种本地静态方法,用于将元素从源数组复制到目标数组。 public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length) Object src : 原数组 int srcPos : 从元数据的起始位置开始 Object dest : 目标数组 int destPos : 目标数组的开始起始位置 int length : 要copy的数组的长度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 以"2*3-4*5"为例子,看看是如何计算的 第一轮情况 left and right 2 3-4*5 left and right 3 4*5 left and right 4 5 leftlist and rightlist [4] * [5] leftlist and rightlist [3] - [20] left and right 3-4 5 left and right 3 4 leftlist and rightlist [3] - [4] leftlist and rightlist [-1] * [5] leftlist and rightlist [2] * [-17, -5] //也就是(3-4)*5和3-(4*5),这也解释了为什么calculate为什么是两个循环。第一和第二个结果出来了 第二轮情况 left and right 2*3 4*5 left and right 2 3 leftlist and rightlist [2] * [3] left and right 4 5 leftlist and rightlist [4] * [5] leftlist and rightlist [6] - [20] //第三个结果 第三轮情况 left and right 2*3-4 5 left and right 2 3-4 left and right 3 4 leftlist and rightlist [3] - [4] leftlist and rightlist [2] * [-1] left and right 2*3 4 left and right 2 3 leftlist and rightlist [2] * [3] leftlist and rightlist [6] - [4] leftlist and rightlist [-2, 2] * [5] //第四和第五个结果 答案为[-34, -10, -14, -10, 10]
932 312 代码随想录 代码随想录 正式开刷!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 List<Integer> a = new ArrayList <>(); a.get(i) a.size() result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right])) result是List<List<Integer>> 这样最后的结果类似于[[1 ,2 ,3 ],[2 ,3 ,4 ]],也就是里面的List<Integer>省略,这个出现在15 ,18 题 String s s.charAt(i) StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ();sb.toString() Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <TreeNode>(); queue.offer(x) queue.poll() HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put(key, value) map.containsKey(key)
数组 704 二分查找 easy 前提是有序,以及没有重复的值,才可以用下面这个算法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int search (int [] nums, int target) { int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { int mid = left + ((right - left) / 2 ); if (nums[mid] == target) return mid; else if (nums[mid] > target) { right = mid - 1 ; } else if (nums[mid] < target){ left = mid + 1 ; } } return -1 ; } }
27 移除元素 easy 注意数组只能覆盖掉哦,所以用到双指针的思路。数组的元素是不能删的,只能覆盖!数组的元素是不能删的,只能覆盖!数组的元素是不能删的,只能覆盖!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int removeElement (int [] nums, int val) { int slow = 0 ; for (int fast = 0 ; fast < nums.length; fast++) { if (nums[fast] != val) { nums[slow] = nums[fast]; slow++; } } return slow; } }
977 有序数组的平方 easy 这题给的数组是非递减数组,有负数,如果用暴力算平方然后排序时间复杂度很高,所以没有意思,下面用的是双指针的办法。本题用while的话
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int [] sortedSquares(int [] nums) { int [] result = new int [nums.length]; int n = nums.length - 1 ; for (int i = 0 ,j = n; i <= j;) { if ((nums[i] * nums[i]) > (nums[j]*nums[j])) { result[n--] = nums[i] * nums[i++]; } else { result[n--] = nums[j] * nums[j--]; } } return result; } }
while的写法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int [] sortedSquares(int [] nums) { int [] result = new int [nums.length]; int n = nums.length - 1 ; int i = 0 ; int j = n; while (i <= j) { if ((nums[i] * nums[i]) > (nums[j]*nums[j])) { result[n--] = nums[i] * nums[i++]; } else { result[n--] = nums[j] * nums[j--]; } } return result; } }
209 长度最小的子数组 medium 注意是最小哦,举个例子,比如target=7,nums= [2,3,1,2,4,3],那么连续子数组[1,2,4]和[4,3]都符合,但是要取最小那个,也就是长度为2。本题有点类似于双指针,但是卡哥表达是滑动窗口。还有需要注意,题目是找出大于等于 target的,一开始还看成等于的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int minSubArrayLen (int target, int [] nums) { int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int left = 0 , sum = 0 ; for (int right = 0 ; right < nums.length; right++) { sum += nums[right]; while (sum >= target) { result = Math.min(result, right - left + 1 ); sum -= nums[left++]; } } return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : result; } }
59 螺旋矩阵2 medium 思路就是一圈圈循环,然后注意控制区间,本题答案是左闭右开写法,这题没涉及什么算法,就是繁琐。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution { public int [][] generateMatrix(int n) { int start = 0 ; int loop = 0 ; int i,j; int count = 1 ; int [][] res = new int [n][n]; while (loop++ < n / 2 ) { for (j = start; j < n - loop; j++) { res[start][j] = count++; } for (i = start; i < n - loop; i++) { res[i][j] = count++; } for (;j >= loop; j--) { res[i][j] = count++; } for (; i >= loop; i--) { res[i][j] = count++; } start++; } if (n % 2 == 1 ) { res[start][start] = count; } return res; } }
卡哥这个图很生动
链表 务必熟悉定义链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode() {}; ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this .next = next; this .val = val; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 一些总结: cur一般指向head,pre一般指向null ,如果有虚拟节点,就指向dump,这样保证了head(cur的指向)之前是pre 203 :移除元素需要设置虚拟节点,pre和cur,循环的时候while (cur!=null ),那么为什么不是cur.next!=null 呢,因为如果你现在到最后一个元素,next必然是空,那么这时候就不会循环,但是如果最后一个元素就是目标val,需要进行操作,而不会进入到循环中另外,如果一直遇到val,pre不变位置,而是一直指向cur的next,然后cur一直移动 206 :对应反转链表,虚拟节点不好操作,因为你最后要反的,但是pre和cur是要的,pre的话这里没有dump,就先设置为null 19 :删除倒数第n个节点,虚拟节点的设置,以及fast和slow需要初试化在dump上而不是head上,因为可能[1 ]1 ,如果这样的话,一开始在节点上就不能操作,所以都设置在head的前面另外,循环是用fast.next!=null ,如果是这样,fast最后是在最后一个元素上,如果直接用fast,则会在null 元素上。然后slow会在需要删除节点的前面一个位置,最后进行改变指针即可
203 移除链表元素 easy 这个是带虚拟头节点的,方便操作,然后设置一个pre和cur指针,如果cur遇到val,就修改pre的next指向,否则pre指向cur,然后cur一直移动。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public ListNode removeElements (ListNode head, int val) { if (head == null ) { return head; } ListNode dump = new ListNode (0 ); dump.next = head; ListNode pre = dump; ListNode cur = pre.next; while (cur != null ) { if (cur.val == val) { pre.next = cur.next; } else { pre = cur; } cur = cur.next; } return dump.next; } }
注意下如何声明链表,因为可能是ACM模式,本解答是在原链表上进行移除,也就是不带虚拟头节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public ListNode removeElements (ListNode head, int val) { while (head != null && head.val == val) { head = head.next; } if (head == null ) { return null ; } ListNode pre = head; ListNode cur = pre.next; while (cur != null ) { if (cur.val == val) { pre.next = cur.next; } else { pre = cur; } cur = cur.next; } return head; } }
707 设计链表 medium 本答案的链表设计是有虚拟头节点的,这样是为了所有节点可以用一样的操作,不然要分为头节点和其他节点,使用单链表,这个题比较容易漏掉size的数值变化增长。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode() {}; ListNode(int val) { this .val = val; } ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this .val = val; this .next = next; } } class MyLinkedList { int size; ListNode head; public MyLinkedList () { size = 0 ; head = new ListNode (0 ); } public int get (int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) { return -1 ; } ListNode currentNode = head; for (int i = 0 ; i <= index; i++) { currentNode = currentNode.next; } return currentNode.val; } public void addAtHead (int val) { addAtIndex(0 , val); } public void addAtTail (int val) { addAtIndex(size, val); } public void addAtIndex (int index, int val) { if (index > size) { return ; } if (index < 0 ) { index = 0 ; } size ++; ListNode pred = head; for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) { pred = pred.next; } ListNode toAdd = new ListNode (val); toAdd.next = pred.next; pred.next = toAdd; } public void deleteAtIndex (int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) { return ; } size--; ListNode pred = head; for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) { pred = pred.next; } pred.next = pred.next.next; } }
1 2 3 4 这里之前有个疑问,为什么每次操作链表都要先声明一个listnode? ListNode currentNode = head;这样操作的话是cur在动,而head没有动 假设你直接用head操作,这样你第一次getindex是可以的,但是第二次getindex的话,head的位置早就变了。
206 反转链表 easy 直接在链表的基础上进行反转,也就是改变next的指向,让其反过来,思路就是设置一个pre和cur,然后用temp保存cur的next,再把cur反转到pre。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = head; ListNode temp = null ; while (cur != null ) { temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } }
24 两两交换链表中的节点 meduim 这个题用了虚拟节点,必须要画图,这样才好理解,定义pre和cur,以两个为一组操作,然后先保存下一组的第一个数,接着操作第一组,改变指针指向。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs (ListNode head) { ListNode dump = new ListNode (0 ); dump.next = head; ListNode temp = null ; ListNode pre = dump; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null && cur.next != null ) { temp = cur.next.next; pre.next = cur.next; pre.next.next = cur; cur.next = temp; pre = cur; cur = cur.next; } return dump.next; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs (ListNode head) { ListNode dump = new ListNode (0 ); dump.next = head; ListNode pre = dump; while (pre.next != null && pre.next.next != null ) { ListNode temp = head.next.next; pre.next = head.next; pre.next.next = head; head.next = temp; pre = head; head = head.next; } return dump.next; } }
19 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 medium 这个题一开始想不通怎么去处理倒数这个条件。这就用到了双指针啦,也就是先让fast先跑n步(卡哥说n+1但是我计算后觉得还是n),然后slow和fast同时跑,直到fast移动到末尾(是null哦,不是最后一个元素,也就是最后一个元素的下一个),这时候slow的指向就是待删除的元素,那么在跑的时候,我们再定义一个pre,就可以删除slow元素了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode dump = new ListNode (0 ); dump.next = head; ListNode slow = dump; ListNode fast = dump; while (n-- > 0 ) { fast = fast.next; } ListNode pre = null ; while (fast != null ) { pre = slow; fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } pre.next = slow.next; return dump.next; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode dump = new ListNode (0 ); dump.next = head; ListNode slow = dump; ListNode fast = dump; while (n-- > 0 ) { fast = fast.next; } while (fast.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } slow.next = slow.next.next; return dump.next; } }
面试题 02.07. 链表相交 easy 同160题 题目链接 ,这个题需要注意交点不是数值相等,而是指针相等。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { ListNode curA = headA; ListNode curB = headB; int lenA = 0 , lenB = 0 ; while (curA != null ) { curA = curA.next; lenA++; } while (curB != null ) { curB = curB.next; lenB++; } curA = headA; curB = headB; if (lenB > lenA) { int temp = lenA; lenA = lenB; lenB = temp; ListNode tem = curA; curA = curB; curB = tem; } int gap = lenA - lenB; while (gap-- > 0 ) { curA = curA.next; } while (curA != null ) { if (curA == curB) { return curA; } curA = curA.next; curB = curB.next; } return null ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 8 [4,1,8,4,5] [5,0,1,8,4,5] 2 3 上面的输入,对齐后是 [5,0,1,8,4,5] [4,1,8,4,5] 根据输入,完美可以知道应该是返回8这个节点,但是如果我们用了curA.val == curB.val,则会返回1,这个是错误的
卡哥的图,主要理解curA移动到和curB对齐的地方这个操作
环形链表 141 环形链表 easy 判断一个链表是否有环,很简单,设置快慢指针,如果最终快指针追上慢指针,说明有环。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class Solution { public boolean hasCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) { return true ; } } return false ; } }
142 环形链表II medium 之前做过又忘记!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow) { ListNode index1 = fast; ListNode index2 = head; while (index1 != index2) { index1 = index1.next; index2 = index2.next; } return index1; } } return null ; } }
卡哥的详细解释
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 卡哥的答案确实比较详细,这里简单总结下 一个快指针,一个慢指针,快指针走两步,慢指针走一步。 这样子,其实快指针是在慢慢一步步靠近慢指针,如果有环的话,一定会相遇。 当他们相遇的时候,这时候我们重新声明两个指针,一个指向fast,一个指向头,然后他们一步步走,最终相遇的时候,就是入口,这里面涉及一些公式推导,去卡哥网站上看吧。 这里解释下卡哥这句话 那么fast指针走到环入口3的时候,已经走了k + n 个节点,slow相应的应该走了(k + n) / 2 个节点。 因为k是小于n的(图中可以看出),所以(k + n) / 2 一定小于n (n + n) / 2 = n ,k < n,所以(k + n) / 2 一定小于n。 也就是说你的fast已经走到了环入口三,而slow还没走到环入口三,并且一开始fast在环入口2的前面,也就是他们已经相遇过了。
哈希表 242 有效的字母异位词 easy 若 s 和 t 中每个字符出现的次数都相同,则称 s 和 t 互为字母异位词。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public boolean isAnagram (String s, String t) { int [] record = new int [26 ]; for (char c:s.toCharArray()) { record[c - 'a' ] += 1 ; } for (char c:t.toCharArray()) { record[c - 'a' ] -= 1 ; } for (int i : record) { if (i != 0 ) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
349 两个数组的交集 easy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int [] intersection(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet <>(); Set<Integer> set2 = new HashSet <>(); for (int i : nums1) { set1.add(i); } for (int i : nums2) { if (set1.contains(i)) { set2.add(i); } } int [] result = new int [set2.size()]; int index = 0 ; for (int i : set2) { result[index++] = i; } return result; } }
202 快乐数 easy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public boolean isHappy (int n) { Set<Integer> result = new HashSet <>(); while (n != 1 && !result.contains(n)) { result.add(n); n = getnextnum(n); } return n == 1 ; } private int getnextnum (int n) { int sum = 0 ; while (n > 0 ) { int temp = n % 10 ; sum += temp * temp; n = n / 10 ; } return sum; } }
1 两数之和 easy 一开始就行想着暴力解法,虽然过了,用了两个循环,但是看了卡哥的解释还是太年轻了,这里有个细节,一定要先判断,然后再put元素进去,否则遇到[3,3] targer=6 这种情况,res答案就会变成[1,1],而不是[0,1]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { int [] result = new int [2 ]; Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { int temp = target -nums[i]; if (map.containsKey(temp)) { result[0 ] = i; result[1 ] = map.get(temp); } map.put(nums[i], i); } return result; } }
454 四数相加2 medium 第一次看到这么巧妙的做法,看来还是练题太少了。这个题不用考虑重复的四个元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int fourSumCount (int [] nums1, int [] nums2, int [] nums3, int [] nums4) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); int temp = 0 , res = 0 ; for (int i :nums1) { for (int j : nums2) { temp = i + j; if (map.containsKey(temp)) { map.put(temp, map.get(temp) + 1 ); } else { map.put(temp, 1 ); } } } for (int i : nums3) { for (int j : nums4) { temp = i + j; if (map.containsKey(0 - temp)) { res += map.get(0 - temp); } } } return res; } }
让语句写更少一些,主要在map的修改上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int fourSumCount (int [] nums1, int [] nums2, int [] nums3, int [] nums4) { int res = 0 ; int temp; Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i : nums1) { for (int j : nums2) { temp = i + j; map.put(temp, map.getOrDefault(temp, 0 ) + 1 ); } } for (int i : nums3) { for (int j : nums4) { temp = i + j; if (map.containsKey(0 - temp)) { res += map.get(0 - temp); } } } return res; } }
383 赎金信 easy 一开始想得挺复杂,看到卡哥提点都是小写字母,可以用一个26大小的char数组保存这句话,就写出来了,没想到和卡哥答案一样,嘻嘻。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public boolean canConstruct (String ransomNote, String magazine) { int [] result = new int [26 ]; for (char i : magazine.toCharArray()) { result[i - 'a' ] += 1 ; } for (char i : ransomNote.toCharArray()) { result[i - 'a' ] -= 1 ; } for (int i : result) { if (i < 0 ) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
15 三数之和 medium(非哈希法) 哈希法太复杂,这里是双指针,而且和454的区别是,454是4个数组,这个题是一个数组,而且不能是重复的三元组,这个题要多看看,可能第二遍又忘记了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(nums); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] > 0 ) { return result; } if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) { continue ; } int left = i + 1 ; int right = nums.length - 1 ; while (right > left) { int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum > 0 ) { right--; } else if (sum < 0 ) { left++; } else { result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right])); while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1 ]) right--; while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1 ]) left++; right--; left++; } } } return result; } }
18 四数之和 medium 和上一题的区别是,这个是四元组,而且和不是为0,是任意值target。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> fourSum (int [] nums, int target) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(nums); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (i > 0 && nums[i - 1 ] == nums[i]) { continue ; } for (int j = i + 1 ; j < nums.length; j++) { if (j > i + 1 && nums[j - 1 ] == nums[j]) { continue ; } int left = j + 1 ; int right = nums.length - 1 ; while (right > left) { long sum = (long ) nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum > target) { right--; } else if (sum < target) { left++; } else { result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right])); while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1 ]) right--; while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1 ]) left++; left++; right--; } } } } return result; } }
字符串 344 反转字符串 easy 简简单单。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution { public void reverseString (char [] s) { char temp; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length / 2 ; i++) { temp = s[i]; s[i] = s[s.length - 1 -i]; s[s.length - 1 - i] = temp; } } }
一样的效果,只是一个for,一个是用while。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public void reverseString (char [] s) { char temp; int left = 0 , right = s.length - 1 ; while (left < right) { temp = s[left]; s[left] = s[right]; s[right] = temp; left++; right--; } } }
541 反转字符串2 easy 比较繁琐,需要定义判断多种情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public String reverseStr (String s, int k) { int n = s.length(); char [] arr = s.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i += k * 2 ) { reverse(arr, i, Math.min(i + k, n) - 1 ); } return new String (arr); } public void reverse (char [] arr, int left, int right) { while (left < right) { char temp = arr[left]; arr[left] = arr[right]; arr[right] = temp; left++; right--; } } }
剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格 easy 题目链接 ,一开始想法的替换空格,但是忘记一个事,%20是三个字符,所以要申请空间,干脆用SrtingBuilder。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public String replaceSpace (String s) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { if (s.charAt(i) == ' ' ) { sb.append("%20" ); } else { sb.append(s.charAt(i)); } } return sb.toString(); } }
151 颠倒字符串中的单词 medium 这个题比较多繁琐的东西,下面详细讲。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution { public String reverseWords (String s) { StringBuilder sb = RemoveSpace(s); ReverseString(sb, 0 , sb.length() - 1 ); ReverseEachWords(sb); return sb.toString(); } public StringBuilder RemoveSpace (String s) { int start = 0 , end = s.length() - 1 ; while (s.charAt(start) == ' ' ) start++; while (s.charAt(end) == ' ' ) end--; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); while (start <= end) { char c = s.charAt(start); if (c != ' ' || sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1 ) != ' ' ) { sb.append(c); } start++; } return sb; } public void ReverseString (StringBuilder sb, int start, int end) { while (start < end) { char temp = sb.charAt(start); sb.setCharAt(start, sb.charAt(end)); sb.setCharAt(end, temp); start++; end--; } } public void ReverseEachWords (StringBuilder sb) { int start = 0 ; int end = 1 ; int n = sb.length(); while (start < n) { while (end < n && sb.charAt(end) != ' ' ) { end++; } ReverseString(sb, start, end - 1 ); start = end + 1 ; end = start + 1 ; } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 总体思路是 1.去除多余的空格 比如[ the sky ],去除后是[the sky],要去掉多余的两边空格,以及中间只需要保留一个空格。 函数里面while (start <= end),这里有个等于号,如果没有的话,会漏掉最后一个字符,因为我们是用start去提取字符,自然start要到最后 重点看if (c != ' ' || sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1) != ' ') 这句前面部分,是为了保证非空格元素添加进去,而后面则是为了去除两个单词之间多余的空格 举个例子[the sky],中间有两个空格,start为4的时候,为第一个空格,此时sb是the,如果看前面第一个条件,是不允许添加的,但是这个是或,后面那个条件sb提取出来的是e,所以,这时候位置4的空格可以添加进去, 这时候sb是[the ],然后开始第五个位置,同样,前面第一个条件不通过,第二个条件也不通过,因为此时sb最后一个字符是空格,这样的话,两个单词之间,就可以做到保留一个空格 2.翻转字符串 这个没啥好说的,就是字面意思 3.翻转单词 这个就有意思了,我们检测到空格位置,就说明检测完一个单词,然后再把这个单词放进翻转字符串,即可完成,这里别忘了,翻转字符串的end是位置,不是长度, 所以ReverseString(sb, start, end - 1);这个容易漏掉end-1
剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串 easy 题目链接 ,感觉卡哥写的还复杂。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public String reverseLeftWords (String s, int n) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = n; i < s.length(); i++) { sb.append(s.charAt(i)); } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { sb.append(s.charAt(i)); } return sb.toString(); } }
28 实现 strStr() easy(KMP) 别看是easy题,这是KMP算法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 KMP算法的目的就是解决字符串匹配,其实挺神奇的,不过具体的数学原理是啥,有点懵,先把一些概念解释清楚 首先理解前缀和后缀,以及前缀表 以要在文本串:aabaabaafa 中查找是否出现过一个模式串:aabaaf这个为例子。 我们要构建模式串(needle)的前缀表。 1. 前缀的理解,概念是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串a aa aab aaba aabaa 上面五个都是前缀,不包含最后一个字符哦 2. 后缀的理解,指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串。f af aaf baaf abaaf 上面五个都是后缀,不包含第一个字符哦 3. 前缀表,也就是最长相等前后缀(均用不减1 的操作,有些KMP的next数组用减1 )。a 0 aa 1 这里前缀a,后缀a,相等的长度就是1 aab 0 aaba 1 只有前缀a和后缀a相等 aabaa 2 前缀aa和后缀aa相等 aabaaf 0 0 1 0 1 2 0 就是我们模式串的前缀表。再举一个例子asdfasdfasdf next表是[0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ] 前缀asdfasdf 后缀asdfasdf 也就是前缀和后缀是有重叠位置的时候 所以这里是强化下我们的概念,前缀是不包含最后一个字符,后缀是不包含第一个字符,所以他们即便是重叠的,都没关系,我们重点关注的是概念! 大致的解题思路是 1. 首先构建好前缀表2. 循环文本串,然后循环匹配,如果不匹配,则寻找之前匹配的位置,如果匹配,j++,最后如果出现了文本串则根据题目要求返回相应值。
下面这个图很好解释了为什么当我们遇到不匹配的字符后,因为next数组记录了相等前后缀长度,遇到不匹配的字符后,j回退到next[j-1],这个next[j-1]就是他们之前的最长相等前后缀长度,也就是回退到这个位置的时候,模式串从0到这个位置的字符,是和主串i位置之前的字符相等,之前字符的长度,就是模式串从0到这个位置的字符的长度,这是核心理解。至于next数组为什么那么求,目前还没有深刻的理解,但是至少理解了,为什么要回退这个步骤。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public int strStr (String haystack, String needle) { int [] next = new int [needle.length()]; int j = 0 ; getNext(next, needle); for (int i = 0 ; i < haystack.length(); i++) { while (j > 0 && needle.charAt(j) != haystack.charAt(i)) { j = next[j - 1 ]; } if (haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) { j++; } if (j == needle.length()) { return i - needle.length() + 1 ; } } return -1 ; } private void getNext (int [] next, String s) { int j = 0 ; next[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < s.length(); i++) { while (j > 0 && s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)){ j = next[j - 1 ]; } if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) { j++; } next[i] = j; } } }
459 重复的子字符串 easy(KMP) 重点理解周期长度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern (String s) { int n = s.length(); if (n == 0 ) return false ; int [] next = new int [s.length()]; getNext(next, s); if (n % (n - next[n - 1 ]) == 0 && next[n - 1 ] != 0 ) { return true ; } return false ; } public void getNext (int [] next, String s) { int j = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < s.length(); i++) { while (j > 0 && s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) j = next[j - 1 ]; if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) j++; next[i] = j; } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 这个题也是kmp的题目,寻找重复的子串 注意理解一个概念: 数组长度减去最长相同前后缀的长度相当于是第一个周期的长度,也就是一个周期的长度,如果这个周期可以被整除,就说明整个数组就是这个周期的循环。 所以我们求完next数组后 n % (n - next[n - 1 ]) == 0 n是长度,next[n - 1 ]也就是最长的相同前后缀的长度 next[n - 1 ] != 0 这个是为了保证,next数组最后一个长度不是0 ,否则判断出错,下面举个例子 "abac" 的next数组是[0 , 0 , 1 , 0 ],如果没有next[n - 1 ] != 0 这个条件,那就是4 % (4 - 0 ) == 0 就返回了true ,实际上是false ,所以要保证最长相同前后缀长度不为0 先"aaaa" 的next数组是[0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ],那么4 %(4 - 3 ) ==0 返回true ,4 -3 =1 也就是说这个周期长度是1
栈与队列 232 用栈实现队列 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class MyQueue { Stack<Integer> Stackin; Stack<Integer> Stackout; public MyQueue () { Stackin = new Stack <>(); Stackout = new Stack <>(); } public void push (int x) { Stackin.push(x); } public int pop () { dumpStackin(); return Stackout.pop(); } public int peek () { dumpStackin(); return Stackout.peek(); } public boolean empty () { return Stackin.isEmpty() && Stackout.isEmpty(); } public void dumpStackin () { if (!Stackout.isEmpty()) return ; while (!Stackin.isEmpty()) { Stackout.push(Stackin.pop()); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 这个题是用两个栈来实现队列的操作 队列:先进先出 栈:先进后出 pop:移除元素并返回该元素 peak:返回队列开头元素 push:添加元素 那么用栈去完成队列的功能,需要两个栈,一个为作为入栈,一个作为出栈。 入栈:直接就是push元素进去 pop:检查出栈有无元素,有的话直接操作出栈的元素,如果出栈是空的话,那么将入栈的目前所有的元素全部移动到出栈中,再操作出栈pop peak:和pop一样的道理 pip和peak都是java内置的,所以直接调用,我们主要是负责把入栈的元素移动到出栈中,这样才可以实现队列先进先出的功能 那么判断栈是否为空,只要两个都是空,那么就是空栈
225 用队列实现栈 easy 题目要求必须要用两个队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class MyStack { Deque<Integer> que1; Deque<Integer> que2; public MyStack () { que1 = new ArrayDeque <>(); que2 = new ArrayDeque <>(); } public void push (int x) { que1.addLast(x); } public int pop () { int n = que1.size(); n--; while (n-- > 0 ) { que2.addLast(que1.peekFirst()); que1.pollFirst(); } int res = que1.pollFirst(); que1 = que2; que2 = new ArrayDeque (); return res; } public int top () { return que1.peekLast(); } public boolean empty () { return que1.isEmpty(); } }
下面是用双端队列,抖机灵用的,只用一个队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class MyStack { Deque<Integer> que; public MyStack () { que = new ArrayDeque <>(); } public void push (int x) { que.addLast(x); } public int pop () { int res = que.pollLast(); return res; } public int top () { return que.peekLast(); } public boolean empty () { return que.isEmpty(); } }
20 有效的括号 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public boolean isValid (String s) { Stack<Character> que = new Stack <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { if (s.charAt(i) == '(' ) { que.push(')' ); } else if (s.charAt(i) == '[' ) { que.push(']' ); } else if (s.charAt(i) == '{' ) { que.push('}' ); } else if (que.isEmpty() || que.peek() != s.charAt(i)) { return false ; } else if (que.peek() == s.charAt(i)) { que.pop(); } } return que.isEmpty(); } }
1047 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项 easy 这个可以看卡哥的动画,瞬间就可以明白
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public String removeDuplicates (String s) { ArrayDeque<Character> que = new ArrayDeque <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { char ch = s.charAt(i); if (que.isEmpty() || que.peek() != ch) { que.push(ch); } else { que.pop(); } } String result = "" ; while (!que.isEmpty()) { result = que.pop() + result; } return result; } }
150 逆波兰表达式求值 medium 这个题看动画就秒懂了,这个是后缀表达式,可以依次顺序来计算结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public int evalRPN (String[] tokens) { Deque<Integer> que = new ArrayDeque <>(); for (String ch:tokens) { if ("+" .equals(ch) || "-" .equals(ch) || "*" .equals(ch)|| "/" .equals(ch)){ int temp1 = que.pop(); int temp2 = que.pop(); if ("+" .equals(ch)) { que.push(temp2 + temp1); } else if ("-" .equals(ch)) { que.push(temp2 - temp1); } else if ("*" .equals(ch)) { que.push(temp2 * temp1); } else if ("/" .equals(ch)) { que.push(temp2 / temp1); } } else { que.push(Integer.valueOf(ch)); } } return que.pop(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int evalRPN (String[] tokens) { Deque<Integer> que = new ArrayDeque <>(); for (String ch:tokens) { if ("+" .equals(ch)) { que.push(que.pop() + que.pop()); } else if ("-" .equals(ch)) { que.push(-que.pop() + que.pop()); } else if ("*" .equals(ch)) { que.push(que.pop() * que.pop()); } else if ("/" .equals(ch)) { int temp1 = que.pop(); int temp2 = que.pop(); que.push(temp2 / temp1); } else { que.push(Integer.valueOf(ch)); } } return que.pop(); } }
239 滑动窗口最大值 hard 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 巩固知识 add/offer/offerLast添加队尾,三个方法等价; push/offerFirst添加队头,两个方法等价。 remove/pop/poll/pollFirst删除队头,四个方法等价; pollLast删除队尾。 add/remove源自集合,添加到队尾 / 从队头删除; offer/poll源自队列 添加到队尾/ 从队头删除; push/pop源自栈 添加到队头/ 从队头删除; offerFirst/offerLast/pollFirst/pollLast源自双端队列(两端都可以进也都可以出),offerFirst添加到队头,offerLast添加到队尾,pollFirst从队头删除,pollLast从队尾删除。 peek()方法用于返回此双端队列表示的队列的头元素,但不删除该元素。 java最好别用Stack来实现栈的功能,官方说的,不推荐使用,所以可以用deque来做栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) { ArrayDeque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque <>(); int n = nums.length; int [] res = new int [n - k + 1 ]; int x = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() < i - k + 1 ) { deque.poll(); } while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]) { deque.pollLast(); } deque.offer(i); if (i >= k - 1 ) { res[x++] = nums[deque.peek()]; } } return res; } }
347 前k个高频元素 medium 之前做过,但是发现之前的方法有点复杂,下面是小顶堆的方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int [] topKFrequent(int [] nums, int k) { int [] result = new int [k]; Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int num : nums) { map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0 ) + 1 ); } Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet(); PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> queue = new PriorityQueue <>((o1, o2) -> o1.getValue() - o2.getValue()); for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : entries) { queue.offer(entry); if (queue.size() > k) { queue.poll(); } } for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { result[i] = queue.poll().getKey(); } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 思路是首先是先用map来存储key和value,value就是统计次数。 set来保存这个键值后构建小顶堆,小顶堆poll掉的是小数,留下来的是大数,然后判断队列中的大数是否超过k 超过k就poll掉,最后用一个数组来保留结果。 下面是一些语法记录:以[1 ,1 ,1 ,2 ,2 ,3 ], k = 2 为例子 map不能直接使用迭代器,所以用set map有一个方法叫做entrySet(),这方法可以将Map的键值对的映射关系作为set集合的元素存储到Set集合当中,而这种映射关系的类型就是Entry的类型。 Map.Entry是Map声明的一个内部接口,此接口为泛型,定义为Entry<K,V>。它表示Map中的一个实体(一个key-value对)。接口中有getKey(),getValue方法。 Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet(); 上面这句话打印出来的entries是[1 =3 , 2 =2 , 3 =1 ] 当然了,直接打印map.entrySet()打印出来也是[1 =3 , 2 =2 , 3 =1 ],用set还是为了能够迭代 构建小顶堆的作用是能保证每次取出的元素都是队列中权值最小的 如果是大顶堆则是new PriorityQueue <>((o1, o2) -> o2.getValue() - o1.getValue()); PriorityQueue(优先队列) add和remove是一对,源自Collection; offer和poll是一对,源自Queue; push和pop是一对,源自Deque,其本质是栈(Stack类由于某些历史原因,官方已不建议使用,使用Deque代替); offerFirst/offerLast和pollFirst/pollLast是一对,源自Deque,其本质是双端队列。
二叉树 递归三部曲:
务必熟悉定义二叉树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode() {}; TreeNode(int val) { this .val = val; } TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { this .val = val; this .left = left; this .right = right; } }
94/144/145 二叉数递归遍历(递归法) easy 递归遍历三步骤:1.确定输入的参数和返回值(定义递归函数入口) 2.确定终止条件 3.确定递归逻辑(函数内容)
144 前序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <Integer>(); preOrder(root, result); return result; } public void preOrder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) return ; result.add(root.val); preOrder(root.left, result); preOrder(root.right, result); } }
94 中序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <Integer>(); inOrder(root, result); return result; } public void inOrder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) return ; inOrder(root.left, result); result.add(root.val); inOrder(root.right, result); } }
145 后序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <Integer>(); postOrder(root, result); return result; } public void postOrder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) return ; postOrder(root.left, result); postOrder(root.right, result); result.add(root.val); } }
94/144/145 二叉数递归遍历(迭代法) easy 144 前序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <Integer>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); if (node.right != null ) { stack.push(node.right); } if (node.left != null ) { stack.push(node.left); } } return result; } }
94 中序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); while (!stack.isEmpty() || root != null ) { if (root != null ) { stack.push(root); root = root.left; } else { root = stack.pop(); result.add(root.val); root = root.right; } } return result; } }
145 后序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <Integer>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); if (node.left != null ) { stack.push(node.left); } if (node.right != null ) { stack.push(node.right); } } Collections.reverse(result); return result; } }
94/144/145 二叉数递归遍历(统一迭代法) easy 因为迭代法的写法是针对每种遍历顺序定制的,没有统一的规律,所以才有统一迭代法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (node != null ) { if (node.right != null ) stack.push(node.right); if (node.left != null ) stack.push(node.left); stack.push(node); stack.push(null ); } else { node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); } } return result; } }
因为不推荐用stack,这里用LinkedList替代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new LinkedList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode temp = stack.pop(); if (temp != null ) { if (temp.right != null ) stack.push(temp.right); if (temp.left != null ) stack.push(temp.left); stack.push(temp); stack.push(null ); } else { temp = stack.pop(); result.add(temp.val); } } return result; } }
94 中序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (node != null ) { if (node.right != null ) stack.push(node.right); stack.push(node); stack.push(null ); if (node.left != null ) stack.push(node.left); } else { node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); } } return result; } }
145 后序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (node != null ) { stack.push(node); stack.push(null ); if (node.right != null ) stack.push(node.right); if (node.left != null ) stack.push(node.left); } else { node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); } } return result; } }
102 二叉树的层序遍历 medium 用队列先进先出的特性,对每层保存然后poll出来,顺序就是层序遍历。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <List<Integer>>(); if (root == null ) return result; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { List<Integer> ietmList = new ArrayList <Integer>(); int len = queue.size(); while (len-- > 0 ) { TreeNode temp = queue.poll(); ietmList.add(temp.val); if (temp.left != null ) queue.offer(temp.left); if (temp.right != null ) queue.offer(temp.right); } result.add(ietmList); } return result; } }
226 翻转二叉树 easy 递归法,可以对比下前序遍历的递归(后序也可以,但是不可以用中序)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return null ; swapTree(root); invertTree(root.left); invertTree(root.right); return root; } public void swapTree (TreeNode node) { TreeNode temp = node.left; node.left = node.right; node.right = temp; } }
层序遍历,可以好好看看
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return null ; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int len = queue.size(); while (len-- > 0 ) { TreeNode temp = queue.poll(); swapTree(temp); if (temp.left != null ) queue.offer(temp.left); if (temp.right != null ) queue.offer(temp.right); } } return root; } public void swapTree (TreeNode node) { TreeNode temp = node.left; node.left = node.right; node.right = temp; } }
101 对称二叉树 easy 判断是不是对称二叉树,返回true或者false,用了递归法内外是否一样。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { return compare(root.left, root.right); } public boolean compare (TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { if (left == null && right == null ) return true ; if (left == null && right != null ) return false ; if (left != null && right == null ) return false ; if (left.val != right.val) return false ; boolean outSide = compare(left.left, right.right); boolean inSide = compare(left.right, right.left); return outSide && inSide; } }
104 二叉树最大深度 easy 使用递归法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int left = maxDepth(root.left); int right = maxDepth(root.right); int depth = 1 + Math.max(left, right); return depth; } }
111 二叉树的最小深度 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int minDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int left = minDepth(root.left); int right = minDepth(root.right); if (root.left == null && root.right != null ) { return 1 + right; } if (root.left != null && root.right == null ) { return 1 + left; } int depth = 1 + Math.min(left, right); return depth; } }
222 完全二叉树的节点个数 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; Deque<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <TreeNode>(); int result = 0 ; queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int len = queue.size(); while (len-- > 0 ) { result += 1 ; TreeNode temp = queue.poll(); if (temp.left != null ) queue.offer(temp.left); if (temp.right != null ) queue.offer(temp.right); } } return result; } }
110 平衡二叉树 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) { return getHeight(root) != -1 ; } public int getHeight (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int left = getHeight(root.left); int right = getHeight(root.right); if (left == -1 ) return -1 ; if (right == -1 ) return -1 ; if (Math.abs(left - right) > 1 ) return -1 ; return 1 + Math.max(left, right); } }
257 二叉树的所有路径 easy 代码此链接
1 2 3 4 5 6 以前做过,为什么又忘记,这次复查到的问题: constructpath(root, "" , paths); StringBuffer是append,还有需要toString() ArrayList是add 递归函数里面的if else 是套在第一个if 中的 递归:1. 确定参数2. 终止条件3. 确定递归逻辑
这个代码主要是为了方便理解回溯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) { List<String> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return res; List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); preorderdfs(root, res, path); return res; } public void preorderdfs (TreeNode root, List<String> res, List<Integer> path) { path.add(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right== null ) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer (); for (int i = 0 ; i < path.size() - 1 ; i++) { sb.append(path.get(i)).append("->" ); } sb.append(path.get(path.size() - 1 )); res.add(sb.toString()); return ; } if (root.left != null ) { preorderdfs(root.left, res, path); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } if (root.right != null ) { preorderdfs(root.right, res, path); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } } }
全局变量的写法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { List<String> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return result; backtrack(root); return result; } public void backtrack (TreeNode root) { path.add(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < path.size() - 1 ; i++) { sb.append(path.get(i)).append("->" ); } sb.append(path.get(path.size() - 1 )); result.add(sb.toString()); return ; } if (root.left != null ) { backtrack(root.left); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } if (root.right != null ) { backtrack(root.right); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } } }
404 左叶子之和 easy 有点像求深度那个题,也是左右中的顺序,不同点是判断左叶子节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int left = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left); int right = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right); int mid = 0 ; if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null ) { mid = root.left.val; } int sum = left + right + mid; return sum; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) { LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); if (root == null ) return 0 ; int sum = 0 ; queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left != null && node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null ) { sum += node.left.val; } if (node.left != null ) queue.offer(node.left); if (node.right != null ) queue.offer(node.right); } return sum; } }
513 找树左下角的值 medium 用层序遍历的思路即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); int result = 0 ; int flag = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int len = queue.size(); while (len > 0 ) { TreeNode temp = queue.poll(); if (flag == 0 ) result = temp.val; if (temp.left != null ) queue.offer(temp.left); if (temp.right != null ) queue.offer(temp.right); len--; if (len == 0 ) { flag = 0 ; } else { flag = 1 ; } } } return result; } }
迭代法一直没调试好while,就是类似于层序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); int result = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int len = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { TreeNode temp = queue.poll(); if (i == 0 ) result = temp.val; if (temp.left != null ) queue.offer(temp.left); if (temp.right != null ) queue.offer(temp.right); } } return result; } }
路径总和 112 路径总和 easy 这个题目表达的不太清楚,实际上是判断路径有没有符合targetsum,只要有一个符合就返回true。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null ) return false ; if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) return targetSum == root.val; return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val); } }
113 路径总和2 easy 这个题要结合257 ,还有就是257的返回值和这个题不一样,257需要箭头指向,也就是类型是String,具体看是如何处理的,和112的区别是需要把target值都符合的添加进来,这三个题都要好好敲一遍。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return res; List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); preorderdfs(root, targetSum, res, path); return res; } public void preorderdfs (TreeNode root, int targetSum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path) { path.add(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { if (targetSum == root.val) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } return ; } if (root.left != null ) { preorderdfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val, res, path); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } if (root.right != null ) { preorderdfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val, res, path); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } } }
通过中序和前序/后序构建二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 首先要务必清楚要有中序遍历,前序和后序是不能组成二叉树的。 这里只讲后序和中序构造二叉树。 后序是:左右根 中序是:左根右 所以我们先从后序的最后一个数字可以定位根节点,然后在中序中找到这个值,就可以区分左子树和右子树啦 也就是定义一个helper,这是用中序来构建二叉树。 以后序遍历为例子的思路: 首先把中序的值按照<值,序号>来存到map中,因为后面我们要用后序数组的值来寻找中序数组的序号,所以用<值>可以找到中序的<下标序号> 然后在主方法中,先找到后序根的值,然后用map来定位到中序的index,然后新建root即可,注意后序的话要先构建右子树,再构建左子树
105 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { int [] preorder; int [] inorder; int pre_idx; Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <Integer, Integer>(); public TreeNode helper (int left, int right) { if (left > right) { return null ; } int rootval = preorder[pre_idx]; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (rootval); pre_idx++; int index = map.get(rootval); root.left = helper(left, index - 1 ); root.right = helper(index + 1 , right); return root; } public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) { this .preorder = preorder; this .inorder = inorder; int pre_idx = 0 ; int idx = 0 ; for (Integer val : inorder) { map.put(val, idx++); } return helper(0 , preorder.length - 1 ); } }
106 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { int [] inorder; int [] postorder; int post_idx; Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <Integer, Integer>(); public TreeNode helper (int left, int right) { if (left > right) { return null ; } int rootval = postorder[post_idx]; post_idx--; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (rootval); int index = map.get(rootval); root.right = helper(index + 1 , right); root.left = helper(left, index - 1 ); return root; } public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int [] postorder) { this .inorder = inorder; this .postorder = postorder; post_idx = postorder.length - 1 ; int idx = 0 ; for (Integer val : inorder) { map.put(val, idx++); } return helper(0 , inorder.length - 1 ); } }
654 最大二叉树 medium 首先就是找到最大的值的下标,然后切成左边和右边,用前序遍历递归构造。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) { return construct(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); } public TreeNode construct (int [] nums, int l, int r) { if (l > r) return null ; int max_i = max(nums, l ,r); TreeNode root = new TreeNode (nums[max_i]); root.left = construct(nums, l , max_i - 1 ); root.right = construct(nums, max_i + 1 , r); return root; } public int max (int [] nums, int l, int r) { int max_i = l; for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) { if (nums[max_i] < nums[i]) { max_i = i; } } return max_i; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) { return construct(nums, 0 , nums.length); } public TreeNode construct (int [] nums, int l, int r) { if (l == r) return null ; int max_i = max(nums, l ,r); TreeNode root = new TreeNode (nums[max_i]); root.left = construct(nums, l , max_i); root.right = construct(nums, max_i + 1 , r); return root; } public int max (int [] nums, int l, int r) { int max_i = l; for (int i = l; i < r; i++) { if (nums[max_i] < nums[i]) { max_i = i; } } return max_i; } }
617 合并二叉树 easy 总体比较简单,看递归的返回值处理,其实就是两个二叉树覆盖在一起,思路就是重新构造一个二叉树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null ) return root2; if (root2 == null ) return root1; int val = root1.val + root2.val; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (val); root.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left); root.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right); return root; } }
700 二叉搜索树的搜索 easy 需要注意的是,在递归的时候是用return,另外要了解搜索树的构造。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null || root.val == val) return root; return searchBST(root.val > val ? root.left: root.right, val); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null || root.val == val) return root; if (root.val < val) return searchBST(root.right, val); if (root.val > val) return searchBST(root.left, val); return null ; } }
98 验证二叉搜索树 medium 第二次做又忘记,二叉搜索树中序遍历是升序的,根据这个特性来完成。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE; public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return true ; if (!isValidBST(root.left)) { return false ; } if (root.val <= pre) { return false ; } pre = root.val; return isValidBST(root.right); } }
下面这个代码只是为了说明pre的位置也很重要,这个代码更好理解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE; public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return true ; boolean l = isValidBST(root.left); if (root.val <= pre) { return false ; } pre = root.val; boolean r = isValidBST(root.right); return l && r; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 下面重点来解释 首先利用二叉搜索树升序的特性来做,也就是左子树<根<右子树 所以递归顺序是左根右 先说第一个long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE; 为什么不用int ,因为测试案例的原因,不解释了 这里主要解释为什么要用min,因为后台测试数据中有int 最小值,也就是有极端情况 有这个案例:[-2147483648 ]这个是int 的最小值,如果你的pre随便设置,最后结果是false ,但是其实这个也算二叉搜索树,因为递归过程中会比较pre和root.val,你的pre这时候是大于val的,所以会false 第二个重点解释 pre = root.val;的位置问题,如果根据第二个解答写在r的下面 对于[5 ,1 ,4 ,null ,null ,3 ,6 ]案例是错误的答案,输出是true ,但是实际上是false 画出这个二叉树,可以发现右子树中是出现一个3 ,二叉搜索树的定义是根要比所有的右子树都小,你现在根比右边大,就是不合理的。 所以进入右边之前,要保存上一个root的val,但是其实我觉得还有一个理解就是递归顺序就是左-根-右,这个pre其实就是递归到根的情况 这样才可以用中序遍历 左边小于右边来比较
530 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 medium 根据二叉搜索树的定义,用中序遍历完成。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <Integer>(); traversal(root, result); int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < result.size() - 1 ; i++) { res = Math.min(res, result.get(i + 1 ) - result.get(i)); } return res; } public void traversal (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) return ; traversal(root.left, result); result.add(root.val); traversal(root.right, result); } }
下面这个代码更精简
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { TreeNode pre; int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; traversal(root); return result; } public void traversal (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return ; traversal(root.left); if (pre != null ) { result = Math.min(result, root.val - pre.val); } pre = root; traversal(root.right); } }
501 二叉搜索树的众数 easy 用了中序遍历,也是利用二叉搜索树的性质,中序遍历是按照顺序升序的,主要是理解处理的逻辑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { TreeNode pre = null ; ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); int count = 0 ; int maxcount = 0 ; public int [] findMode(TreeNode root) { traversal(root); int result[] = new int [list.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { result[i] = list.get(i); } return result; } public void traversal (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return ; traversal(root.left); if (pre != null && pre.val != root.val) { count = 1 ; } else { count++; } if (count > maxcount) { list.clear(); list.add(root.val); maxcount = count; } else if (count == maxcount){ list.add(root.val); } pre = root; traversal(root.right); } }
236 二叉树的最近公共祖先 medium 这个题需要好好看卡哥的讲解。这里容易漏掉一种情况,就是p是q的祖先,或者反过来,第二次看这个题还是没有想到为什么用后序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null || root == p || root == q) { return root; } TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); if (left == null && right == null ) { return null ; } else if (left != null && right == null ) { return left; } else if (left == null && right != null ) { return right; } else { return root; } } }
235 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 easy 用上面一个代码也是可以的,不过我们可以利用二叉搜索树的性质来完成。也就是如果root的值都小于p和q,那就去右区间找,如果都大于就在左区间找,如果在p和q的区间内,说明找到,就返回root。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); else if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); else return root; } }
701 二叉搜索树中的插入操作 medium 利用二叉搜索树的性质来插入。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public TreeNode insertIntoBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null ) { return new TreeNode (val); } if (root.val < val) { root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val); } else if (root.val > val) { root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val); } return root; } }
450 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 medium 有点难度的题,下面有具体解释。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int key) { if (root == null ) return null ; if (root.val > key) { root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key); } else if (root.val < key) { root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key); } else if (root.val == key) { if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) return null ; if (root.right == null ) return root.left; if (root.left == null ) return root.right; TreeNode temp = root.right; while (temp.left != null ) { temp = temp.left; } root.val = temp.val; root.right = deleteNode(root.right, temp.val); } return root; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 一共五种情况 1. 没找到删除的节点,直接返回null 然后开始搜索正确的位置,找到节点的情况 2. 左右孩子都是空的,返回null 3. 右孩子空,把左孩子补上去4. 左孩子空,把有孩子补上去5. 有左右孩子,这个情况最复杂,则将删除节点的左子树头结点(左孩子)放到删除节点的右子树的最左面节点的左孩子上,返回删除节点右孩子为新的根节点,下面详细讲操作。先找到这个key的右孩子,然后一直找这个右孩子的最左边的孩子,这时候就顺便把这个孩子的节点值设为root,然后递归删除这个值。
669 修剪二叉搜索树 medium 把范围之外的节点清除。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int low, int high) { if (root == null ) return null ; if (root.val < low) { return trimBST(root.right, low, high); } if (root.val > high) { return trimBST(root.left, low, high); } root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high); root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high); return root; } }
108 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 easy 可以对比下构造二叉树那个题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) { return bst(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); } public TreeNode bst (int [] nums, int left, int right) { if (left > right) return null ; int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (nums[mid]); root.left = bst(nums, left, mid - 1 ); root.right = bst(nums, mid + 1 , right); return root; } }
538 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 medium 这个先看定义,就是使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。中序遍历是升序,这样不方便累加,要从后往前,也就是中反的中序遍历,右中左。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution { int sum = 0 ; public TreeNode convertBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return null ; convertBST(root.right); sum += root.val; root.val = sum; convertBST(root.left); return root; }
回溯算法 一般用于组合,切割,子集,排列,棋盘问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 void backtracking (参数) { if (终止条件) { 存放结果; return ; } for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) { 处理节点; backtracking(路径,选择列表); 回溯,撤销处理结果 } } 关于剪枝操作,这是卡哥原话 剪枝精髓是:for 循环在寻找起点的时候要有一个范围,如果这个起点到集合终止之间的元素已经不够 题目要求的k个元素了,就没有必要搜索了。
77 组合 medium 注意取过的数字不再取,也就是没有(4,4)这种情况,组合是无序(也就是(1,2)和(2,1)是一样的,取一个就可以),排列是有序(两个答案都要)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) { backtrack(n, k ,1 ); return result; } public void backtrack (int n, int k, int startindex) { if (path.size() == k) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = startindex; i <= n; i++) { path.add(i); backtrack(n, k, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
1 2 3 4 LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); 注意这个才有removeLast的操作,arraylist是没有的。 对剪枝的理解 比如 n = 7 , k = 4 ,那么从 5 开始搜索就已经没有意义了,这是因为即使把 5 选上,后面的数只有 6 和 7 ,一共就 3 个候选数,凑不出 4 个数的组合。因此,搜索起点有上界。
216 组合总和 III medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) { backtrack(k, n, 0 , 1 ); return result; } public void backtrack (int k, int n, int sum, int startindex) { if (sum > n) { return ; } if (path.size() == k) { if (n == sum) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } return ; } for (int i = startindex; i <= 9 ; i++){ path.add(i); backtrack(k, n, sum + i, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) { backtrack(k, n, 0 , 1 ); return result; } public void backtrack (int k, int n, int sum, int startindex) { if (sum > n) { return ; } if (path.size() == k) { if (n == sum) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } return ; } for (int i = startindex; i <= 9 ; i++){ path.add(i); sum += i; backtrack(k, n, sum, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); sum -= i; } } }
17 电话号码的字母组合 medium 这个题和上一题的区别是,这个题相当于多个区间进行取值,而上个题是一个区间内。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { List<String> result = new ArrayList <>(); public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) { if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0 ) { return result; } String[] numString = {"" ,"" ,"abc" ,"def" ,"ghi" ,"jkl" ,"mno" ,"pqrs" ,"tuv" ,"wxyz" }; backtrack(numString, digits, 0 ); return result; } StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder (); public void backtrack (String[] numString, String digits, int num) { if (num == digits.length()) { result.add(temp.toString()); return ; } String str = numString[digits.charAt(num) - '0' ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length(); i++) { temp.append(str.charAt(i)); backtrack(numString, digits, num + 1 ); temp.deleteCharAt(temp.length() - 1 ); } } }
39 组合总和 medium 结合216来看,和216的区别是,这里给了一个数组的范围,其次,数组元素的可以重复使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { Arrays.sort(candidates); backtrack(candidates, target, 0 , 0 ); return result; } public void backtrack (int [] candidates, int target, int sum, int idx) { if (sum == target) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = idx; i < candidates.length; i++) { if (sum + candidates[i] > target) break ; path.add(candidates[i]); backtrack(candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], i); path.removeLast(); } } }
40 组合总和 II medium 这里实际上要完成两个任务,一个是不能有重复元素(是指这个数组中不能重复用这个数,但是数组本身是可以有重复是数字的,比如这个数组可以存在两个1,但是每个1只能用一次),第二个是不能有重复组合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) { Arrays.sort(candidates); backtrack(candidates, target, 0 , 0 ); return result; } public void backtrack (int [] candidates, int target, int sum, int idx) { if (sum == target) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = idx; i < candidates.length; i++) { if (i > idx && candidates[i - 1 ] == candidates[i]) { continue ; } if (sum + candidates[i] > target) break ; path.add(candidates[i]); backtrack(candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
131 分割回文串 medium 回文串 是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList <>(); List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<String>> partition (String s) { backtrack(s,0 ); return result; } public void backtrack (String s, int startindex) { if (startindex == s.length()) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = startindex; i < s.length(); i++) { if (ishuiwen(s, startindex, i)) { String str = s.substring(startindex, i + 1 ); path.add(str); } else { continue ; } backtrack(s, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } public boolean ishuiwen (String s, int startindex, int end) { for (int i = startindex, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) { if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 首先我们要明白startindex的作用就是相当于切割线的作用 这个题的for 循环是切了第一根线(横向),然后回溯递归的过程是纵向(切第二跟线),这样可以实现切割不同字符串的效果。 那么又有一个疑问,为什么是两条线,因为第一条线固定第一个位置,然后第二根线是一个个位置继续切。 问题1 :为什么回溯结束条件是if (startindex == s.length()) 当切割线到了最后,说明后面不能再切了,所以这里要设置结束条件并添加结果。 可是,这里没有判断回文呀? 其实不是的,下面for 循环的时候,已经判断回文,如果不是回文的话,不参加递归,所以,只要参加了递归,就一定是回文。 这个题要好好看卡哥的画图,可以理解这个切割线。 substring(start,end)是左开右闭,也就是end序号是没有截取到了,而我们判断回本的时候,end是参与了判断的,所以这里要加1 让这个字符串截取到。
93 复原ip地址 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution { List<String> result = new ArrayList <>(); public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) { backtrack(s, 0 , 0 ); return result; } public void backtrack (String s, int startindex, int pointnum) { if (pointnum == 3 ) { if (isvalid(s, startindex, s.length() - 1 )) { result.add(s); } } for (int i = startindex; i < s.length(); i++) { if (isvalid(s, startindex, i)) { s = s.substring(0 , i + 1 ) + "." + s.substring(i + 1 ); pointnum++; backtrack(s, i + 2 , pointnum); pointnum--; s = s.substring(0 , i + 1 ) + s.substring(i + 2 ); } else { break ; } } } public boolean isvalid (String s, int start, int end) { if (start > end) { return false ; } if (s.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end) { return false ; } int num = 0 ; for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { if (s.charAt(i) < '0' || s.charAt(i) > '9' ) { return false ; } num = num * 10 + (s.charAt(i) - '0' ); if (num > 255 ) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 这个题和上面题的区别: 1. 没有path变量这个题从头到尾都需要整个s,而之前的题目的类似于从里面选若干个元素。 2. ip有效判断首先最主要的判断是区间必须是左小右大,也就是start>end是非法的 first:0 开头的数字不合法,但是如果单独0 的话是可以的,比如[0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ] second:遇到⾮数字字符不合法(这个可以不需要,因为案例中都是数字) third:大于255 的不合法
78 子集 medium 和77的区别是这个是回溯的if条件的不同,这里是小于等于,还有就是不能有return。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) { backtrack(nums, 0 ); return result; } public void backtrack (int [] nums, int startindex) { if (path.size() <= nums.length) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } for (int i = startindex; i < nums.length; i++) { path.add(nums[i]); backtrack(nums, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
90 子集2 medium 遇到这个重复元素的,想都不用想,先排序,然后再处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup (int [] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); backtrack(nums, 0 ); return result; } public void backtrack (int [] nums, int startindex) { if (path.size() <= nums.length) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } for (int i = startindex; i < nums.length; i++) { if (i > startindex && nums[i - 1 ] == nums[i]) { continue ; } path.add(nums[i]); backtrack(nums, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
491 递增子序列 medium 这个题不能排序,要用到原数组的顺序,所以可能会出现[4,6,4,7]这种数组,所以上一题子集不能重复的代码思想不能用到,要用map要判断。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences (int [] nums) { backtrack(nums, 0 ); return result; } public void backtrack (int [] nums, int startindex) { if (path.size() > 1 ) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = startindex; i < nums.length; i++) { if (!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.getLast() || map.getOrDefault(nums[i], 0 ) >= 1 ) { continue ; } map.put(nums[i], map.getOrDefault(nums[i], 0 ) + 1 ); path.add(nums[i]); backtrack(nums, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
if条件也可以写成这样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public void backtrack (int [] nums, int startindex) { if (path.size() > 1 ) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = startindex; i < nums.length; i++) { if (!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.getLast()) { continue ; } if (map.getOrDefault(nums[i], 0 ) >= 1 ) { continue ; } map.put(nums[i], map.getOrDefault(nums[i], 0 ) + 1 ); path.add(nums[i]); backtrack(nums, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } }
46 全排列 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path= new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) { backtrack(nums); return result; } public void backtrack (int [] nums) { if (path.size() == nums.length) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (path.contains(nums[i])) { continue ; } path.add(nums[i]); backtrack(nums); path.removeLast(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 讲解组合和排列的区别 组合也就是[1 ,2 ,3 ]和[1 ,3 ,2 ]是一样的 而排列则视为他们是两个不同的结果。 所以在组合问题中使用了startindex来控制横向遍历中的重复元素问题 而排列则不需要,因为我们还会使用以前用过的数字,所以排列的时候,for 就是全体元素的遍历,但是用过的数是不能用的,所以用path.contains来排除 这也是组合和排列的区别啦
47 全排列2 medium 这题的数组中可以有重复的数字,那么又如何去重呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); boolean [] used; public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique (int [] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); used = new boolean [nums.length]; Arrays.fill(used, false ); backtrack(nums); return result; } public void backtrack (int [] nums) { if (path.size() == nums.length) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (i > 0 && nums[i - 1 ] == nums[i] && used[i -1 ] == false ) { continue ; } if (used[i] == false ) { used[i] = true ; path.add(nums[i]); backtrack(nums); path.removeLast(); used[i] = false ; } } } }
332 重新安排行程 hard 51 N皇后 hard 21 解数独 hard 贪心算法 455 分发饼干 easy 思路很简单,一个for循环就行,先排序,小饼干分给小胃口,然后注意越界问题就行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int findContentChildren (int [] g, int [] s) { Arrays.sort(g); Arrays.sort(s); int count = 0 ; int j = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length; i++) { if (j < g.length && s[i] >= g[j]) { count++; j++; } } return count; } }
376 摆动序列 medium 可动态规划,要明确返回的是原始序列的长度哦,但是这个原始序列不一定就是题目给的全体,可能是子序列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int wiggleMaxLength (int [] nums) { int pre = 0 ; int cur = 0 ; int result = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { cur = nums[i] - nums[i - 1 ]; if ((cur > 0 && pre <= 0 ) || (cur < 0 && pre >= 0 )) { result++; pre = cur; } } return result; } }
53 最大子数组和 medium 可动态规划,这里不要太关注数组下标,一开始老想着这个left和right,和209进行一个对比(这个题是算长度,以及人家有目标值),要注意是连续的子区间。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { count += nums[i]; if (count > result) { result = count; } if (count < 0 ) { count = 0 ; } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 如果 -2 1 在一起,计算起点的时候,一定是从1 开始计算,因为负数只会拉低总和,这就是贪心贪的地方! 利用两个数来完成这个题,result来记录最大的值,同时也是结果值,而count是记录区间的值 我们要知道最大和,意味着我们不能加上负数,否则只会越来越小,而count是记录区间的大小,当区间大小为负数的时候,我们就不要这个区间了,在下个位置重新开始记录初始化为0 ,在这个过程中一直对比最大值即可。 和209 的区别,209 是求最小的长度,而且是有targer的,当和大于等于这个targer后在慢慢看最小的长度,而本题是计算和
122 买卖股票的最佳时机II medium 可动态规划,贪心思想:局部最优:收集每天的正利润,全局最优:求得最大利润。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int result = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) { result += Math.max((prices[i] - prices[i - 1 ]),0 ); } return result; } }
55 跳跃游戏 medium 贪心算法局部最优解:每次取最大跳跃步数(取最大覆盖范围),整体最优解:最后得到整体最大覆盖范围,看是否能到终点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public boolean canJump (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 1 ) return true ; int cover = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= cover; i++) { cover = Math.max(i + nums[i], cover); if (cover >= nums.length - 1 ) return true ; } return false ; } }
45 跳跃游戏2 medium 和上一题的区别是这题要算出一个最小的步数,只需要考虑覆盖的范围是不是到最后一个,而本题没那么简单。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int jump (int [] nums) { int end = 0 ; int maxcount = 0 ; int step = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; i++) { maxcount = Math.max((i + nums[i]), maxcount); if (i == end) { end = maxcount; step++; } } return step; } }
1005 K 次取反后最大化的数组和 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public int largestSumAfterKNegations (int [] nums, int k) { Arrays.sort(nums); int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] < 0 && k > 0 ) { nums[i] = -nums[i]; k--; } } while (k > 0 ) { Arrays.sort(nums); for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { nums[i] = -nums[i]; k--; } } for (int x : nums) { result += x; } return result; } }
134 加油站 medium 要充分利用贪心的思想。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int canCompleteCircuit (int [] gas, int [] cost) { int cursum = 0 ; int totalsum = 0 ; int start = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < gas.length; i++) { cursum += gas[i] - cost[i]; totalsum += gas[i] - cost[i]; if (cursum < 0 ) { cursum = 0 ; start = i + 1 ; } } if (totalsum < 0 ) return -1 ; return start; } }
135 分发糖果 hard 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public int candy (int [] ratings) { int [] candys = new int [ratings.length]; int result = 0 ; Arrays.fill(candys,1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < ratings.length; i++) { if (ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1 ]) { candys[i] = candys[i - 1 ] + 1 ; } } for (int i = ratings.length - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { if (ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1 ]) { candys[i] = Math.max(candys[i], candys[i + 1 ] + 1 ); } } for (int x : candys) { result += x; } return result; } }
860 柠檬树找零 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public boolean lemonadeChange (int [] bills) { int five = 0 ; int ten = 0 ; int twenty = 0 ; int temp = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < bills.length; i++) { temp = bills[i] / 5 ; if (temp == 1 ) { five++; } else if (temp == 2 ) { if (five < 0 ) return false ; ten++; five--; } else { twenty++; if (ten > 0 && five > 0 ) { ten--; five--; } else if (five >= 3 ) { five = five - 3 ; } else return false ; } } return true ; } }
406 根据身高重建队列 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int [][] reconstructQueue(int [][] people) { Arrays.sort(people,(a, b) -> { if (a[0 ] == b[0 ]) return a[1 ] - b[1 ]; return b[0 ] - a[0 ]; } ); LinkedList<int []> que = new LinkedList <>(); for (int [] p : people) { que.add(p[1 ],p); } return que.toArray(new int [people.length][]); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 输入是[[7 ,0 ],[4 ,4 ],[7 ,1 ],[5 ,0 ],[6 ,1 ],[5 ,2 ]],最终结果是[[5 ,0 ],[7 ,0 ],[5 ,2 ],[6 ,1 ],[4 ,4 ],[7 ,1 ]] 这里好多语法是第一次见,详细记录一下 if (a[0 ] == b[0 ]) return a[1 ] - b[1 ];return b[0 ] - a[0 ];a和b分别代表第一个数组和第二个数组 0 和1 就是这个数组的身高和比他高的人数LinkedList.add(int index,E elemnt) 也就是按照数组第二个位置进行插入即可 将que转成数组,下面是打印出第一个数的情况 int [][] res = que.toArray(new int [people.length][]);System.out.print(Arrays.toString(res[0 ])); 二维数组可以不定义列数,但必须定义行数。
452 用最小数量的箭引爆气球 medium 学习下这个二维数组的排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public int findMinArrowShots (int [][] points) { if (points.length == 0 ) return 0 ; Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0 ],b[0 ])); int count = 1 ; int rightedge = points[0 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < points.length; i++) { if (points[i][0 ] > rightedge) { count++; rightedge = points[i][1 ]; } else { rightedge = Math.min(rightedge, points[i][1 ]); } } return count; } }
435 无重叠区间 medium 去掉重叠的区间,[1,2],[2,3]不算重叠,然后计算需要去掉的个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int eraseOverlapIntervals (int [][] intervals) { Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0 ], b[0 ])); int rightedge = intervals[0 ][1 ]; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++) { if (intervals[i][0 ] < rightedge) { count++; rightedge = Math.min(rightedge, intervals[i][1 ]); } else { rightedge = intervals[i][1 ]; } } return count; } }
763 划分字母区间 medium 字符串划分为尽可能多的片段,同一字母最多出现在一个片段中。返回一个表示每个字符串片段的长度的列表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public List<Integer> partitionLabels (String s) { List<Integer> list = new LinkedList <>(); int [] edge = new int [26 ]; char [] chars = s.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { edge[chars[i] - 'a' ] = i; } int last = -1 ; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { index = Math.max(index, edge[chars[i] - 'a' ]); if (index == i) { list.add(i - last); last = i; } } return list; } }
56 合并区间 mediun 这个题注意下返回的输出格式。注意[1,4],[4,5]也要合并的,变成[1,5]。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { List<int []> result = new LinkedList <>(); Arrays.sort(intervals, (a ,b) -> Integer.compare(a[0 ], b[0 ])); int leftedge = intervals[0 ][0 ]; int rightedge = intervals[0 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++) { if (intervals[i][0 ] > rightedge) { result.add(new int []{leftedge, rightedge}); leftedge = intervals[i][0 ]; rightedge = intervals[i][1 ]; } else { rightedge = Math.max(intervals[i][1 ], rightedge); } } result.add(new int []{leftedge, rightedge}); return result.toArray(new int [result.size()][]); } }
上面452,435,56题,需要好好理解什么时候是需要比较max的右边界的,而且上面三个题,都是左边区间排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 别忘了均是左边区间排序,从小到大,还有循环都是从1 开始 452 在右边界内,也就是当前数组的左边区间小于右边界,说明重叠了,可以穿过同一只箭,不需要更新箭的数量,但是这时候要更新右边区间,要缩小右边区间的范围,所以要用min来对比 反之如果大于这个右区间,就要增加箭的数量,然后更新右边界 435 去掉重叠的区间注意[1 ,2 ][2 ,3 ]不重叠 在右边界内,也就是当前数组的左边区间小于右边界,说明需要去掉一个数组,count++,同时需要更新右边界min来比较,为什么要min呢,可以这么想,万一第一个的右边界很大,覆盖了全部数组,那必须得去掉啊 如果不在边界,就直接更新右边界的值即可 56 注意[4 ,5 ],[5 ,6 ]也是需要合并的 这个题要记录左右边界 在右边界外,也就是当前数组的左边区间大于右边界,可以直接添加元素了,为什么不用小于等于呢(别忘了上面一行什么情况需要合并),其实也可以的,只是里面内容不一样而已,添加了元素后,要更新左右边界 反正,只需要更新右边界,因为不确定下一个是不是还是重叠的,所以这里不添加元素,只是改变右边界 循环完后,会漏掉最后一个区间的,所以最后加上 这个题的的返回值要注意下
动态规划 1 2 3 4 5 1. 确定dp[i]的含义2. 确定递推公式(转移方程)3. 初始化dp数组4. 确定遍历顺序5. 举例推导dp数组
509 斐波那契数 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. dp[i] 第i个数的斐波那契数2. 转移方程 dp[i] = dp[i - 1 ] + dp[i - 2 ];3. 初始化dp[0 ],dp[1 ]4. dp[i]依赖dp[i-1 ]和dp[i-2 ],按照顺序遍历5. 自己推导一下0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 这里注意一个点就是求dp[n],也就是初始化数组的大小是n+1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int fib (int n) { if (n < 2 ) return n; int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 0 ; dp[1 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++ ) { dp[i] = dp[i - 1 ] + dp[i - 2 ]; } return dp[n]; } }
70 爬楼梯 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 先理解题目,每次可以爬两级或者爬一级,也就是你可以在dp[i-2 ]的级上爬两级,也可以在dp[i-1 ]的级上爬一级,那么爬楼梯的方法就有dp[i-1 ]加上dp[i-2 ] 本题不需要dp[0 ],因为这样没有意义,没有说爬0 级的楼梯,所以dp[1 ]和dp[2 ]需要初始化,由于是求dp[n],所以数组的长度也就是需要n+1 1. dp[i]爬到第i层楼梯的方法数2. 根据我上面写的题意可以推出 dp[i]=dp[i-1 ]+dp[i-2 ]3. 第0 层没意义,但是会生成数组的时候会自动初始化0 ,我们也不需要管,dp[1 ]=1 ,dp[2 ]=2 4. dp[i]依赖dp[i-1 ]和dp[i-2 ],按照顺序遍历5. 可以自己推导下前面几个,比如 1 2 3 5 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int climbStairs (int n) { if (n < 3 ) return n; int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[1 ] = 1 ; dp[2 ] = 2 ; for (int i = 3 ; i <= n; i++) { dp[i] = dp[i - 1 ] + dp[i - 2 ]; } return dp[n]; } }
746 使用最小花费爬楼梯 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 这个题需要好好看看讲解哦,本题的要求是花费最小的体力值,然后首先看下面的例子理解下顶部是哪里!!!这个一开始我很懵,跟70 一样,也是一次可以跳1 级或者2 级 例子1 :cost = [10 ,15 -,20 ],支付 15 ,向上爬两个台阶,到达楼梯顶部,顶部这里是没有体现的,也就是跳到cost[2 ]是一级,然后再跳到顶部是一级,一共两级 这里-标记了跳的台阶 例子2 :cost = [1 -,100 ,1 -,1 ,1 -,100 ,1 -,1 -,100 ,1 -],一共支付6 ,从下标为0 的台阶开始 - 支付 1 cost[0 ],向上爬两个台阶,到达下标为 2 的台阶。 - 支付 1 cost[2 ],向上爬两个台阶,到达下标为 4 的台阶。 - 支付 1 cost[4 ],向上爬两个台阶,到达下标为 6 的台阶。 - 支付 1 cost[6 ],向上爬一个台阶,到达下标为 7 的台阶。 - 支付 1 cost[7 ],向上爬两个台阶,到达下标为 9 的台阶。 - 支付 1 cost[9 ],向上爬一个台阶,到达楼梯顶部。 看到题目的例子后,需要注意,最后一个楼梯顶部,在数组中是没有体现他的位置的,也就是后移一个,其实不需要纠结这个问题 因为你只要最后取数组倒数两个进行比较就行,哪个花费体力小就用哪个,这样他们都可以跳到楼顶 1. dp[i]到达第i个台阶需要花费的最少体力2. 因为我们需要花费最少的体力,然后可以跳1 级或者2 级,也就是 dp[i]=dp[i-1 ]+dp[i-2 ]3. 初始化2 个就行,dp[0 ]和dp[1 ]4. dp[i]依赖dp[i-1 ]和dp[i-2 ],按照顺序遍历5. 推导一下cost = [1 , 100 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 100 , 1 , 1 , 100 , 1 ] 的dp数组是[1 ,100 ,2 ,3 ,3 ,103 ,4 ,5 ,104 ,6 ]这里的转移方程详细说下,dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ]) + cost[i]; 这里为什么是cost[i]而不是cost[i-1 ]或者cost[i-2 ] 因为我们想,我们现在是取到了前面两个比较小的值,然后本级需要跳,就要花费,先不考虑我们这个级跳1 级还是2 级的问题,因为我们先把整个dp数组弄出来,最后比较最后两个的值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { if (cost == null || cost.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } if (cost.length == 1 ) { return cost[0 ]; } int [] dp = new int [cost.length]; dp[0 ] = cost[0 ]; dp[1 ] = cost[1 ]; for (int i = 2 ; i < cost.length; i++) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ]) + cost[i]; } return Math.min(dp[cost.length - 2 ], dp[cost.length - 1 ]); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { int [] dp = new int [cost.length]; dp[0 ] = cost[0 ]; dp[1 ] = cost[1 ]; for (int i = 2 ; i < cost.length; i++) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ]) + cost[i]; } return Math.min(dp[cost.length - 2 ], dp[cost.length - 1 ]); } }
62 不同路径 medium 1 2 3 4 5 1. dp[i][j]代表到从(0 ,0 )出发,到(i, j) 有dp[i][j]条不同的路径。2. 题目说只能从右边还有下边走,所以只依赖两个方向的路径,dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j] + dp[i][j - 1 ]3. dp初始化,第一行和第一列的坐标都是1 ,因为只有一个方向走4. 遍历顺序就是从左到右5. 自己手动画下推导数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) { int [][] dp = new int [m][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { dp[0 ][i] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < n; j++) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j] + dp[i][j - 1 ]; } } return dp[m - 1 ][n - 1 ]; } }
63 不同路径2 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 和上一题五部曲差不多,这里直说区别 首先初始化问题 初始化只在第一行和第一列,但是如果遇到障碍,需要break ,而不是continue ,这个的意思是,障碍后面的格子,都是0 了,但是如果你是continue 的话,只是单纯障碍这一格子是0 ,但是后面是1 而我们需要知道,你只要有障碍,后面都不能通过了 在具体递推公式的时候,遇到障碍则跳过,不是break ,因为你break 的话就全部结束了,而continue 只是跳过这个格子,这样这个格子就会为0 ,在其他位置需要加他的时候,就是加0 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int uniquePathsWithObstacles (int [][] obstacleGrid) { int m = obstacleGrid.length; int n = obstacleGrid[0 ].length; int [][] dp = new int [m][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { if (obstacleGrid[i][0 ] == 1 ) break ; dp[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (obstacleGrid[0 ][i] == 1 ) break ; dp[0 ][i] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1 ) continue ; dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j] + dp[i][j - 1 ]; } } return dp[m - 1 ][n - 1 ]; } }
343 整数拆分 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 这个题感觉没那么容易理解 1. dp[i] 分拆数字i,可以得到的最大乘积为dp[i]。2. 当i>=2 时,假设对正整数 i 拆分出的第一个正整数是 j(1 <=j<i),则有以下两种方案:1. 将 i拆分成j和i−j的和,且i−j 不再拆分成多个正整数,此时的乘积是j*(i-j);2. 将 ii 拆分成 jj 和 i-ji−j 的和,且 i-ji−j 继续拆分成多个正整数,此时的乘积是j*dp[i-j]。上面其实不容易懂,需要这样理解,j * (i - j) 是单纯的把整数拆分为两个数相乘,而j * dp[i - j]是拆分成两个以及两个以上的个数相乘,因为题目要求可以至少拆分出2 个。 3. 首先要清楚,dp[0 ]和dp[1 ],因为0 无法拆分,1 也无法拆分,所以初始化要从2 开始,2 =1 +1 ,然后1 *1 =1 ,dp[2 ]=1 ,然后注意数组长度是n+1 4. 遍历顺序也是第一次见,需要i和j,然后也是顺序遍历5. 自己可以手动推导,比如n=10 ,dp数组是1 ,2 ,4 ,6 ,9 ,12 ,18 ,27 ,36
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int integerBreak (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[2 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 3 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= i - j; j++) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j * (i - j), dp[i - j] * j)); } } return dp[n]; } }
96 不同的二叉搜索树 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 这个题其实算困难了,尤其是递推关系,没做过压根不知道,可以看卡哥的图 1. dp[i] : 1 到i为节点组成的二叉搜索树的个数为dp[i]2. 递推公式元素1 为头结点搜索树的数量 = 右子树有2 个元素的搜索树数量 * 左子树有0 个元素的搜索树数量 元素2 为头结点搜索树的数量 = 右子树有1 个元素的搜索树数量 * 左子树有1 个元素的搜索树数量 元素3 为头结点搜索树的数量 = 右子树有0 个元素的搜索树数量 * 左子树有2 个元素的搜索树数量 有2 个元素的搜索树数量就是dp[2 ] 有1 个元素的搜索树数量就是dp[1 ] 有0 个元素的搜索树数量就是dp[0 ] 所以dp[3 ] = dp[2 ] * dp[0 ] + dp[1 ] * dp[1 ] + dp[0 ] * dp[2 ] 递推公式:dp[i] += dp[j - 1 ] * dp[i - j] 这个不好记,可以看dp[3 ],第一个是dp[2 ]*dp[0 ],i=3 ,然后j是从1 开始,所以可以想到i-j,然后另外一个规律就是2 +0 =2 ,前面3 -1 =0 ,另外一个就是j-1 =0 ,此时j=1 哦 3. dp[0 ] = 1 ,dp[1 ]=1 ,1 的话好理解,但是0 的话不好理解,但是我们后面用到乘法,所以初始化为1 更好。4. 节点数为i的状态是依靠 i之前节点数的状态,从前往后即可5. 可以推导下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int numTrees (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; dp[1 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <=n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= i; j++) { dp[i] += dp[i - j] * dp[j - 1 ]; } } return dp[n]; } }
416 分割等和子集 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 0 -1 背包问题nums里面可以看成物品,每个物品只能用一次,题目拆解后可以发现target是背包容量 对于一维dp数组,务必先遍历物品,反正倒着遍历容量(因为每次元素不能重复使用),其次还要注意j>=nums[i],而不是0 这里 dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]); max中的dp[j]可以理解为二维数组中的dp[i-1 ],因为如果用一维数组dp[i - 1 ]那一层拷贝到dp[i]上 五部曲 1. dp[j]表示容量为j的背包,所背物品价值最高是dp[j]2. dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]);本题的物品,既是容量,也是价值3. 题目给的价值都是正整数的话,都可以初始化为0 4. 遍历顺序:使用一维数组的话,物品遍历的for 循环放在外层,遍历背包的for 循环放在内层,且内层for 循环倒序遍历!5. 自己递推试试,注意本题的容量是target,所以数组的长度是target+1 这里有个细节就是,target可能不能被整除,所以先要判断能不能被2 取模
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public boolean canPartition (int [] nums) { int sum = 0 ; for (int x : nums) { sum += x; } if (sum % 2 != 0 ) return false ; int target = sum / 2 ; int [] dp = new int [target + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { for (int j = target; j >= nums[i]; j--) { dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]); } } return dp[target] == target; } }
1049 最后一块石头的重量II medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 这个题和上个题的区别是,上个题能不能正好装满,这个题是求最多能装多少 其实一开始看这个题,有点懵,一直纠结一直拿两块石头应该怎么拿。 看了分析后,其实这个题的本意是尽量让石头分成重量相同的两堆,这样相撞后的石头最小。同样,本题物品的重量为store[i],物品的价值也为store[i]。 也就是当我们把所有重量求和/2 ,就可以求我们的dp数组,然后这个题不需要考虑sum能否被整除2 ,因为本题说了是最多能装多少 最后,我们理解下题目需要返回什么,按照上面的思路,其实石头被分成两堆,一堆是dp[target],一堆是sum-dp[target],然后相减就是剩下石头的重量 五部曲和上面一题一样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int lastStoneWeightII (int [] stones) { int sum = 0 ; for (int x : stones) { sum += x; } int target = sum / 2 ; int [] dp = new int [target + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < stones.length; i++) { for (int j = target; j >= stones[i]; j--) { dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - stones[i]] + stones[i]); } } return sum - 2 * dp[target]; } }
494 目标和 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 涉及组合问题,而且这个题和其他背包问题不太一样,有点难度,下面详细讲下,本题也是0 -1 背包。 首先理解一点是如何表达target 我们可以计算出这个数组的总和sum,然后我们想想都是加号的数字和为a,都是减号的数字和为b, 那么a-b就是sum,然后a+b就是target(这里和卡哥有点出入,我按照自己的理解去写,他是反过来的) b= a-sum a+a-sum=target a=(target+sum)/2 a即为bagsize 这里需要考虑2 个问题,一个是target的绝对值如果大于sum,是不可能组成的,因为可能有这种案例 第二个考虑就是(target+sum)%2 ==1 的话,也是不行的,例如sum 是5 ,target是2 的话其实就是无解的,根本无法组合出来,4 -1 =3 ,3 -2 =1 ,压根组合不到2 ,也就是要求sum+target一定为偶数才行,至于为啥,还没想通。 那么这里a就可以理解为背包容量,为什么呢,我们理解为组成加号和为a情况有多少种 那么dp[a+1 ],这是dp数组长度 五部曲 1. dp[j] 表示:填满j(包括j)这么大容积的包,有dp[j]种方法2. 这里的递推公式不一样!!!!其实也不算完全理解不考虑nums[i]的情况下,填满容量为j的背包,有dp[j]种方法。 那么考虑nums[i]的话(只要搞到nums[i]),凑成dp[j]就有dp[j - nums[i]] 种方法。 例如:dp[j],j 为5 已经有一个1 (nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[4 ]种方法 凑成 dp[5 ]。 已经有一个2 (nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[3 ]种方法 凑成 dp[5 ]。 已经有一个3 (nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[2 ]中方法 凑成 dp[5 ]。 已经有一个4 (nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[1 ]中方法 凑成 dp[5 ]。 已经有一个5 (nums[i])的话,有 dp[0 ]中方法 凑成 dp[5 ]。 那么凑整dp[5 ]有多少方法呢,也就是把 所有的 dp[j - nums[i]] 累加起来。 这个是组合类问题,递推公式为:dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]] 3. 初始化这里必须要设置dp[0 ]为1 ,这个可以理解为容量为0 的背包,有一种方法,就是装0 件物品。但是如果初始化是0 后面无法推导。 4. 遍历顺序,物品放外面(数组),容量放里面(bagsize)。5. 推导数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int findTargetSumWays (int [] nums, int target) { int sum = 0 ; for (int x : nums) { sum += x; } if ((sum + target) % 2 == 1 ) return 0 ; if (Math.abs(target) > sum) return 0 ; int bagsize = (sum + target) / 2 ; int [] dp = new int [bagsize + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { for (int j = bagsize; j >= nums[i]; j--) { dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]]; } } return dp[bagsize]; } }
474 零和一 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 这个题 也没那么容易,本质也是0 -1 背包问题 sts数组就是物品,然后这里很难理解的就是m和n,这里不能理解为多重背包,这里要理解为有两个维度的背包。 1. dp[i][j]:最多有i个0 和j个1 的strs的最大子集的大小为dp[i][j],也就是里面存的是大小2. dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - zeroNum][j - oneNum] + 1 );3. 初始化就是0 4. 遍历顺序,这个题有点不一样哦,里面是两个维度的容量,但是总体上还是物品在外面遍历,容量在里面遍历(倒着)5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int findMaxForm (String[] strs, int m, int n) { int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; for (String str:strs) { int onenum = 0 , zeronum = 0 ; for (char c : str.toCharArray()) { if (c == '0' ) { zeronum++; } else { onenum++; } } for (int i = m; i >= zeronum; i--) { for (int j = n; j >= onenum; j--) { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - zeronum][j - onenum] + 1 ); } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
背包问题解析合集 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 总结一下,0 -1 背包物品先,容量倒着来,完全背包物品先,容量顺着来 组合问题物品先,容量顺着来,排列问题容量先从头来 至于是写dp[j]还是dp[i],是根据你把j和i定义成什么,其实都是dp[容量],也就是用容量的下标来表示 1. 0 -1 背包表示物品只能拿一次,先遍历物品(顺序),再遍历容量(倒着,保证物品只被添加一次) for (int i = 0 ; i < weight.size(); i++) { for (int j = bagWeight; j >= weight[i]; j--) { dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]); } } 倒着的原因,这里举个例子 重量 价值 物品0 1 15 物品1 3 20 物品2 4 30 如果是正序遍历 dp[1 ] = dp[1 - weight[0 ]] + value[0 ] = 15 dp[2 ] = dp[2 - weight[0 ]] + value[0 ] = 30 我们可以看到dp[2 ]这样是加了两次物品0 的重量 但是如果是倒序遍历 dp[2 ] = dp[2 - weight[0 ]] + value[0 ] = 15 (dp数组已经都初始化为0 ) dp[1 ] = dp[1 - weight[0 ]] + value[0 ] = 15 最后再次说明dp[j]的意思是容量为j的背包,所背的物品价值可以最大为dp[j]。 2. 完全背包表示物品可以添加多次,先遍历物品(顺序),再遍历容量(顺序,可以添加多次) for (int i = 0 ; i < weight.size(); i++) { for (int j = weight[i]; j <= bagWeight ; j++) { dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]); } } 另外说一些额外的: 01 背包中二维dp数组的两个for 遍历的先后循序是可以颠倒了,一维dp数组的两个for 循环先后循序一定是先遍历物品,再遍历背包容量。完全背包中,对于一维dp数组来说,其实两个for 循环嵌套顺序同样无所谓!但是代码还是有点不一样,这里就看个参考,不要记了 for (int j = 0 ; j <= bagWeight; j++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < weight.size(); i++) { if (j - weight[i] >= 0 ) dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]); } cout << endl; } 3. 组合数和排列数问题,组合不强调元素之间的顺序(也就是[1 ,5 ]和[5 ,1 ]是一回事),排列强调元素之间的顺序,初始化dp[0 ]为1 ,至于为什么,没有原因。494 是组合问题,初始化dp[0 ]为1 组合代码,和完全背包一样,都是先遍历物品,再遍历容量 for (int i = 0 ; i < coins.size(); i++) { for (int j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++) { dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]]; } } 排列代码 ,这个不一样哦,先遍历容量,再遍历,而且背包遍历容量,是从0 开始的,注意背包 如果把遍历nums(物品)放在外循环,遍历target的作为内循环的话,举一个例子:计算dp[4 ]的时候,结果集只有 {1 ,3 } 这样的集合,不会有{3 ,1 }这样的集合,因为nums遍历放在外层,3 只能出现在1 后面! for (int j = 0 ; j <= amount; j++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < coins.size(); i++) { if (j - coins[i] >= 0 ) dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]]; } }
377 组合总和Ⅳ medium 这个其实是排列+完全背包问题
1 2 3 4 5 1. dp[i]: 凑成目标正整数为i的排列个数为dp[i]2. 求排列 dp[i] += dp[i - nums[j]];3. dp[0 ] = 1 ,组合排列都是这样初始化,其他位置为0 4. 外层for 遍历背包,内层for 循环遍历物品,且注意背包容量要大于物品,不然会越界5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int combinationSum4 (int [] nums, int target) { int [] dp =new int [target + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int j = 0 ; j <= target; j++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (j - nums[i] >= 0 ) dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]]; } } return dp[target]; } }
518 零钱兑换II medium 完全背包+组合,注意这里是求凑成总金额的硬币组合数。
1 2 3 4 5 1. dp[j]:凑成总金额j的货币组合数为dp[j]2. 组合数,dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]]3. dp[0 ] = 1 ,组合排列都是这样初始化,其他位置为0 4. 顺序遍历物品(金币),顺序遍历容量(钱总额)5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int change (int amount, int [] coins) { int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < coins.length; i++) { for (int j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++) { dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]]; } } return dp[amount]; } }
322 零钱兑换 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 和上题的区别 本题求的是硬币的最小个数,最小的话,有顺序和没有顺序都可以,也就是排列组合都没有关系,但是符合完全背包(钱币可以无限用) 1. dp[j]:凑足总额为j所需钱币的最少个数为dp[j]2. 递推公式:dp[j] = min(dp[j - coins[i]] + 1 , dp[j]);,其实这里我还没理解为啥加1 3. 首先凑足总金额为0 所需钱币的个数一定是0 ,那么dp[0 ] = 0 ;其次其他下标需要为最大值4. 完全背包,先遍历顺序物品,然后顺序遍历容量5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) { int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < coins.length; i++) { for (int j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++) { if (dp[j - coins[i]] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j],dp[j - coins[i]] + 1 );} } } return dp[amount] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : dp[amount]; } }
完全背包也可以先写容量,再写物品,但是要多加一个判断。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) { int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= amount; j++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < coins.length; i++) { if (j - coins[i] >= 0 && dp[j - coins[i]] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - coins[i]] + 1 ); } } return dp[amount] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : dp[amount]; } }
279 完全平方数 medium 和前面一题差不多,这里把完全平方数看做物品。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int numSquares (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { for (int i = 1 ; i * i <= j; i++) { dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - i * i] + 1 ); } } return dp[n]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int numSquares (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i * i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (j - i * i >= 0 ) dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - i * i] + 1 ); } } return dp[n]; } }
139 单词拆分 medium 这道题类似于完全平方数分割。单词就是物品,字符串s就是背包,完全背包问题,求能否组成背包,因为分割子串的特殊性,遍历背包放在外循环,将遍历物品放在内循环更方便一些。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public boolean wordBreak (String s, List<String> wordDict) { boolean [] dp = new boolean [s.length() + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = true ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= s.length(); j++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < j; i++) { if (wordDict.contains(s.substring(i, j)) && dp[i] == true ) { dp[j] = true ; } } } return dp[s.length()]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public boolean wordBreak (String s, List<String> wordDict) { int n = s.length(); boolean [] dp = new boolean [n + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = true ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (wordDict.contains(s.substring(j,i)) && dp[j] == true ) { dp[i] = true ; } } } return dp[n]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 卡哥将得很详细,复制一下记录 单词就是物品,字符串s就是背包,单词能否组成字符串s,就是问物品能不能把背包装满。substring(start,end)是左开右闭。 拆分时可以重复使用字典中的单词,说明就是一个完全背包! 动规五部曲分析如下: 1.确定dp数组以及下标的含义 dp[i] : 字符串长度为i的话,dp[i]为true,表示可以拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。 2.确定递推公式 如果确定dp[j] 是true,且 [j, i] 这个区间的子串出现在字典里,那么dp[i]一定是true。(j < i)。 所以递推公式是 if([j, i] 这个区间的子串出现在字典里 && dp[j]是true) 那么 dp[i] = true。 3.dp数组如何初始化 从递归公式中可以看出,dp[i] 的状态依靠 dp[j]是否为true,那么dp[0]就是递归的根基,dp[0]一定要为true,否则递归下去后面都都是false了。 那么dp[0]有没有意义呢? dp[0]表示如果字符串为空的话,说明出现在字典里。 但题目中说了“给定一个非空字符串 s” 所以测试数据中不会出现i为0的情况,那么dp[0]初始为true完全就是为了推导公式。 下标非0的dp[i]初始化为false,只要没有被覆盖说明都是不可拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。 4.确定遍历顺序 题目中说是拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词,所以这是完全背包。 还要讨论两层for循环的前后循序。 如果求组合数就是外层for循环遍历物品,内层for遍历背包。 如果求排列数就是外层for遍历背包,内层for循环遍历物品。 本题最终要求的是是否都出现过,所以对出现单词集合里的元素是组合还是排列,并不在意! 那么本题使用求排列的方式,还是求组合的方式都可以。 即:外层for循环遍历物品,内层for遍历背包 或者 外层for遍历背包,内层for循环遍历物品 都是可以的。 但本题还有特殊性,因为是要求子串,最好是遍历背包放在外循环,将遍历物品放在内循环。 如果要是外层for循环遍历物品,内层for遍历背包,就需要把所有的子串都预先放在一个容器里。(如果不理解的话,可以自己尝试这么写一写就理解了) 所以最终我选择的遍历顺序为:遍历背包放在外循环,将遍历物品放在内循环。内循环从前到后。 5.举例推导dp[i] 以输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"]为例,dp状态如图: (在下方) dp[s.size()]就是最终结果。 ps: 五部曲中第一部是最困难的. 一般都是遵循"题目问什么, 就把`dp[]设置成什么 作者:carlsun-2 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-break/solution/dai-ma-sui-xiang-lu-139-dan-ci-chai-fen-50a1a/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
198 打家劫舍 medium 居然一开始和背包问题联系起来了,其实不是一回事啊!!
1 2 3 4 5 1. dp[i]表示考虑下标i(包括i)以内的房屋,最多可以偷窃的金额为dp[i]。2. 确定递推公式,决定dp[i]的因素就是第i房间偷还是不偷。偷第i间房子,那么dp[i] = dp[i-2 ]+nums[i],因为不能导致报警,如果不偷第i间房子,dp[i]=dp[i-1 ],这里不是表明要偷i-1 房哦,要牢记dp[i]的概念,i以内的房间,所以dp[i] = max(dp[i - 2 ] + nums[i], dp[i - 1 ]);3. 从递推公式可以看出,要初始化dp[0 ]和dp[1 ],这里注意dp[1 ]是要求最大值哦,不是单纯赋值nums[1 ]4. 确定遍历顺序,从前到后5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int rob (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 1 ) return nums[0 ]; int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; dp[0 ] = nums[0 ]; dp[1 ] = Math.max(nums[1 ], nums[0 ]); for (int i = 2 ; i < nums.length; i++) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ] + nums[i]); } return dp[nums.length - 1 ]; } }
213 打家劫舍2 medium 和上一题的区别是,上一题的房子都是在一条街道,而本题的房子,是围成一圈,第一间和最后一间挨着。
1 2 3 没做过的话,确实不好想 其实就是分成两部分,一部分不包含最后一个元素,一部分不包含第一个元素,然后比较他们的最大值 其余的和上一题一样。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int rob (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 1 ) return nums[0 ]; int end = nums.length - 1 ; return Math.max(robRange(nums, 0 , end - 1 ), robRange(nums, 1 , end)); } public int robRange (int [] nums, int start, int end) { if (start == end) return nums[start]; int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; dp[start] = nums[start]; dp[start + 1 ] = Math.max(nums[start], nums[start + 1 ]); for (int i = start + 2 ; i <= end; i++) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 2 ] + nums[i], dp[i - 1 ]); } return dp[end]; } }
337 打家劫设3 medium 这题用上了二叉树了,树形dp是第一次遇到!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 首先要用后序遍历,因为通过递归函数的返回值来做下一步计算。 1. 用长度为2 的大小数组来保存,dp[0 ]表示不偷当前节点所获得的最大金钱,dp[1 ]表示偷当前节点所获得的最大金钱。2. 到了这里不是递推公式了,而是初始化,if (cur == NULL) return vector<int >{0 , 0 };,相当于初始化3. 确定遍历顺序,通过递归左节点,得到左节点偷与不偷的金钱。通过递归右节点,得到右节点偷与不偷的金钱。4. 确定单层递归的逻辑,如果是偷当前节点,那么左右孩子就不能偷,如果不偷当前节点,那么左右孩子就可以偷,至于到底偷不偷一定是选一个最大的,因为只要不挨着就行,所以不一定要偷的5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int rob (TreeNode root) { int [] res = dfs(root); return Math.max(res[0 ], res[1 ]); } public int [] dfs(TreeNode root) { int [] res = new int [2 ]; if (root == null ) { return res; } int [] left = dfs(root.left); int [] right = dfs(root.right); res[0 ] = Math.max(left[0 ],left[1 ]) + Math.max(right[0 ], right[1 ]); res[1 ] = root.val + left[0 ] + right[0 ]; return res; } }
121 买卖股票的最佳时机 easy 只买卖一次!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 需要强化一个概念,持有不代表今天买,不持有不代表今天卖,可能是维持前一天的状态!!!!! 1. dp[i][0 ]代表第i天持有股票的最多现金,dp[i][1 ]代表第i天不持有股票股票所得最多现金,注意注意这里说的是“持有”,“持有”不代表就是当天“买入”!也有可能是昨天就买入了,今天保持持有的状态,也就是第二维的0 和1 代表持有和不持有,第一维只代表天2. 确定递推公式第i天持有股票即dp[i][0 ] 持有表示可能之前就买了,那么就保持上一天的状态呗,也就是等于dp[i-1 ][0 ] 也可能表示今天买了,那么就是-price[i] 所以dp[i][0 ] = max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], -prices[i]); 第i天不持有股票即dp[i][1 ] 不持有表示之前早就卖了,那就维持前一天的状态,dp[i-1 ][1 ] 也可能今天卖了,那就是dp[i-1 ][0 ]+prices[i],也就是前一天还是持有的状态,然后今天卖了,其实前一天的价格是负数,因为你持有了,加上今天的价格,就是利润 dp[i][1 ] = max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], prices[i] + dp[i - 1 ][0 ]); 3. 从递推公式可以看到,需要依赖dp[0 ][0 ]和dp[0 ][1 ]4. 遍历顺序,从前往后5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[0 ][1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], -prices[i]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + prices[i]); } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][1 ]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int result = 0 ; int low = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < prices.length; i++) { low = Math.min(low, prices[i]); result = Math.max(result, prices[i] - low); } return result; } }
122 买卖股票的最佳时机2 medium 和上一题的区别是,这个题可以每天进行买卖,也就是可以多次买卖。最多只能持有一股股票,也可以先购买,然后在同一天出售。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[0 ][1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ] - prices[i], dp[i - 1 ][0 ]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + prices[i], dp[i - 1 ][1 ]); } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][1 ]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int result = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) { result += Math.max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1 ], 0 ); } return result; } }
123 买卖股票最佳时机3 hard 限制了最多可以完成两笔交易!也就是买卖一次,可以买卖两次,也可以不买卖。这题难不少!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 这题和之前的状态不一样,之前的第二个维度,0 代表持有,1 代表不持有 1. 确定下标含义而本题只能最多买卖2 次,那么可以设置5 个状态,也是第二个维度来表示 0 代表不操作1 代表第一次持有2 代表第一次不持有3 代表第二次持有4 代表第二次不持有2. 递推公式以dp[i][1 ]为例 操作一:第i天买入股票了,那么dp[i][1 ] = dp[i-1 ][0 ] - prices[i],注意这里是前一天的0 操作二:第i天没有操作,而是沿用前一天买入的状态,即:dp[i][1 ] = dp[i - 1 ][1 ] 取他们最大 其他一样递推 3. 只需要初始化买入状态,即便第二次买入可能要考虑第一次买入 总之 dp[0 ][1 ],dp[0 ][3 ] = -price[0 ] 4. 遍历顺序就是从左到右5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][5 ]; dp[0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[0 ][3 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = dp[i - 1 ][0 ]; dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] - prices[i]); dp[i][2 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][2 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i]); dp[i][3 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][3 ], dp[i - 1 ][2 ] - prices[i]); dp[i][4 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][4 ], dp[i - 1 ][3 ] + prices[i]); } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][4 ]; } }
188 买卖股票最佳时机4 hard 最多可以完成k笔交易,和上一题没啥区别,就是k次而已。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int k, int [] prices) { if (prices.length == 0 ) return 0 ; int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][2 * k + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < 2 * k + 1 ; i = i + 2 ) { dp[0 ][i] = -prices[0 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < 2 * k + 1 ; j++) { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + (int )Math.pow(-1 ,j) * prices[i]); } } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][2 * k]; } }
309 最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期 medium 比122多了一个冷冻期,支持多次交易,但是也不会太容易
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 关键在于有一个冷冻期,那么本题设置4 种状态 1. 持有(可能是保持前一天的持有状态,可能是今天买入)2. 不持有(这个不一样,反正今天不能卖!),两天前就卖出了股票,度过了冷冻期,一直没操作,今天保持卖出股票状态3. 卖出(也就是把之前股票问题的不持有状态拆成两个状态,一个不持有,一个卖出,等下讲解)4. 冷冻期,只有一天2. 递推公式1. 持有状态下1.1 保持前一天的持有状态1.2 昨天是冷冻期,今天买入1.3 之前早就卖出股票并且度过了冷冻期,今天可以买入2. 不持有状态下2.1 保持前一天的不持有的状态2.2 冷冻期(这个不容易想到,因为冷冻期代表你已经卖了股票了,你可以保持这个状态表示不持有)3. 卖出3.1 前一天持有了才能卖出4. 冷冻期4.1 前一天卖出就会触发冷冻期3. 初始化只需要设置持有状态下就可以,其他均为0 ,也就是dp[0 ][0 ] = -price[0 ] 4. 遍历顺序就是从前到后5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][4 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][3 ] - prices[i], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] - prices[i])); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][3 ]); dp[i][2 ] = dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + prices[i]; dp[i][3 ] = dp[i - 1 ][2 ]; } return Math.max(dp[prices.length - 1 ][1 ], Math.max(dp[prices.length - 1 ][2 ], dp[prices.length - 1 ][3 ])); } }
714 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费 medium 也是无限次交易,只是多了一个手续费,参考122就行啦,多一个手续费。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) { int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] - prices[i]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + prices[i] - fee); } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][1 ]; } }
300 最长递增子序列 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. dp[i]表示i之前包括i的以nums[i]结尾最长上升子序列的长度2. 位置i的最长升序子序列等于j从0 到i-1 各个位置的最长升序子序列 + 1 的最大值。所以要用双重循环if (nums[i] > nums[j]) dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1 );这里注意j是大小是从0 到i(不包含i),我们需要取dp[j] + 1 的最大值 3. 初始化,这里和之前的dp问题有些不一样,每一个i的长度至少都是可以为1 ,所以全部先设置为1 4. 顺序遍历5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) { int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; Arrays.fill(dp, 1 ); int result = dp[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (nums[i] > nums[j]) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1 ); result = Math.max(result, dp[i]); } } } return result; } }
674 最长连续递增序列 easy 和上一题的区别是,本题要求连续,上一题的话可以隔开元素。
1 2 3 4 5 1. dp[i]:以下标i为结尾的数组的连续递增的子序列长度为dp[i]。2. if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1 ]) dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[i - 1 ] + 1 );因为要连续,所以需要比较上一个,而不是像上一题一样从0 到j去找3. 初始化,也是全部初试化为1 ,因为每个i4. 确定遍历顺序,就是从前到后5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int findLengthOfLCIS (int [] nums) { int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; Arrays.fill(dp, 1 ); int result = dp[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1 ]) { dp[i] = dp[i - 1 ] + 1 ; result = Math.max(dp[i], result); } } return result; } }
718 最长重复子数组 medium 也是连续子序列问题,但是这里是两个数组的对比
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 本题的含义不一样!!!注意看!!!本题的含义不一样!!!注意看!!!本题的含义不一样!!!注意看!!! 1. dp[i][j] :以下标i-1 为结尾的A(指第一个数组),和以下标j-1 为结尾的B(指第二个数组),最长重复子数组长度为dp[i][j]。 (特别注意: “以下标i-1 为结尾的A(指第一个数组)” 标明一定是 以A[i-1 ]为结尾的字符串 )以前都是下标i,但是本题是下标i-1 ,我是这么觉得的,因为比较的时候,从0 开始的话,往前面推是-1 ,因为这里涉及两个数组,不方便,而且我们回过头去看之前的dp问题,也是有i-1 的元素在的,而本题是同时比较两个数组 2. 当A[i - 1 ] 和B[j - 1 ]相等的时候,dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ;3. 初始化,0 即可,dp[i][0 ] 和dp[0 ][j]初始化为0 ,java的话本来就默认0 4. 循环遍历,从前到后,第一组先,然后再第二组5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int findLength (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int [][] dp = new int [nums1.length + 1 ][nums2.length + 1 ]; int result = dp[0 ][0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= nums1.length; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= nums2.length; j++) { if (nums1[i - 1 ] == nums2[j - 1 ]) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; result = Math.max(result, dp[i][j]); } } } return result; } }
1143 最长公共子序列 medium 连续的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. dp[i][j]:长度为[0 , i - 1 ]的字符串text1与长度为[0 , j - 1 ]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列长度为 dp[i][j]2. 确定递推公式text1[i-1 ] 与 text2[j-1 ]相同情况下 如果text1[i - 1 ] 与 text2[j - 1 ]相同,那么找到了一个公共元素,所以dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; text1[i-1 ] 与 text2[j-1 ]不相同情况下(重点理解这里,不是太好理解) 如果text1[i - 1 ] 与 text2[j - 1 ]不相同,那就看看text1[0 , i - 2 ]与text2[0 , j - 1 ]的最长公共子序列 和 text1[0 , i - 1 ]与text2[0 , j - 2 ]的最长公共子序列,取最大的。 dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); 3. 统一初始化为0 4. 从前到后遍历5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int longestCommonSubsequence (String text1, String text2) { int [][] dp = new int [text1.length() + 1 ][text2.length() + 1 ]; int result = dp[0 ][0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= text1.length(); i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= text2.length(); j++) { if (text1.charAt(i - 1 ) == text2.charAt(j - 1 )) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); } result =Math.max(dp[i][j], result); } } return result; } }
最长序列问题总结 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 总体分为几种情况的组合,单数组和双数组,连续或者子序 1. 定义如果是单数组,就直接定义一维的,直接按照0 ~i-1 的位置来即可,定义长度就是数组长度,但是如果是双数组,用i-1 代表dp[i][j]更好,也就是长度需要加1 ,同时双数组就定义两个维度。 2. 状态转移方程需要根据题目意思来3. 确定初始化,对于单数组,都是比较自己,因为单独一个元素就是一个长度序列,所以应该全部初始化为1 ,但是对于双数组,则需要比较,所以在比较的情况下再确定长度,也就是初始化为0 即可。4. 从前到后遍历5. 推导数组另外说几点,对于求连续的,不需要max来比较,直接前一个位置+1 就行 但是对于子序,需要考虑前面的所有情况 另外说下关于返回值的问题,以前我们的dp问题,都能用数组的最后一个位置的值返回,但是本系列只有1143 可以这么做 我的理解是这样的,最重要是看dp的定义 300 :i之前包括i的以nums[i]结尾最长上升子序列的长度,以他为结尾,意味着他要包含进去,但是包含他的,不一定是最长的长度,所以要不断找最大值674 :以下标i为结尾的数组的连续递增的子序列长度为dp[i],也是和上面一样的意思去判断718 :以下标i-1 为结尾的A,和以下标j-1 为结尾的B,最长重复子数组长度为dp[i][j],也是和上面一样所以上面三个题,都需要来比较来找到最大值 1143 :长度为[0 ,i-1 ]的字符串text1与长度为[0 ,j-1 ]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列长度为dp[i][j]当然了,其实我是在知道定义后写的,至于1143 为什么不是以结尾来定义,还没弄明白,如果觉得不好记,统一用max比较也可以
1035 不相交的线 medium 需要拆解为,两个字符串的最长公共子序列的长度!也就是和上一题一毛一样!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int maxUncrossedLines (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int [][] dp = new int [nums1.length + 1 ][nums2.length + 1 ]; int result = dp[0 ][0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= nums1.length; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= nums2.length; j++) { if (nums1[i - 1 ] == nums2[j - 1 ]) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); } result = Math.max(result, dp[i][j]); } } return result; } }
53 最大子数组和 medium 这个题是连续部分,不是子序,这个题一开始还有点懵,需要理解一下。
1 2 3 4 5 1. dp[i]:包括下标i之前的最大连续子序列和为dp[i]。2. 两个方向来推:2.1 dp[i-1 ]+nums[i],即:nums[i] 2.2 加入当前连续子序列和nums[i],即:从头开始计算当前连续子序列和3. 初始化为0 4. 从前到后遍历5. 推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; int sum = nums[0 ]; dp[0 ] = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ] + nums[i], nums[i]); sum = Math.max(sum, dp[i]); } return sum; } }
392 判断子序列 medium 和1143,1035差不多,但是本题注意是s是否t的子序列,也就是最长子序列长度必须要为s的长度才可以。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public boolean isSubsequence (String s, String t) { int [][] dp = new int [s.length() + 1 ][t.length() + 1 ]; int max = dp[0 ][0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= s.length(); i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= t.length(); j++) { if (s.charAt(i - 1 ) == t.charAt(j - 1 )) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); } max = Math.max(max, dp[i][j]); } } return max == s.length(); } }
115 不同的子序列 hard 这个题真的超级难懂
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 1143 是找最长公共子序列而本题是字符串s有很多个子序列(不一定连续),这些子序列字符串中,字符串t出现了多少次? 也就是计算在 s 的子序列中 t 出现的个数。 1. dp[i][j]:以i-1 为结尾的s子序列中出现以j-1 为结尾的t的个数为dp[i][j]。2. 递推顺序(https:第一种情况s[i-1 ]与t[j-1 ]不相等 第一种解释:我们发现当sub_s新增了一个长度后,如果新增的字符(当前sub_s尾字符),与sub_t尾字符不匹配,那么似乎在sub_s上多了个"没用" 的字符,sub_s所有子序列字符串中sub_t出现的次数没有任何变化。因此在这种状态下:dp[i][j]=dp[i-1 ][j]; 第二种解释:s[i−1 ]不能和t[j−1 ] 匹配,因此只考虑t[j-1 ]作为s[i-2 ]的子序列,子序列个数为dp[i-1 ][j]dp[i−1 ][j] 第二种情况:s[i-1 ]与t[j-1 ]相等 第一种解释:如果新加入sub_s的这个字符与sub_t尾字符相匹配时,在没有增加这个字符的情况下,sub_t出现的次数是dp[i-1 ][j], 现在增加了并且和sub_t尾字符相匹配,因此还要在这个基础上加上两者此前的状态下的次数,即dp[i-1 ][j-1 ],因为相比此前,两者都多了同一个字符,与两者没有加上这个相同字符时情况是一样的。因此这种情况下总和是dp[i-1 ][j]+dp[i-1 ][j-1 ] 3. 初始化如果 j=0 即 t[j]为空字符串,由于空字符串是任何字符串的子序列,因此对任意dp[i][0 ]=1 ; 如果 i=0 即 s[i]为空字符串,t[j]为非空字符串,由于非空字符串不是空字符串的子序列,因此 dp[0 ][j]=0 。 4. 从前到后遍历,从1 开始5. 推导数组这个题为什么没有加1 操作,因为这个题是求出现的次数,如果你下一个字符是相等的,那么他们的出现次数是和之前一样的(我自己理解,不一定对)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int numDistinct (String s, String t) { int [][] dp = new int [s.length() + 1 ][t.length() + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= s.length(); i++) { dp[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= s.length(); i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= t.length(); j++) { if (s.charAt(i - 1 ) == t.charAt(j - 1 )) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + dp[i - 1 ][j]; } else { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j]; } } } return dp[s.length()][t.length()]; } }
583 两个字符串的删除操作 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 和上一题的区别是,本题可以任意删除其中一个字符串 1. dp[i][j]:以i-1 为结尾的字符串word1,和以j-1 位结尾的字符串word2,想要达到相等,所需要删除元素的最少次数。2. 确定递推公式情况1 :当word1[i-1 ]与word2[j-1 ]相同的时候 可以理解为,相同,所以不用删,那就复用上一次的结果 dp[i][j]=dp[i-1 ][j-1 ]; 情况2 :当word1[i-1 ]与word2[j-1 ]不相同的时候,有三种情况 删word1[i - 1 ],最少操作次数为dp[i - 1 ][j] + 1 删word2[j - 1 ],最少操作次数为dp[i][j - 1 ] + 1 同时删word1[i - 1 ]和word2[j - 1 ],操作的最少次数为dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 2 ,因为每操作一次,就要加一,这里同时各操作了一次 dp[i][j] = min({dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 2 , dp[i - 1 ][j] + 1 , dp[i][j - 1 ] + 1 }); 3. 初始化dp[i][0 ]:word2为空字符串,以i-1 为结尾的字符串word1要删除多少个元素,才能和word2相同呢,很明显dp[i][0 ] = i。 dp[0 ][i]:word1为空字符串,以i-1 为结尾的字符串word2要删除多少个元素,才能和word1相同呢,很明显dp[0 ][i] = i。 4. 从前到后遍历5. 推导数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int [][] dp = new int [word1.length() + 1 ][word2.length() + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= word1.length(); i++) { dp[i][0 ] = i; } for (int i = 0 ; i <= word2.length(); i++) { dp[0 ][i] = i; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= word1.length(); i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= word2.length(); j++) { if (word1.charAt(i - 1 ) == word2.charAt(j - 1 )) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 2 , Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j] + 1 , dp[i][j - 1 ] + 1 )); } } } return dp[word1.length()][word2.length()]; } }
72 编辑距离 hard 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 上一题是任何一个字符串都能删除,本题的话,可以进行删,改,增,或者不操作 我看题解的时候,官方表达的意思是两个字符都能操作,但是实际题目意思,我感觉是只能操作1 ,然后让其变成2 1. dp[i][j] 表示以下标i-1 为结尾的字符串word1,和以下标j-1 为结尾的字符串word2,最近编辑距离为dp[i][j]。2. 确定递推公式,分为两个情况情况1 :word1[i-1 ] == word2[j-1 ] dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j] + 1 情况2 :word1[i-1 ] != word2[j-1 ] 操作1 :word1删除一个元素 dp[i][j] = dp[i-1 ][j] + 1 操作2 :word2删除一个元素(相当于word1的插入操作) dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-1 ]+1 操作3 :word1替换操作 dp[i][j] = dp[i-1 ][j-1 ]+1 然后取他们的最小值,即 dp[i][j] = min({dp[i-1 ][j-1 ], dp[i-1 ][j], dp[i][j-1 ]}) + 1 ; 3. 初始化dp和上一题一样 dp[i][0 ]就应该是i,对word1里的元素全部做删除操作,即:dp[i][0 ] = i; dp[0 ][i]就应该是i,对word2里的元素全部做删除操作,即:dp[0 ][i] = i; 4. 遍历顺序从前到后 5. 推导公式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int [][] dp = new int [word1.length() + 1 ][word2.length() + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= word1.length(); i++) { dp[i][0 ] = i; } for (int i = 0 ; i <= word2.length(); i++) { dp[0 ][i] = i; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= word1.length(); i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= word2.length(); j++) { if (word1.charAt(i - 1 ) == word2.charAt(j - 1 )) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j], Math.min(dp[i][j - 1 ], dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ])) + 1 ; } } } return dp[word1.length()][word2.length()]; } }
647 回文子串 medium 本题遍历顺序不一样,注意看!!!本题是连续的字符串,而且是算个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 注意本题的dp数组是布尔类型 1. 布尔类型的dp[i][j]:表示区间范围[i,j] (注意是左闭右闭)的子串是否是回文子串,如果是dp[i][j]为true ,否则为false 2. 确定递推公式分为两种情况 情况1 :s[i]与s[j]相等 2.1 下标i与j相同,同一个字符例如a,是回文子串2.2 下标i与j相差为1 ,例如aa,也是回文子串2. 3i与j相差大于1 的时候,例如cabac,此时s[i]与s[j]已经相同了,我们看i到j区间是不是回文子串就看aba是不是回文就可以了,那么aba的区间就是i+1 与j-1 区间,这个区间是不是回文就看dp[i+1 ][j-1 ]是否为true 情况1 :s[i]与s[j]不相等 直接为false 3. 初始化dp一开始当然都是false 啦,都没有匹配上 4. 遍历顺序,不是按顺序,不是按顺序,不是按顺序!!!!我们可以看到2.3 这情况,根据dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ]是否为true ,在对dp[i][j]进行赋值true 的,然后dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ]在dp[i][j]左下角,也就是遍历顺序是下到上,左到右,可以理解为从斜左下角推导到右上角。 5. 推导数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int countSubstrings (String s) { boolean [][] dp = new boolean [s.length()][s.length()]; int result = 0 ; for (int i = s.length() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { for (int j = i; j < s.length(); j++) { if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j) && (j - i <= 1 || dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ])) { result++; dp[i][j] = true ; } } } return result; } }
516 最长回文子序列 medium 注意本题是求子序的最长长度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. dp[i][j]:字符串s在[i, j]范围内最长的回文子序列的长度为dp[i][j]。2. 确定递推公式s[i]与s[j]相同,那么dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ] + 2 ; s[i]与s[j]不相同(可以看卡哥的图),说明s[i]和s[j]的同时加入 并不能增加[i,j]区间回文子串的长度,那么分别加入s[i]、s[j]看看哪一个可以组成最长的回文子序列。 加入s[j]的回文子序列长度为dp[i + 1 ][j]。加入s[i]的回文子序列长度为dp[i][j - 1 ]。那么dp[i][j]一定是取最大的,即:dp[i][j] = max(dp[i + 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); 3. 初始化dp首先要理解定义,所以i和j相等,那长度肯定是1 的,因为他们就是指示一个字符 dp[i][i] = 1 ; 4. 遍历顺序,和上面一题一样,也是从左下角到右上角,也就是从下到上,从左到右5. 推导数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int longestPalindromeSubseq (String s) { int [][] dp = new int [s.length()][s.length()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { dp[i][i] = 1 ; } int result = dp[0 ][0 ]; for (int i = s.length() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < s.length(); j++) { if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) { dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ] + 2 ; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i + 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); } result = Math.max(result, dp[i][j]); } } return result; } }
单调栈 1 2 如果找更大的元素,需要构建单调递减栈 如果找更小的元素,需要构建单调递增栈
739 每日温度 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 分为三种情况 栈里面是存储数组的下标,而不是值 1. 当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况把T[i]的下标入栈 2. 当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况把T[i]的下标入栈 3. 当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况计算距离放入result中,将栈顶元素弹出。 等到不符合条件了(也就是栈里面的元素下标已经大于当前T[i]),那么这时候就把T[i]入栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) { int [] result = new int [temperatures.length]; Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList <>(); stack.push(0 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < temperatures.length; i++) { if (temperatures[i] <= temperatures[stack.peek()]) { stack.push(i); } else { while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) { result[stack.peek()] = i - stack.peek(); stack.pop(); } stack.push(i); } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) { int [] result = new int [temperatures.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < temperatures.length; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < temperatures.length; j++) { if (temperatures[j] > temperatures[i]) { result[i] = j - i; break ; } } } return result; } }
496 下一个更大元素1 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 首先我们用一个map把数组1 的<数值,下标>存进去 然后操作数组2 ,数组2 的操作逻辑也是 1. 当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况把T[i]的下标入栈 2. 当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况把T[i]的下标入栈 3. 当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况这时候可以找到右边第一个比自己大的元素 判断栈顶元素是否在nums1里出现过,(注意栈里的元素是nums2的元素),如果出现过,开始记录结果。 然后出栈 当不满足大于栈顶元素,就把当前元素入栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int [] nextGreaterElement(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList <>(); int [] result = new int [nums1.length]; Arrays.fill(result, -1 ); HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums1.length; i++) { map.put(nums1[i], i); } stack.push(0 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < nums2.length; i++) { if (nums2[i] <= nums2[stack.peek()]) { stack.push(i); } else { while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums2[i] > nums2[stack.peek()]) { if (map.containsKey(nums2[stack.peek()])) { Integer index = map.get(nums2[stack.peek()]); result[index] = nums2[i]; } stack.pop(); } stack.push(i); } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int [] nextGreaterElement(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int [] result = new int [nums1.length]; Arrays.fill(result, -1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums1.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < nums2.length; j++) { if (nums1[i] == nums2[j]) { for (int x = j + 1 ; x < nums2.length;x++) { if (nums2[x] > nums1[i]) { result[i] = nums2[x]; break ; } } } } } return result; } }
503 下一个更大元素2 medium 本题关键在于 如何处理循环数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int [] nextGreaterElements(int [] nums) { int [] result = new int [nums.length]; Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList <>(); Arrays.fill(result, -1 ); stack.push(0 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < 2 * nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i % nums.length] <= nums[stack.peek()]) { stack.push(i % nums.length); } else { while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i % nums.length] > nums[stack.peek()]) { result[stack.peek()] = nums[i % nums.length]; stack.pop(); } stack.push(i % nums.length); } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public int [] nextGreaterElements(int [] nums) { int [] result = new int [nums.length]; Arrays.fill(result, -1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < nums.length; j++) { if (nums[j] > nums[i]) { result[i] = nums[j]; break ; } for (int x = 0 ; x < i; x++) { if (nums[x] > nums[i]) { result[i] = nums[x]; break ; } } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; i++) { if (nums[i] > nums[nums.length - 1 ]) { result[nums.length - 1 ] = nums[i]; break ; } } return result; } }
42 接雨水 hard 高频率题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 单调栈做法 单调递减栈 注意用单调栈的做法计算面积和双指针略有不同,双指针直接就是先找到最左边最高,最右边最高,然后用他们比较小的那个减去当前高度就是体积(因为当前高度的宽是1 ,不用长*宽了) 栈:先进去的是栈底, 当前元素小于等于栈顶元素,那么就入栈 如果大于了栈顶元素,这时候就可以找出三个元素 right下标就是当前i小标 mid就是栈顶下标,用了之后要取出来,为什么要取出来,因为用过了。 left就是下一个栈顶下标,这里不用取出来,因为下一次还要用 h是高度,右边下标的对应的值(是指,不是下标数)和左边小标对应的值找到较小那个-当前i的高度 w是宽度,用右边下标-左边下标-1 (-1 是因为算两个栈中间的区域长度,0 1 2 3 ,比如0 和3 ,中间的长度就是2 ,3 -0 -1 =2 ) 然后h*w即可 这里为什么和双指针那个算法不一样,其实我认为是因为单调栈这样出栈顺序,不是他的左边最高和右边最高,这样出栈是单纯能算出体积
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int sum = 0 ; Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList <>(); stack.push(0 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < height.length; i++) { if (height[i] <= height[stack.peek()]) { stack.push(i); } else { while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()]) { int mid = stack.poll(); if (!stack.isEmpty()) { int right = i; int left = stack.peek(); int h = Math.min(height[right], height[left]) - height[mid]; int w = right - left - 1 ; sum += h * w; } } stack.push(i); } } return sum; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 本题用双指针解法(但是力扣官方是写暴力解法),这个比较容易懂 首先清楚,第一根柱子和最后一根柱子,是不接雨水的,所以遍历的时候跳过这两个 然后要清楚,雨水是如何计算的 对于每一列,我们都要找出他左边最高的一个柱子(包含第一格),同时找出右边最高的柱子(包含最后一格) 然后选出他们两个高度之间小的那个,减去本列的高度,就是雨水的体积,因为长度都是1 ,所以1 *高度就是雨水体积 那么我们只要找到每一格的高度,就可以完成任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < height.length - 1 ; i++) { int lheight = height[i]; int rheight = height[i]; for (int l = 0 ; l < i; l++) { if (height[l] > lheight) lheight = height[l]; } for (int r = i + 1 ; r < height.length; r++) { if (height[r] > rheight) rheight = height[r]; } int high = Math.min(lheight, rheight) - height[i]; if (high > 0 ) sum += high; } return sum; } }
84 柱状图中最大的矩形 hard 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 找每个柱子左右侧的第一个高度值小于该柱子的柱子,注意和上一题的区别 单调栈:栈顶到栈底:从大到小(每插入一个新的小数值时,都要弹出先前的大数值) 栈顶,栈顶的下一个元素,即将入栈的元素:这三个元素组成了最大面积的高度和宽度 情况一:当前遍历的元素heights[i]大于栈顶元素的情况 情况二:当前遍历的元素heights[i]等于栈顶元素的情况 情况三:当前遍历的元素heights[i]小于栈顶元素的情况 这里是找到左右侧高度小于当前的,所以用单调递增栈 当前高度大于等于栈顶,入栈 当前高度小于栈顶 mid高度栈顶下标,用了需要取出来 right就是当前元素下标 left就是栈顶下标(之前取出了一个mid,这个是新栈顶) 面积就是 (right-left-1 )*mid 减去1 可以继续看下面的图理解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public int largestRectangleArea (int [] heights) { int [] newheights = new int [heights.length + 2 ]; int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < heights.length; i++) { newheights[i + 1 ] = heights[i]; } heights = newheights; Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList <>(); stack.push(0 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < heights.length; i++) { if (heights[i] >= heights[stack.peek()]) { stack.push(i); } else { while (!stack.isEmpty() && heights[i] < heights[stack.peek()]) { int mid = heights[stack.poll()]; int right = i; int left = stack.peek(); int width = right - left - 1 ; result = Math.max(result, width * mid); } stack.push(i); } } return result; } }
借用别人画的图来理解如何计算面积
比如计算6(下标是3)的最大面积
hot100 3 无重复字符的最长子串 1 2 3 4 5 用一个map来保存字符 双指针的做法 一个start 一个end 如果发现重复了(map中),需要重新找到start的位置,新start的位置需要这个字符在map的位置然后加1 ,但是start不能往回走(因为单纯加1 的话,可能会回退,因为字符可能在最开始的位置),所以要在start和 这个字符在map的数字加1 比较,确定新start的位置 长度就是end-start+1 ,在过程中记录即可,然后把字符加入到map中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { int n = s.length(), ans = 0 ; Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int end = 0 , start = 0 ; end < n; end++) { char alpha = s.charAt(end); if (map.containsKey(alpha)) { start = Math.max(map.get(alpha) + 1 , start); } ans = Math.max(ans, end - start + 1 ); map.put(s.charAt(end), end); } return ans; } }
5 最长回文子串 medium 思路挺简单的,仔细阅读下代码,用的是暴力法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public String longestPalindrome (String s) { int len = 1 ; int begin = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < s.length(); j++) { if (j - i + 1 > len && valid(s, i, j)) { len = j-i+1 ; begin = i; } } } return s.substring(begin, begin + len); } public boolean valid (String s, int start, int end) { for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++,j--) { if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
11 盛水最多的容器 medium 需要和42 84一起看
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int maxArea (int [] height) { int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < height.length; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < height.length; j++) { int high = Math.min(height[i], height[j]); int width = j - i; result = Math.max(result, high * width); } } return result; } }
128 最长连续序列 medium 注意这个题,是指内部可以组成的连续的序列,比如1,2,3,4,5,累加1这种,但是,不是指必须他们在位置上连续,他们一开始是打乱的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) { HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet <>(); for (int x : nums) { set.add(x); } int result = 0 ; int temp = 0 ; for (int i : nums) { if (!set.contains(i - 1 )) { while (set.contains(i)) { temp++; i++; } result = Math.max(result, temp); } temp = 0 ; } return result; } }
146 LRU缓存 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 LinkedHashMap是尾插 LinkedHashMap和HashMap不一样,HashMap是无序的,前者是有序的,所以不能用hashmap来做这个题 1. 查询操作存在的话,先对他进行最近操作处理,然后返回值 否则返回-1 2. 插入操作如果这个key本身存在的话,先对他进行最近操作处理,然后把value更新,并且中断操作 如果key不存在,先判断插入的时候,是否满了,先删除头部的老节点,然后再插入 最近操作处理 先存这个value,然后删除key,然后再重新put即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class LRUCache { int capacity; LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> cache = new LinkedHashMap <>(); public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .capacity = capacity; } public int get (int key) { if (cache.containsKey(key)) { makeRecently(key); return cache.get(key); } return -1 ; } public void put (int key, int value) { if (cache.containsKey(key)) { makeRecently(key); cache.put(key, value); return ; } if (cache.size() == this .capacity) { int oldKey = cache.keySet().iterator().next(); cache.remove(oldKey); } cache.put(key, value); } private void makeRecently (int key) { int value = cache.get(key); cache.remove(key); cache.put(key, value); } }
152 乘积最大子数组 medium 对比53题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 这题最大的不同点在于需要维护两个dp数组,一个最大的,一个最小的 一般我们都是维护一个最大的即可,这里说下如果不维护一个最小的 比如[-2 ,3 ,-4 ] dp[0 ] = -2 dp[1 ] = 3 dp[2 ] = 3 但是,其实正确答案是24 ,因为可能中间是负数,后面是负数,就可以变成正数,但是单纯用max的话,会忽略掉中间负数的情况
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int maxProduct (int [] nums) { int [] dpmax = new int [nums.length]; int [] dpmin = new int [nums.length]; dpmax[0 ] = nums[0 ]; dpmin[0 ] = nums[0 ]; int result = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { dpmax[i] = Math.max(Math.max(nums[i] * dpmax[i - 1 ], nums[i] * dpmin[i - 1 ]), nums[i]); dpmin[i] = Math.min(Math.min(nums[i] * dpmax[i - 1 ], nums[i] * dpmin[i - 1 ]), nums[i]); result = Math.max(result, dpmax[i]); } return result; } }
136 只出现一次的数字 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int singleNumber (int [] nums) { int single = 0 ; for (int num : nums) { single ^= num; } return single; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int singleNumber (int [] nums) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i : nums) { map.put(i, map.getOrDefault(i, 0 ) + 1 ); } for (int i : nums) { if (map.get(i) == 1 ) { return i; } } return 0 ; } }
283 移动零 easy 注意题目要在原数组上操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int left = 0 ; for (int right = 0 ; right < nums.length; right++) { if (nums[right] != 0 ) { swap(nums, left, right); left++; } } } public void swap (int [] nums, int left, int right) { int temp = nums[left]; nums[left] = nums[right]; nums[right] = temp; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int slow = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] != 0 ) { nums[slow] = nums[i]; slow++; } } for (int j = slow; j < nums.length; j++) { nums[j] = 0 ; } } }
169 多数元素 easy 统计次数,用map
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int majorityElement (int [] nums) { int result = nums[0 ]; HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i : nums) { map.put(i, map.getOrDefault(i, 0 ) + 1 ); if (map.get(i) > nums.length / 2 ) { result = i; } } return result; } }
234 回文链表 easy 自己写的,看
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (ListNode head) { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder (); ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null ) { s.append(cur.val); cur = cur.next; } String a = s.toString(); int j = a.length() - 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length(); i++) { if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) { return false ; } j--; } return true ; } }
448 找到所有数组中消失的数字 easy 用set来保存数,然后遍历1~n,看看哪个数不在就添加
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers (int [] nums) { List<Integer> list = new LinkedList <>(); Set<Integer> set = new HashSet <>(); for (int i : nums) { set.add(i); } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (!set.contains(i + 1 )) { list.add(i + 1 ); } } return list; } }
287 寻找重复数 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int findDuplicate (int [] nums) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); int result = nums[0 ]; for (int i : nums) { map.put(i, map.getOrDefault(i, 0 ) + 1 ); if (map.get(i) > 1 ) { result = i; } } return result; } }
560 和为 K 的子数组 medium 1 2 这个解法很少见,先找到每个下标,然后从这个下标开始倒着加,如果中途满足k,就计数 当然顺着加也可以(注释中的语句),即先固定左边界,然后枚举右边界哈,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) { int count = 0 ; for (int start = 0 ; start < nums.length; start++) { int sum = 0 ; for (int end = start; end >= 0 ; end--) { sum += nums[end]; if (sum == k) { count++; } } } return count; } }
前缀和解法,前缀和就是前i个数的和,left和right区间内的前缀和相减如果等于k,就说明中间有连续数组是为k
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) { int [] presum = new int [nums.length + 1 ]; presum[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { presum[i + 1 ] = presum[i] + nums[i]; } int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= nums.length; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j <= nums.length; j++) { if (presum[j] - presum[i] == k) { count++; } } } return count; } }
581 最短无序连续子数组 medium 1 2 3 其实就是新建一个拍好序的数组,然后从左边遍历看第一个不正确的数,记录left 然后从右边遍历第一个不正确的数,记录right。这里需要注意,不能用sortnum = num,因为这样操作是浅拷贝,如果你把sortnum排序了,那么num也会变的!!!! 比如[2 ,6 ,4 ,8 ,10 ,9 ,15 ],最终记录left为1 ,right为5 ,然后务必+1 才是长度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int findUnsortedSubarray (int [] nums) { int left = 0 ; int right = nums.length - 1 ; int sortnum[] = new int [nums.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { sortnum[i] = nums[i]; } Arrays.sort(sortnum); while (left < nums.length && nums[left] == sortnum[left]) { left++; } while (right > 0 && nums[right] == sortnum[right]) { right--; } if (right == 0 ){ return 0 ; } return right - left + 1 ; } }
461 汉明距离 easy 单纯计算二进制,然后比较
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int hammingDistance (int x, int y) { int result = 0 ; while (x != 0 || y != 0 ) { if (x % 2 != y % 2 ) { result++; } x = x / 2 ; y = y / 2 ; } return result; } }
2 两数相加 medium 1 2 3 4 5 这个题的关键是遇到两位数的和,需要把十位上的数,累加到下一次中,举个例子 [2 ,4 ,3 ] [5 ,6 ,7 ] 他们的和是7 ,10 ,10 ,第二个数已经超过了10 ,把0 保留,1 留在下一个中,就是7 ,0 ,11 ,然后11 又超过了两位数,所以把1 留下,最后是7 ,0 ,1 ,1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public ListNode addTwoNumbers (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dump = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode cur = dump; int carry = 0 ; while (l1 != null || l2 != null ) { int x = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val; int y = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val; int sum = x + y + carry; carry = sum / 10 ; sum = sum % 10 ; cur.next = new ListNode (sum); cur = cur.next; if (l1 != null ) { l1 = l1.next; } if (l2 != null ) { l2 = l2.next; } } if (carry == 1 ) { cur.next = new ListNode (1 ); } return dump.next; } }
338 比特位计数 easy 很简单,计算二进制即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int [] countBits(int n) { int [] result = new int [n + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i++) { result[i] = count(i); } return result; } public int count (int x) { int sum = 0 ; while (x != 0 ) { if (x % 2 == 1 ) { sum++; } x = x / 2 ; } return sum; }
23 合并K个升序链表 hard 思想参考21题,放在本题就是合并两两链表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists (ListNode[] lists) { ListNode dump = null ; for (int i = 0 ; i < lists.length; i++) { dump = mergetwoLists(dump, lists[i]); } return dump; } public ListNode mergetwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode dump = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode cur = dump; while (list1 != null && list2 != null ) { if (list1.val < list2.val) { cur.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } else { cur.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1; return dump.next; } }
238 除自身以外数组的乘积 medium 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 先算左侧数字累积,也就是当前元素之前元素的累积(不含当前元素) 然后倒过来算累计,也就是当前元素之后元素的累积,在左侧数字累积的基础上相乘,这样就可以算出除自身外的累积 总体思想也就是左侧数字的累积乘以右侧数字的累积,也就是除了这个数的累积。 不能用暴力,否则超时 比如[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ] 左侧数字累积是[1 ,1 ,2 ,6 ] 算完之后用一个R来保存右侧的累积,初始化R为1 虽然在第一轮中,4 这个位置的左边已经全部算好了,但是我们需要改变R的累积来为3 这个数字服务,所以倒着的时候还是先从最后一个数开始
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int [] productExceptSelf(int [] nums) { int [] result = new int [nums.length]; result[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { result[i] = result[i - 1 ] * nums[i - 1 ]; } int Right = 1 ; for (int i = nums.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { result[i] = Right * result[i]; Right = Right * nums[i]; } return result; } }
148 排序链表 medium 和下一个方法一样的思路,但是这个方法可能好理解一点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class Solution { public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head.next.next; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode head2 = slow.next; slow.next=null ; return mergeTwoLists(sortList(head), sortList(head2)); } public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode dump = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode cur = dump; while (list1 != null && list2 != null ) { if (list1.val < list2.val) { cur.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } else { cur.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = list1 == null ? list2 :list1; return dump.next; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class Solution { public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } ListNode midNode = middleNode(head); ListNode rightHead = midNode.next; midNode.next = null ; ListNode left = sortList(head); ListNode right = sortList(rightHead); return mergeTwoLists(left, right); } public ListNode middleNode (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head.next.next; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } return slow; } public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode dump = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode cur = dump; while (list1 != null && list2 != null ) { if (list1.val < list2.val) { cur.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } else { cur.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = list1 == null ? list2 :list1; return dump.next; } }
自己写的解法,思路很简单,先用Arraylist来记录数字,然后排序,这里注意是用Collections.sort(list);进行排序,而不是Arrays.sort(list)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); int len = 0 ; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null ) { list.add(cur.val); cur = cur.next; } Collections.sort(list); ListNode dump = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode temp = dump; for (int x : list) { temp.next = new ListNode (x); temp = temp.next; } return dump.next; } }
200 岛屿数量 medium 对比695
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public int numIslands (char [][] grid) { int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < grid.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < grid[0 ].length; j++) { if (grid[i][j] == '1' ) { dfs(grid, i, j); result++; } } } return result; } public void dfs (char [][] grid, int cur_i, int cur_j) { if (cur_i < 0 || cur_j < 0 || cur_i == grid.length || cur_j == grid[0 ].length || grid[cur_i][cur_j] != '1' ) { return ; } grid[cur_i][cur_j] = '0' ; int [] next_cur_i = {0 ,0 ,1 ,-1 }; int [] next_cur_j = {1 ,-1 ,0 ,0 }; for (int index = 0 ; index < 4 ; index++) { int next_i = cur_i + next_cur_i[index]; int next_j = cur_j + next_cur_j[index]; dfs(grid, next_i, next_j); } } }
208 实现Trie(前缀树) medium 具体看解释看 ,前缀树的用处:一次建树,多次查询
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Trie { class TrieNode { private boolean isEnd; TrieNode[] next; public TrieNode () { isEnd = false ; next = new TrieNode [26 ]; } } private TrieNode root; public Trie () { root = new TrieNode (); } public void insert (String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (char c : word.toCharArray()) { if (node.next[c - 'a' ] == null ) { node.next[c - 'a' ] = new TrieNode (); } node = node.next[c - 'a' ]; } node.isEnd = true ; } public boolean search (String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (char c : word.toCharArray()) { node = node.next[c - 'a' ]; if (node == null ) { return false ; } } return node.isEnd; } public boolean startsWith (String prefix) { TrieNode node = root; for (char c : prefix.toCharArray()) { node = node.next[c - 'a' ]; if (node == null ) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
额外练习 21 合并两个有序链表 easy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode head = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode cur = head; while (list1 != null && list2 != null ) { if (list2.val >= list1.val) { cur.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } else if (list2.val < list1.val) { cur.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1; return head.next; } }
先递增再递减数组找最大值 别人面试碰到的题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 int FindMax (int *A, int m) { if (m == 0 ) return -1 ; int begin = 0 ; int end = m - 1 ; int MP = (begin + end)/2 ; while (MP > 0 && MP < m -1 ) { if (A[MP] > A[MP+1 ] && A[MP] > A[MP-1 ]){ return MP; }else if (A[MP] < A[MP+1 ]){ begin = MP+ 1 ; MP= begin + (end - begin)/2 ; }else { end = MP- 1 ; MP= begin + (end - begin)/2 ; } } if (MP == 0 ) return 0 ; if (MP == m-1 ) return m-1 ; return -1 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) { Set<Integer>set=new HashSet <>(); for (int i:nums) { set.add(i); } int len=0 ,max=0 ; for (int i:nums) { if (!set.contains(i-1 )){ while (set.contains(i)) { len+=1 ; i+=1 ; } if (len>max) { max=len; } } len=0 ; } return max; } } 作者:cranky-gausshdx 链接:https: 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
14 最长公共前缀 easy 注意这个题只是看前缀,而不是共同字符,所以只在最前面开始搜就行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) { String ans = strs[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < strs.length; i++) { int j = 0 ; for ( ;j < ans.length() && j < strs[i].length(); j++) { if (ans.charAt(j) != strs[i].charAt(j)) { break ; } } ans = ans.substring(0 , j); } return ans; } }
错误题解,用来解释的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) { String ans = strs[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < strs.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ;j < ans.length() && j < strs[i].length(); j++) { if (ans.charAt(j) != strs[i].charAt(j)) { ans = ans.substring(0 , j); break ; } } } return ans; } }
83 删除排序链表中的重复数字 easy 其实很简单,为什么自己一开始想的很复杂呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { ListNode dump = new ListNode (-1 ); dump.next = head; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null && cur.next != null ) { if (cur.val == cur.next.val) { cur.next = cur.next.next; } else { cur = cur.next; } } return dump.next; } }
88 合并两个有序数组 easy 在尾巴处进行修改,需要注意的是,本题的nums1大小是m+n,然后最后返回的数组也是nums1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public void merge (int [] nums1, int m, int [] nums2, int n) { int i = m - 1 ; int j = n - 1 ; int k = m + n - 1 ; while (i >= 0 && j >= 0 ) { if (nums2[j] > nums1[i]) { nums1[k--] = nums2[j--]; } else { nums1[k--] = nums1[i--]; } } while (j >= 0 ) nums1[k--] = nums2[j--]; } }